|
Oil And Gas Law In The United States
Oil and gas law in the United States is the area of United States energy law concerning the property law in oil and natural gas, gas under the surface, after its rule of capture, capture, and litigation, statutes, and regulations regarding those rights. Overview The law regulating oil and gas ownership in the US generally differs significantly from laws in Europe; oil and gas are often owned privately in the US as opposed to being owned by the national government as they are in many other countries. Jurisdiction In the United States, U.S., extraction of oil and gas is generally regulated by the individual states through statutes and common law. United States federal law, Federal and United States constitutional law, constitutional law apply as well. Ownership In the United States, oil and gas can be owned by individuals, corporations, LLCs, partnerships, Indian tribes, or by local, state, or federal governments. Oil and gas rights offshore drilling, offshore are owned by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Energy Law
United States energy law is a function of the federal government, states, and local governments. At the federal level, it is regulated extensively through the United States Department of Energy. Every state, the federal government, and the District of Columbia collect some motor vehicle excise taxes.Motor Fuel Excise Tax Rates as of January 1, 2008 from the Federation of Tax Administrators website Retrieved February 24, 2009. Specifically, these are excise taxes on gasoline, diesel fuel, and gasohol. While many western states rely a great deal on severance taxes on oil, gas, and mineral production for revenue, most states get a relatively small amount of their revenue from such sources. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Capture
The rule of capture or law of capture, part of English common law and adopted by a number of U.S. states, establishes a rule of non-liability for captured natural resources including groundwater, oil, gas, and game animals. The general rule is that the first person to "capture" such a resource owns that resource. For example, landowners who extract or “capture” groundwater, oil, or gas from a well that bottoms within the subsurface of their land acquire absolute ownership of the substance even if it is drained from the subsurface of another’s land. The landowner who captures the substance owes no duty of care to other landowners. For example, a water well owner may dry up wells owned by adjacent landowners without fear of liability unless the groundwater was withdrawn for malicious purposes, the groundwater was not put to a beneficial use without waste, or (in Texas) "such conduct is a proximate cause of the subsidence of the land of others." An exception to the rule of capt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States House Of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives is a chamber of the Bicameralism, bicameral United States Congress; it is the lower house, with the U.S. Senate being the upper house. Together, the House and Senate have the authority under Article One of the United States Constitution, Article One of the Constitution of the United States, U.S. Constitution to pass or defeat federal legislation, known as Bill (United States Congress), bills. Those that are also passed by the Senate are sent to President of the United States, the president for signature or veto. The House's exclusive powers include initiating all revenue bills, Impeachment in the United States, impeaching federal officers, and Contingent election, electing the president if no candidate receives a majority of votes in the United States Electoral College, Electoral College. Members of the House serve a Fixed-term election, fixed term of two years, with each seat up for election before the start of the next Congress. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
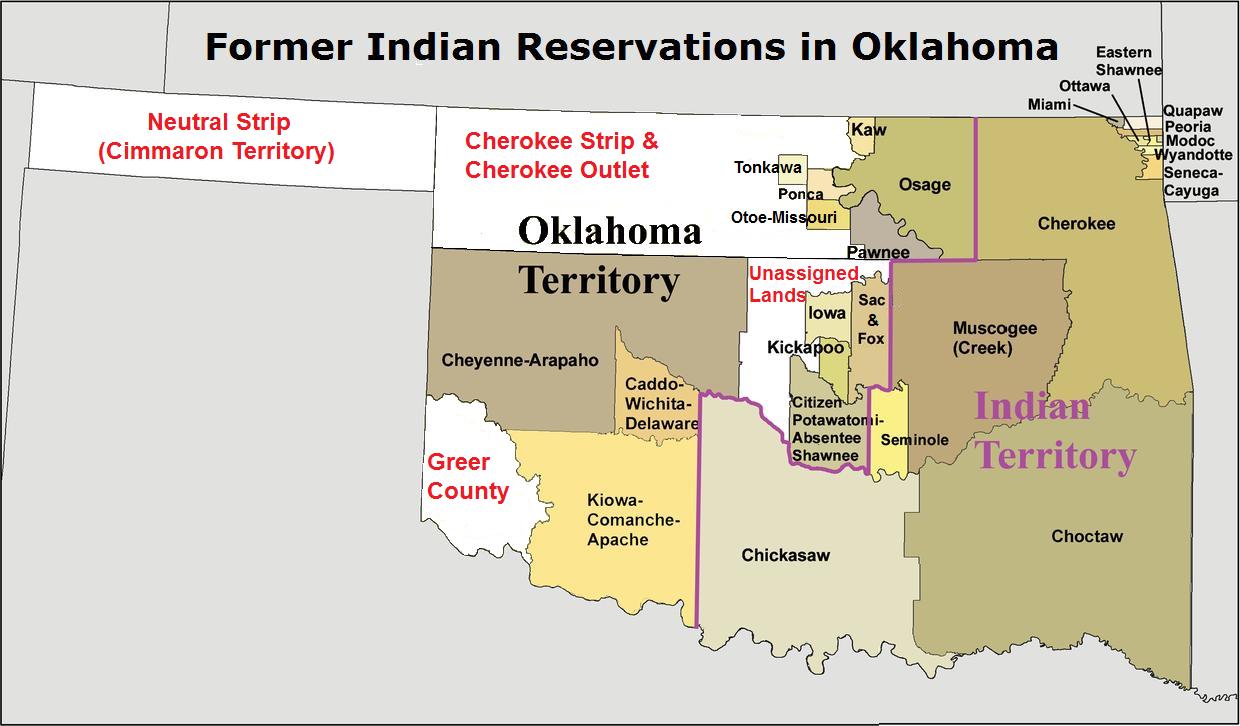
Oklahoma
Oklahoma ( ; Choctaw language, Choctaw: , ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Texas to the south and west, Kansas to the north, Missouri to the northeast, Arkansas to the east, New Mexico to the west, and Colorado to the northwest. Partially in the western extreme of the Upland South, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 20th-most extensive and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 28th-most populous of the 50 United States. Its residents are known as Oklahomans and its capital and largest city is Oklahoma City. The state's name is derived from the Choctaw language, Choctaw words , 'people' and , which translates as 'red'. Oklahoma is also known informally by its List of U.S. state and territory nicknames, nickname, "The Sooner State", in reference to the Sooners, American pioneer, American settlers who staked their claims in formerly American Indian-o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with the surface of Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology to name a weather system with a low-pressure area in the center around which, from an observer looking down toward the surface of the Earth, winds blow counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere. Tornadoes come in many shapes and sizes, and they are often (but not always) visible in the form of a funnel cloud, condensation funnel originating from the base of a cumulonimbus cloud, with a cloud of rotating debris and dust beneath it. Most tornadoes have wind speeds less than , are about across, and travel several kilometers (a few miles) before dissipating. The Tornado records#Highest winds observed in a tornado, most extreme tornadoes can attain wind speeds of mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Of God
In legal usage in the English-speaking world, an act of God, act of nature, or damnum fatale ("loss arising from inevitable accident") is an event caused by no direct human action (e.g. Severe weather, severe or extreme weather and other natural disasters) for which individual persons are not responsible and cannot be held legal liability, legally liable for loss of life, injury, or property damage. An act of God may amount to an exception to liability in contracts (as under the Hague–Visby Rules), or it may be an "insured peril" in an insurance policy. In Scots law, the equivalent term is ''damnum fatale'', while most Common law proper legal systems use the term ''act of God''. It is legally distinct from—though often related to—a common clause found in Contract, contract law known as ''force majeure''. In light of the scientific consensus on climate change, its modern applicability has been questioned by legal scholars. Contract law In the law of contracts, an act of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force Majeure
In contract law, force majeure ( ; ) is a common clause in contracts which essentially frees both parties from liability or obligation when an extraordinary event or circumstance beyond the control of the parties, such as a war, strike, riot, crime, epidemic, or sudden legal change prevents one or both parties from fulfilling their obligations under the contract. Force majeure often includes events described as an act of God, though such events remain legally distinct from the clause itself. In practice, most force majeure clauses do not entirely excuse a party's non-performance but suspend it for the duration of the force majeure.Supreme Court (of India) 1285 it was held that "An analysis of ruling on the subject shows that reference to the expression is made where the intention is to save the defaulting party from the consequences of anything over which he had no control." Even if a force majeure clause covers the relevant supervening event, the party unable to perform will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Due Diligence
Due diligence is the investigation or exercise of care that a reasonable business or person is normally expected to take before entering into an agreement or contract with another party or an act with a certain standard of care. Due diligence can be a legal obligation, but the term more commonly applies to voluntary investigations. It may also offer a defence against legal action. A common example of due diligence is the process through which a potential acquirer evaluates a target company or its assets in advance of a merger or acquisition. The theory behind due diligence holds that performing this type of investigation contributes significantly to informed decision making by enhancing the amount and quality of information available to decision makers and by ensuring that this information is systematically used to deliberate on the decision at hand and all its costs, benefits, and risks. Development of the term The term "due diligence" can be read as "required carefulness" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Good Faith
In human interactions, good faith () is a sincere intention to be fair, open, and honest, regardless of the outcome of the interaction. Some Latin phrases have lost their literal meaning over centuries, but that is not the case with , which is still widely used and interchangeable with its generally accepted modern-day English translation of ''good faith''. It is an important concept within law and business. The opposed concepts are bad faith, (duplicity) and perfidy (pretense). is a Latin phrase meaning "good faith". Its ablative case is , meaning "in good faith", which is often used in English as an adjective to mean "genuine". While may be translated as "faith", it embraces a range of meanings within a core concept of "reliability", in the sense of a trust between two parties for the potentiality of a relationship. For the ancient Romans, ''bona fides'' was to be assumed by both sides, with implied responsibilities and both legal and religious consequences if bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habendum Clause
A habendum clause is a clause in a deed or lease that defines the type of interest and rights to be enjoyed by the grantee or lessee. In a deed, a habendum clause usually begins with the words "to have and to hold". This phrase is the translation of the Latin that historically commenced these clauses in deeds. Technically speaking, the "to have" () is separate from the "to hold" (), such that the tenendum clause is sometimes considered a separate concept. Historically, the habendum clause dealt with "the quantity of interest or estate which the grantee was to have in the property granted", while the tenendum clause addressed "the tenure upon or under which it was to be held". Put differently, the habendum deals with the relationship between the possessor and the land—how the land is to be had—while the tenendum deals with the relationship between the possessor and his immediately superior lord—how the land is to be held. The obsolescence of land tenure, however, renders thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hunt Oil Co
Hunting is the Human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, and killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to obtain the animal's body for meat and useful animal products (fur/hide (skin), hide, bone/tusks, horn (anatomy), horn/antler, etc.), for recreation/taxidermy (see trophy hunting), although it may also be done for resourceful reasons such as removing predators dangerous to humans or domestic animals (e.g. wolf hunting), to pest control, eliminate pest (organism), pests and nuisance animals that damage crops/livestock/poultry or zoonosis, spread diseases (see varmint hunting, varminting), for trade/tourism (see safari), or for conservation biology, ecological conservation against overpopulation and invasive species (commonly called a culling#Wildlife, cull). Recreationally hunted species are generally referred to as the ''game (food), game'', and are usually mammals and birds. A person participating in a hunt is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lease
A lease is a contractual arrangement calling for the user (referred to as the ''lessee'') to pay the owner (referred to as the ''lessor'') for the use of an asset. Property, buildings and vehicles are common assets that are leased. Industrial or business equipment are also leased. In essence, a lease agreement is a contract between two parties: the lessor and the lessee. The lessor is the legal owner of the asset, while the lessee obtains the right to use the asset in return for regular rental payments. The lessee also agrees to abide by various conditions regarding their use of the property or equipment. For example, a person leasing a car may agree to the condition that the car will only be used for personal use. The term rental agreement can refer to two kinds of leases: * A lease in which the asset is tangible property. Here, the user '' rents'' the asset (e.g. land or goods) ''let out'' or ''rented out'' by the owner (the verb ''to lease'' is less precise because it c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |