|
Ogive
An ogive ( ) is the roundly tapered end of a two- or three-dimensional object. Ogive curves and surfaces are used in engineering, architecture, woodworking, and ballistics. Etymology The French Orientalist Georges Séraphin Colin gives as the term's origin the Arabic ''al-ġubb'' () 'cistern', pronounced ''al-ġibb'' () in vernacular Iberian Arabic, through the Spanish ''aljibe'' or archaically ''algibe.'' The earliest use of the word ''ogive'' is found in the 13th-century sketchbook of Villard de Honnecourt, from Picardy in northern France. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' considers the French term's origin obscure; it might come from the Late Latin , the feminine perfect passive participle of , meaning the one who has met or encountered the other. However, Merriam-Webster's dictionary says it is from the "Middle English stone comprising an arch, from Middle French diagonal arch". According to Wiktionary, the French term comes "from Vulgar Latin augīvus, from Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nose Cone Design
Given the problem of the aerodynamic design of the nose cone section of any vehicle or body meant to travel through a compressible fluid medium (such as a rocket or aircraft, missile, shell or bullet), an important problem is the determination of the nose cone geometrical shape for optimum performance. For many applications, such a task requires the definition of a solid of revolution shape that experiences minimal resistance to rapid motion through such a fluid medium. Nose cone shapes and equations Source: General dimensions Source: In all of the following nose cone shape equations, is the overall length of the nose cone and is the radius of the base of the nose cone. is the radius at any point , as varies from , at the tip of the nose cone, to . The equations define the two-dimensional profile of the nose shape. The full body of revolution of the nose cone is formed by rotating the profile around the centerline . While the equations describe the "perfect" shape, pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
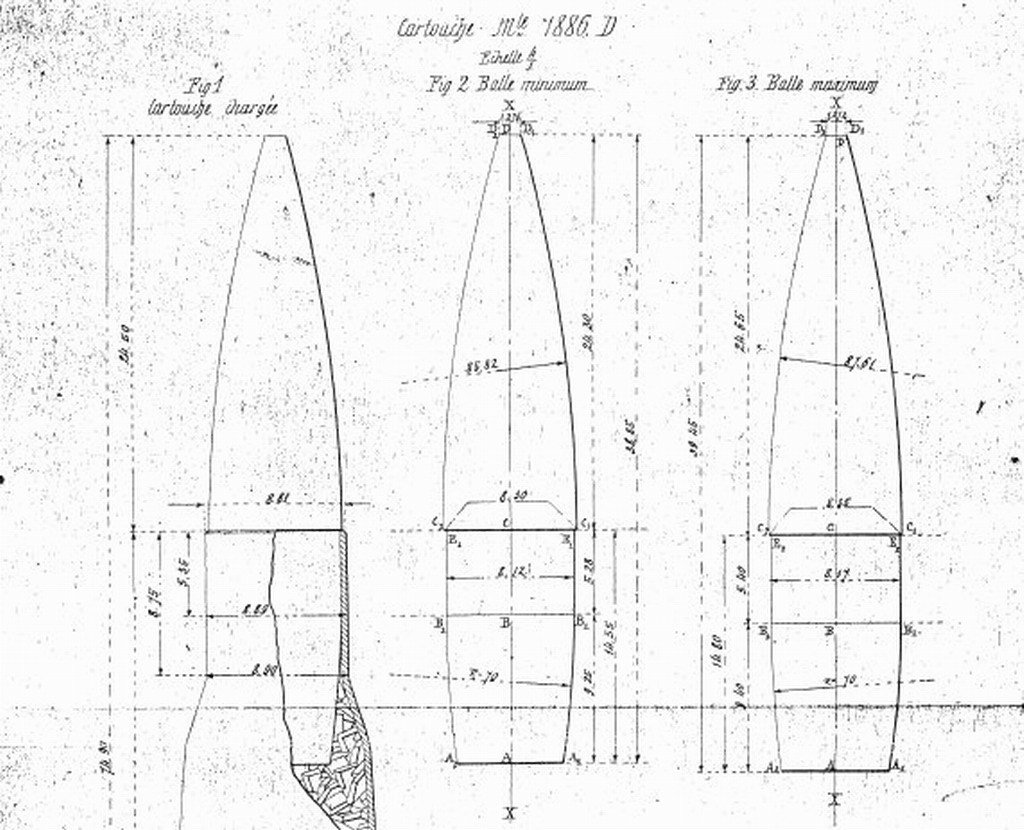
Spitzer (bullet)
A spitzer bullet (from , "point shot") is a munitions term, primarily regarding fully-powered and intermediate small-arms ammunition, describing bullets featuring an aerodynamically pointed nose shape, called a spire point, sometimes combined with a tapered base, called a boat tail (then a spitzer boat-tail bullet), in order to reduce drag and obtain a lower drag coefficient, resulting in an aerodynamically superior torpedo shaped projectile, which decelerates less rapidly and has improved external ballistic behaviour, at the expense of some potential weight and kinetic energy relative to blunter ogive/round/flat-nose flat-base projectiles. The type which was developed for military purposes in the late 19th and early 20th century and was a major design improvement compared to earlier rounder or flatter-tipped bullets in terms of range and accuracy. Its introduction, along with long-range volley sights for service rifles, changed military doctrines. Area targets at rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supersonic
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound (Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times the speed of sound (Mach 5) are often referred to as hypersonic. Flights during which only some parts of the air surrounding an object, such as the ends of rotor blades, reach supersonic speeds are called transonic. This occurs typically somewhere between Mach 0.8 and Mach 1.2. Sounds are traveling vibrations in the form of pressure waves in an elastic medium. Objects move at supersonic speed when the objects move faster than the speed at which sound propagates through the medium. In gases, sound travels longitudinally at different speeds, mostly depending on the molecular mass and temperature of the gas, and pressure has little effect. Since air temperature and composition varies significantly with altitude, the speed of s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothic Architecture
Gothic architecture is an architectural style that was prevalent in Europe from the late 12th to the 16th century, during the High Middle Ages, High and Late Middle Ages, surviving into the 17th and 18th centuries in some areas. It evolved from Romanesque architecture and was succeeded by Renaissance architecture. It originated in the Île-de-France and Picardy regions of northern France. The style at the time was sometimes known as ''opus Francigenum'' (); the term ''Gothic'' was first applied contemptuously during the later Renaissance, by those ambitious to revive the Classical architecture, architecture of classical antiquity. The defining design element of Gothic architecture is the Pointed arch (architecture), pointed arch. The use of the pointed arch in turn led to the development of the pointed rib vault and flying buttresses, combined with elaborate tracery and stained glass windows. At the Abbey of Basilica of Saint-Denis, Saint-Denis, near Paris, the choir was rec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodynamics
Aerodynamics () is the study of the motion of atmosphere of Earth, air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dynamics and its subfield of gas dynamics, and is an important domain of study in aeronautics. The term ''aerodynamics'' is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag were recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achieving Aircraft#Heavier-than-air – aerodynes, heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Otto Lilienthal in 1891. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ) is a surface (mathematics), surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the center (geometry), ''center'' of the sphere, and the distance is the sphere's ''radius''. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental surface in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubble (physics), Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is spherical Earth, often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres rolling, roll smoothly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifle
A rifle is a long gun, long-barreled firearm designed for accurate shooting and higher stopping power, with a gun barrel, barrel that has a helical or spiralling pattern of grooves (rifling) cut into the bore wall. In keeping with their focus on accuracy, rifles are typically designed to be held with both hands and braced firmly against the shooter's shoulder via a buttstock for stability during shooting. Rifles are used in warfare, law enforcement, hunting and shooting sports, target shooting sports. The invention of rifling separated such firearms from the earlier smoothbore weapons (e.g., arquebuses, muskets, and other long guns), greatly elevating their accuracy and general effectiveness. The raised areas of a barrel's rifling are called ''lands''; they make contact with and exert torque on the projectile as it moves down the bore, imparting a spin. When the projectile leaves the barrel, this spin persists and lends gyroscopic stability to the projectile due to conservatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder (geometry)
A cylinder () has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base. A cylinder may also be defined as an infinite curvilinear surface in various modern branches of geometry and topology. The shift in the basic meaning—solid versus surface (as in a solid ball versus sphere surface)—has created some ambiguity with terminology. The two concepts may be distinguished by referring to solid cylinders and cylindrical surfaces. In the literature the unadorned term "cylinder" could refer to either of these or to an even more specialized object, the '' right circular cylinder''. Types The definitions and results in this section are taken from the 1913 text ''Plane and Solid Geometry'' by George A. Wentworth and David Eugene Smith . A ' is a surface consisting of all the points on all the lines which are parallel to a given line and which pass through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius
In classical geometry, a radius (: radii or radiuses) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The radius of a regular polygon is the line segment or distance from its center to any of its Vertex (geometry), vertices. The name comes from the Latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the spoke of a chariot wheel.Definition of Radius at dictionary.reference.com. Accessed on 2009-08-08. The typical abbreviation and mathematical symbol for radius is ''R'' or ''r''. By extension, the diameter ''D'' is defined as twice the radius:Definition of radius at mathwords.com. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc (geometry)
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line (geometry), line, but that does not have to be Linearity, straight. Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point (geometry), point. This is the definition that appeared more than 2000 years ago in Euclid's Elements, Euclid's ''Elements'': "The [curved] line is […] the first species of quantity, which has only one dimension, namely length, without any width nor depth, and is nothing else than the flow or run of the point which […] will leave from its imaginary moving some vestige in length, exempt of any width." This definition of a curve has been formalized in modern mathematics as: ''A curve is the image (mathematics), image of an interval (mathematics), interval to a topological space by a continuous function''. In some contexts, the function that defines the curve is called a ''parametrization'', and the curve is a parametric curve. In this artic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |