|
Online Deliberation
Online deliberation is a broad term used to describe many forms of non-institutional, institutional and experimental online discussions.Bächtiger, A., Dryzek, John S., Mansbridge, Jane J., & Warren, Mark. (2018). The Oxford handbook of deliberative democracy (First ed., Oxford handbooks online). Oxford: Oxford University Press. The term also describes the emerging field of practice and research related to the design, implementation and study of deliberative processes that rely on the use of electronic information and communications technologies (ICT). Although the Internet and social media have fostered discursive participation and deliberation online through computer-mediated communication, the academic study of online deliberation started in the early 2000s. Effective support for online deliberation A range of studies have suggested that group size, volume of communication, interactivity between participants, message characteristics, and social media characteristics can impact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deliberation
Deliberation is a process of thoughtfully weighing options, usually prior to voting. Deliberation emphasizes the use of logic and reason as opposed to power-struggle, creativity, or dialogue. Group decisions are generally made after deliberation through a vote or consensus of those involved. In legal settings a jury famously uses deliberation because it is given specific options, like guilty or not guilty, along with information and arguments to evaluate. In " deliberative democracy", the aim is for both elected officials and the general public to use deliberation rather than power-struggle as the basis for their vote. Trial juries In countries with a jury system, the jury's deliberation in criminal matters can involve both rendering a verdict and determining the appropriate sentence. In civil cases, the jury decision is whether to agree with the plaintiff or the defendant and rendering a resolution binding actions by the parties based on the results of the trial. Typically ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
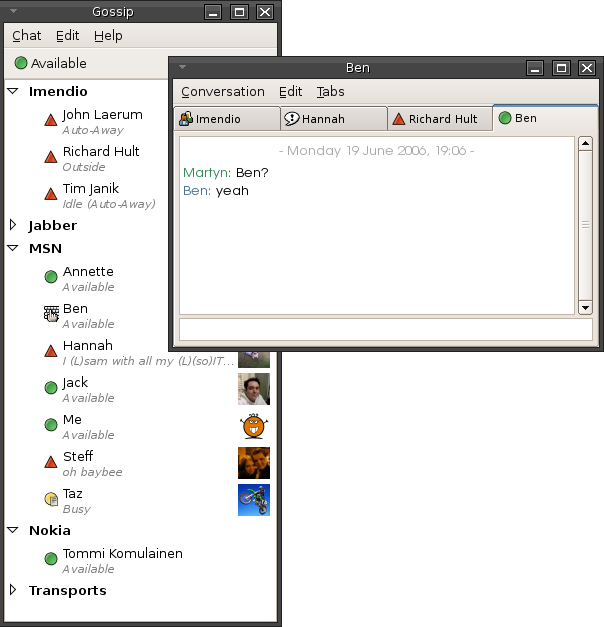
Online Chat
Online chat may refer to any kind of communication over the Internet that offers a real-time text, real-time transmission of text-based, text messages from sender to receiver. Chat messages are generally short in order to enable other participants to respond quickly. Thereby, a feeling similar to a spoken conversation is created, which distinguishes chatting from other text-based online communication forms such as Internet forums and email. Online chat may address Point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point communications as well as multicast communications from one sender to many receivers and voice and video chat, or may be a feature of a web conferencing service. Online chat in a less stringent definition may be primarily any direct text-based or video-based (webcams), one-on-one chat or one-to-many chat room, group chat (formally also known as synchronous conferencing), using tools such as instant messengers, Internet Relay Chat (IRC), talkers and possibly MUDs or ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Research Communities
{{nofootnotes, date=April 2012 An online research community (part of Research 2.0) is a part of an emerging and developing area in market research making use of developments in Web 2.0 technologies and online communities. They allow qualitative research to be conducted efficiently and deeply online. Both public and private online communities offer opportunities for research, but many brands are wary of sharing company information openly. Invitation-only, private online communities centred on a single brand or customer segment may be the solution. These private communities can also engage customer groups or target consumers who might be difficult to reach using traditional off-line methodologies. Consumers enjoy this new, more participative research approach and the interaction with other users re-introduces the social context often missing from other research approaches that conceive of the consumer as an isolated individual. Brands also benefit from online communities by having th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Participation
Online participation is used to describe the interaction between users and online communities on the web. Online communities often involve members to provide content to the website and/or contribute in some way. Examples of such include wikis, blogs, Online multiplayer, online multiplayer games, and other types of social platforms. Online participation is currently a heavily researched field. It provides insight into fields such as web design, online marketing, crowdsourcing, and many areas of psychology. Some subcategories that fall under online participation are: commitment to Online community, online communities, coordination & interaction, and member recruitment. Knowledge sharing infrastructures Some key examples of online knowledge sharing infrastructures include the following: *Wikipedia: An online, publicly editable encyclopedia with hundreds of thousands of editors *Slashdot: A popular technology-related forum, with articles and comments from readers. Slashdot subculture ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Consultation
Online consultations or e-consultations refer to an exchange between government and citizens using the Internet. They are one form of online deliberation. Further, online consultation consists in using the Internet to ask a group of people their opinion on one or more specific topics, allowing for trade-offs between participants. Generally, an agency consults a group of people to get their thoughts on an issue when a project or a policy is being developed or implemented, e.g. to identify or access options, or to evaluate ongoing activities. This enables governments to draft more citizen-centered policy. As the Internet gains popularity with the public for voicing opinion, citizen participation in policy development through cyberspace is changing the face of democracy. The rise of the Internet has given way to buzzwords such as e-democracy, referring to citizen participation in politics, government issues and policy development through electronic technologies and the Internet, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-participation
Electronic participation (e-participation) is ICT-supported participation in processes involving government and citizens. Processes may concern administration, service delivery, decision making and policy making. E-participation is hence closely related to e-government and e-governance participation. The need for the term has emerged as citizen interests and interaction with political service providers have increasingly become digitized due to the rise of e-government. A more detailed definition sees e-participation as a process that enhances and deepens political participation and allows citizens to interact with one another as well as their elected representative through the use of information and communication technologies (ICTs). This definition includes all stakeholders in a democratic decision-making processes and not only citizen related top-down government initiatives. E-participation is largely a part of e-democracy, and heavily involves the use of ICT by governments, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E-democracy
E-democracy (a combination of the words electronic and democracy), also known as digital democracy or Internet democracy, is the use of information and communication technology (ICT) in political and governance processes. The term is believed to have been coined by digital activist Steven Clift. E-democracy incorporates 21st-century information and communications technology to promote democracy; such technologies include civic technology and government technology. It is a form of government in which all adult citizens are presumed to be eligible to participate equally in the proposal, development and creation of laws. E-democracy encompasses social, economic and cultural conditions that enable the free and equal practice of political self-determination. Goals Expanding democracy The Internet has several attributes that encourage thinking about it as a democratic medium. Electronic voting should be done with a proper purpose and with achieving a common constitution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deliberative Opinion Poll
A deliberative opinion poll, sometimes called a deliberative poll, is a form of opinion poll that incorporates the principles of deliberative democracy. Professor James S. Fishkin of Stanford University first described the concept in 1988. The typical deliberative opinion poll takes a random, representative sample of citizens and engages them in deliberation on current issues or proposed policy changes through small-group discussions and conversations with competing experts to create more informed and reflective public opinion. A typical polling utilizes participants drawn from a random and representative sample to engage in small-group deliberations to create more informed and reflective public opinion. Deliberative polls have been tested around the world, including in the European Union, the United States, China, and Australia. Process The Center for Deliberative Democracy at Stanford University describes its process as follows: Fishkin argues that during deliberation, discu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deliberative Democracy
Deliberative democracy or discursive democracy is a form of democracy in which deliberation is central to decision-making. It adopts elements of both consensus decision-making and majority rule. Deliberative democracy differs from traditional democratic theory in that authentic deliberation, not mere voting, is the primary source of legitimacy for the law. Deliberative democracy is closely related to consultative democracy, in which public consultation with citizens is central to democratic processes. While deliberative democracy is generally seen as some form of an amalgam of representative democracy and direct democracy, the actual relationship is usually open to dispute. Some practitioners and theorists use the term to encompass representative bodies whose members authentically and practically deliberate on legislation without unequal distributions of power, while others use the term exclusively to refer to decision-making directly by lay citizens, as in direct democracy. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Supported Cooperative Work
Computer-supported cooperative work (CSCW) is the study of how people utilize technology collaboratively, often towards a shared goal. CSCW addresses how computer systems can support collaborative activity and coordination. More specifically, the field of CSCW seeks to analyze and draw connections between currently understood human psychological and social behaviors and available collaborative tools, or groupware. Often the goal of CSCW is to help promote and utilize technology in a collaborative way, and help create new tools to succeed in that goal. These parallels allow CSCW research to inform future design patterns or assist in the development of entirely new tools. History The origins of CSCW as a field are intertwined with the rise and subsequent fall of office automation as response to some of the criticisms, particularly the failure to address the impact human psychological and social behaviors can have. Greif and Cashman created the term CSCW to help employees seeking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer-mediated Communication
Computer-mediated communication (CMC) is defined as any human communication that occurs through the use of two or more electronic devices. While the term has traditionally referred to those communications that occur via computer-mediated formats (e.g., instant messaging, email, chat rooms, online forums, social network services), it has also been applied to other forms of text-based interaction such as text messaging. Research on CMC focuses largely on the social effects of different computer-supported communication technologies. Many recent studies involve Internet-based social networking supported by social software. Forms Computer-mediated communication can be broken down into two forms: synchronous and asynchronous. Synchronous computer-mediated communication refers to communication that occurs in real-time. All parties are engaged in the communication simultaneously; however, they are not necessarily all in the same location. Examples of synchronous communication are vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collaborative Software
Collaborative software or groupware is application software designed to help people working on a common task to attain their goals. One of the earliest definitions of groupware is "intentional group processes plus software to support them". As regards available interaction, collaborative software may be divided into: real-time collaborative editing platforms that allow multiple users to engage in live, simultaneous and reversible editing of a single file (usually a document), and version control (also known as revision control and source control) platforms, which allow separate users to make parallel edits to a file, while preserving every saved edit by every user as multiple files (that are variants of the original file). Collaborative software is a broad concept that overlaps considerably with computer-supported cooperative work (CSCW). According to Carstensen and Schmidt (1999) groupware is part of CSCW. The authors claim that CSCW, and thereby groupware, addresses "how colla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |