|
OpenHarmony
OpenHarmony (OHOS, OH) is a family of open-source distributed operating systems based on HarmonyOS derived from LiteOS, donated the L0-L2 branch source code by Huawei to the OpenAtom Foundation. Similar to HarmonyOS, the open-source distributed operating system is designed with a layered architecture, consisting of four layers from the bottom to the top: the kernel layer, system service layer, framework layer, and application layer. It is also an extensive collection of free software, which can be used as an operating system or in parts with other operating systems via Kernel Abstraction Layer subsystems. OpenHarmony supports various devices running a mini system, such as printers, speakers, smartwatches, and other smart device with memory as small as 128 KB, or running a standard system with memory greater than 128 MB. The system contains the basic and some advanced capabilities of HarmonyOS such as DSoftBus technology with distributed device virtualization platform, tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
OpenHarmony Logo By OpenAtom
OpenHarmony (OHOS, OH) is a family of open-source software, open-source distributed operating systems based on HarmonyOS derived from LiteOS, donated the L0-L2 branch source code by Huawei to the OpenAtom Foundation. Similar to HarmonyOS, the open-source distributed operating system is designed with a layered architecture, consisting of four layers from the bottom to the top: the Kernel (operating system), kernel layer, system service layer, framework layer, and Application software, application layer. It is also an extensive collection of free software, which can be used as an operating system or in parts with other operating systems via Kernel Abstraction Layer subsystems. OpenHarmony supports various devices running a mini system, such as printers, speakers, smartwatches, and other smart device with memory as small as 128 KB, or running a standard system with memory greater than 128 MB. The system contains the basic and some advanced capabilities of HarmonyOS such as DSoftB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
HarmonyOS
HarmonyOS (HMOS) ( zh, s=鸿蒙, p=Hóngméng, tr=Vast Mist) is a distributed operating system developed by Huawei for smartphones, tablet computer, tablets, smart TVs, smart watches, personal computers and other smart devices. It has a microkernel design with a single framework: the operating system selects suitable kernels from the abstraction layer in the case of devices that use diverse resources. HarmonyOS was officially launched by Huawei, and first used in Honor (brand), Honor smart TVs, in August 2019. It was later used in Huawei wireless routers, Internet of things, IoT in 2020, followed by smartphones, Tablet computer, tablets and smartwatches from June 2021. From 2019 to 2024, HarmonyOS_version_history#Overview, versions 1 to 4 of the operating system were based on code from the Android (operating system), Android Open Source Project (AOSP) and the Linux kernel; many Android apps could be Sideloading, sideloaded on HarmonyOS. The next iteration of HarmonyOS became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
ArkTS
ArkTS (short for Ark TypeScript) is a high-level general-purpose, multi-paradigm, compiled, declarative, static type programming language developed by Huawei which is an extension superset of open-source TypeScript (TS), in turn a superset of JavaScript (JS) formerly used in July 2022 HarmonyOS 3.0 version, alongside its evolved precursor, extended TypeScript (eTS) built for HarmonyOS development as a shift toward declarative programming. ArkTS compiles to machine code via its ahead-of-time compilation Ark Compiler. ArkTS was first released in September 30, 2021 on OpenHarmony, and the ArkTS toolchain has shipped in DevEco Studio since version 3.1, released in 2022. Since, OpenHarmony 4.0 release on October 26, 2023, ArkTS APIs has been added to the open source community to contribute. Huawei intended ArkTS to support many core concepts associated with extended TypeScript (eTS) based on TypeScript and in turn JavaScript from previous versions of HarmonyOS 3.0 with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
EMUI
EMUI (formerly known as Emotion UI) is an interface based on Android (operating system) developed by Chinese technology company Huawei, used on the company's smartphones primarily globally. Instead of Google Mobile Services, EMUI devices have used Huawei Mobile Services, such as the Huawei AppGallery, in January 2020 due to United States sanctions imposed during the trade war against China in May 2019. From Version 13 (2022), Huawei additionally bundled the HarmonyOS TEE microkernel with the Android system; this microkernel for example handled identity security features such as the fingerprint authentication. History On 30 December 2012, Huawei introduced Emotion UI 1.0, based on Android 4.0. It features a voice assistant app (only in Chinese), customizable homescreens and theme-switching. The company rolled out installation files for the Ascend P1 through their website. The company claims that it is "probably the world's most emotional system". On 4 September 2014 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
OpenAtom Foundation
OpenAtom Foundation (), a non-profit legal entity registered with China's Ministry of Civil Affairs, is the first foundation for open-source software in China. It was established in June 2020 with the support of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology and initiated jointly by Alibaba, Baidu, Huawei, Inspur, Qihoo 360, Tencent, China Merchants Bank and other companies for operation and marketing services of open source projects. Projects As of December 2022, the foundation hosts open source projects including xupercore, OpenHarmony, openEuler, TecentOS Tiny, AliOS Things, OpenBlock, PIKA and hapjs. Collaboration On September 28, 2021, the OpenAtom Foundation and the Eclipse Foundation announced their intention to form a partnership to collaborate on OpenHarmony. On October 26 in the same year, both partners launched the Oniro operating system, a compatible implementation of OpenHarmony based on open source and aimed to be transparent, vendor-neutral, and indep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
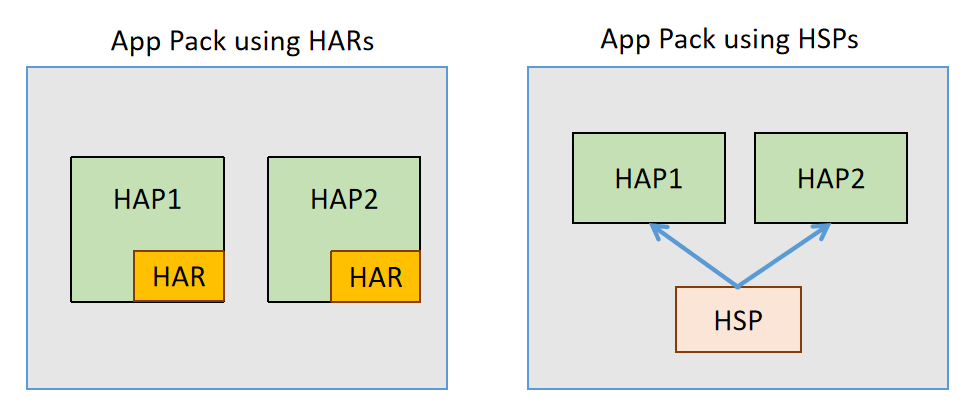
App (file Format)
The HarmonyOS App Pack or the App file, identified with the file extension ".app", serves as the file format used by the HarmonyOS operating system. It functions as a native HarmonyOS app for distribution and installation through Huawei AppGallery, or for distribution through Huawei Ability Gallery in respect of installation-free apps under both former classic dual-framework and current HarmonyOS NEXT system of unified OpenHarmony app framework. The App file is also used by a number of other open source HarmonyOS-based operating systems such as OpenHarmony and Oniro-based operating systems for distribution and installation of applications, video games and middleware. Including non OpenHarmony-based operating systems, such as GNU Linux-based Unity Operating System that supports the app file format. Each HarmonyOS app contains one or more HarmonyOS Ability Package (HAP) files with the file extension ".hap", and the pack.info file that describes the attributes of the App file. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
EulerOS
EulerOS is a commercial Linux distribution developed by Huawei based on Red Hat Enterprise Linux to provide an operating system for server and cloud environments. Its open-source community version is known as openEuler; the source code of openEuler was released by Huawei at Gitee in 2020. openEuler became an open-source project operated by OpenAtom Foundation after Huawei donated the source code of openEuler to the foundation on November 9, 2021. A new programming language for EulerOS and HarmonyOS was announced in September 2021. On March 27, 2020, openEuler 20.03 LTS version was released in the open source repo as the first Long Term Support (LTS) edition. openEuler 21.09 version launched with new file system called EulerFS, also a kernel upgrade that is organized similar to classic HarmonyOS and OpenHarmony multi-kernel architecture that carries both RTOS kernel and Linux kernel on October 1, 2021. Also, the operating system supports, UniProton RTOS kernel and kubeOS contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
LiteOS
Huawei LiteOS is a discontinued lightweight real-time operating system (RTOS) developed by Huawei. It is a POSIX compliant operating system for Internet of things (IoT) devices, and free and open-source software, released under a BSD 3-clause license. Microcontrollers of different architectures such as ARM (M0/3/4/7, A7/17/53, ARM9/11), x86, and RISC-V are supported by the project. Huawei's LiteOS is part of their '1+8+N' Internet of things system, and has been featured in several open source software development kits and industry offerings. Smartwatches by Huawei and its former Honor brand run LiteOS. LiteOS variants of kernels has since been incorporated into the IoT-oriented HarmonyOS with open source OpenHarmony. History On 20 May 2015, at the Huawei Network Conference, Huawei proposed the '1+2+1' Internet of Things solution and release the IoT operating system named Huawei LiteOS. It has been reported development of the real-time operating system goes back as far as 2012 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
LoongArch
Loongson () is the name of a family of general-purpose, MIPS architecture-compatible, later in-house LoongArch architecture microprocessors, as well as the name of the Chinese fabless company (Loongson Technology) that develops them. The processors are alternately called Godson processors, which is described as its academic name. History The ''Godson'' processors, based on MIPS architecture, were initially developed at the ''Institute of Computing Technology'' (ICT), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS). The chief architect was . The development of the first Loongson chip was started in 2001. The aim of the Godson project was to develop "high performance general-purpose microprocessors in China", and to become technologically self-sufficient as part of the Made in China 2025 plan. The development was supported by funding via the Chinese Communist Party's 10th and 11th Five-Year Plans. In 2010 the company was commercialized as a separate entity, and in April 2010 ''Loongson Techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Embedded System
An embedded system is a specialized computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is embedded as part of a complete device often including electrical or electronic hardware and mechanical parts. Because an embedded system typically controls physical operations of the machine that it is embedded within, it often has real-time computing constraints. Embedded systems control many devices in common use. , it was estimated that ninety-eight percent of all microprocessors manufactured were used in embedded systems. Modern embedded systems are often based on microcontrollers (i.e. microprocessors with integrated memory and peripheral interfaces), but ordinary microprocessors (using external chips for memory and peripheral interface circuits) are also common, especially in more complex systems. In either case, the processor(s) us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Free Software
Free software, libre software, libreware sometimes known as freedom-respecting software is computer software distributed open-source license, under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software (including profiting from them) regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program.Selling Free Software (GNU) Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users (not just the developer) ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices. The right to study and modify a computer program entails that the source code—the preferred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
RISC-V
RISC-V (pronounced "risk-five") is an open standard instruction set architecture (ISA) based on established reduced instruction set computer (RISC) principles. The project commenced in 2010 at the University of California, Berkeley. It transferred to the RISC-V Foundation in 2015, and from there to RISC-V International, a Swiss non-profit entity, in November 2019. Similar to several other RISC ISAs, e.g. Amber (processor), Amber (ARMv2)(2001), SuperH#J_Core, J-Core(2015), OpenRISC(2000), or OpenSPARC(2005), RISC-V is offered under royalty-free open-source licenses. The documents defining the RISC-V instruction set architecture (ISA) are offered under a Creative Commons license or a BSD licenses, BSD License. Mainline support for RISC-V was added to the Linux 5.17 kernel in 2022, along with its toolchain. In July 2023, RISC-V, in its 64-bit computing, 64-bit variant called riscv64, was included as an official architecture of Linux distribution Debian, in its Debian version histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |