|
Nicotine Withdrawal
Nicotine withdrawal is a group of symptoms that occur in the first few weeks after stopping or decreasing use of nicotine. Symptoms include intense cravings for nicotine, anger or irritability, anxiety, depression, impatience, trouble sleeping, restlessness, hunger or weight gain, and difficulty concentrating. Withdrawal symptoms make it harder to quit nicotine products, and most methods for quitting smoking involve reducing nicotine withdrawal. Quit smoking programs can make it easier to quit. Nicotine withdrawal is recognized in both the American Psychiatric Association Diagnostic and Statistical Manual and the WHO International Classification of Diseases. Signs and symptoms The most documented symptoms of nicotine withdrawal are cravings for nicotine, anger or irritability, anxiety, depression, impatience, trouble sleeping, restlessness (psychomotor agitation, including indeliberate movement), hunger or weight gain, and difficulty concentrating. Symptoms are usually stronges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychiatry
Psychiatry is the medical specialty devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of mental disorders. These include various maladaptations related to mood, behaviour, cognition, and perceptions. See glossary of psychiatry. Initial psychiatric assessment of a person typically begins with a case history and mental status examination. Physical examinations and psychological tests may be conducted. On occasion, neuroimaging or other neurophysiological techniques are used. Mental disorders are often diagnosed in accordance with clinical concepts listed in diagnostic manuals such as the ''International Classification of Diseases'' (ICD), edited and used by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the widely used '' Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders'' (DSM), published by the American Psychiatric Association (APA). The fifth edition of the DSM (DSM-5) was published in May 2013 which re-organized the larger categories of various diseases and expanded upon the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snus
Snus ( , ) is a tobacco product, originating from a variant of dry snuff in early 18th-century Sweden. It is placed between the upper lip and gum for extended periods, as a form of sublabial administration. Snus is not fermented. Although used similarly to American dipping tobacco, snus does not typically result in the need for spitting and, unlike naswar, snus is steam-pasteurized. The sale of snus is illegal in all the European Union countries except for Sweden. It is the most common type of tobacco product in Norway (which is not in the EU), and is available in Switzerland as well. Some EU countries like Estonia allow the sale of nicotine pouches, snus-like products that contain nicotine but no tobacco. Snus is also available in the United States. Canada makes it difficult to obtain snus through its high taxes on imported tobacco products. Snus has been seen as an alternative to smoking, vaping, chewing, dipping, and dissolvable and snuff tobacco products. Snus usually con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Withdrawal
Drug withdrawal, drug withdrawal syndrome, or substance withdrawal syndrome, is the group of symptoms that occur upon the abrupt discontinuation or decrease in the intake of pharmaceutical or recreational drugs. In order for the symptoms of withdrawal to occur, one must have first developed a form of drug dependence. This may occur as physical dependence, psychological dependence or both. Drug dependence develops from consuming one or more substances over a period of time. Dependence arises in a dose-dependent manner and produces withdrawal symptoms that vary with the type of drug that is consumed. For example, prolonged use of an antidepressant medication is likely to cause a rather different reaction when discontinued compared to discontinuation of an opioid, such as heroin. Withdrawal symptoms from opiates include anxiety, sweating, vomiting, and diarrhea. Alcohol withdrawal symptoms include irritability, fatigue, shaking, sweating, and nausea. Withdrawal from nicotine can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clonidine
Clonidine, sold under the brand name Catapres among others, is an α2-adrenergic agonist medication used to treat high blood pressure, ADHD, drug withdrawal ( alcohol, opioids, or nicotine), menopausal flushing, diarrhea, spasticity, and certain pain conditions. It is used by mouth, by injection, or as a skin patch. Onset of action is typically within an hour with the effects on blood pressure lasting for up to eight hours. Common side effect include dry mouth, dizziness, headaches, hypotension, and sleepiness. Severe side effects may include hallucinations, heart arrhythmias, and confusion. If rapidly stopped, withdrawal effects may occur. Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding is not recommended. Clonidine lowers blood pressure by stimulating α2 receptors in the brain, which results in relaxation of many arteries. Clonidine was patented in 1961 and came into medical use in 1966. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 75th most commonly prescri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nortriptyline
Nortriptyline, sold under the brand name Pamelor, among others, is a medication used to treat depression. This medicine is used for: neuropathic pain, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), smoking cessation and anxiety. As with many antidepressants, its use for young people with depression and other psychiatric disorders may be limited due to increased suicidality in the 18-24 population initiating treatment. Nortriptyline is a less preferred treatment for ADHD and stopping smoking. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include dry mouth, constipation, blurry vision, sleepiness, low blood pressure with standing, and weakness. Serious side effects may include seizures, an increased risk of suicide in those less than 25 years of age, urinary retention, glaucoma, mania, and a number of heart issues. Nortriptyline may cause problems if taken during pregnancy. Use during breastfeeding appears to be relatively safe. It is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) and is believed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytisine
Cytisine, also known as baptitoxine, cytisinicline, or sophorine, is an alkaloid that occurs naturally in several plant genera, such as ''Laburnum'' and ''Cytisus'' of the family Fabaceae. It has been used medically to help with smoking cessation. Although widely used for smoking cessation in Eastern Europe, cytisine remains relatively unknown beyond it. However, it has been found effective in several randomized clinical trials, including some in the United States and a large one in New Zealand, and is being investigated in additional trials in the United States (being conducted by Achieve Life Sciences) and a non-inferiority trial in Australia in which it is being compared head-to-head with the smoking cessation aid varenicline (sold in the United States as Chantix). It has also been used entheogenically via mescalbeans by some Native American groups, historically in the Rio Grande Valley predating even peyote. Sources Cytisine is extracted from the seeds of ''Cytisus la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varenicline
Varenicline (trade name Chantix and Champix) is a medication used for smoking cessation. Varenicline is also used for the treatment of dry eye disease. The most common side-effects include nausea (feeling sick), insomnia (difficulty sleeping), abnormal dreams, headache and nasopharyngitis (inflammation of the nose and throat). It is a high-affinity partial agonist for the α4β2 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subtype (nACh) that leads to the release of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the nucleus accumbens reward center of the brain when activated, and therefore, has the capacity to reduce the feelings of craving and withdrawal caused by smoking cessation. In this respect it is similar to cytisine and different from the nicotinic antagonist bupropion and nicotine replacement therapies (NRTs) like nicotine patches and nicotine gum. It is estimated that varenicline successfully helps one of every eleven people who smoke remain abstinent from tobacco at six months. It is on th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
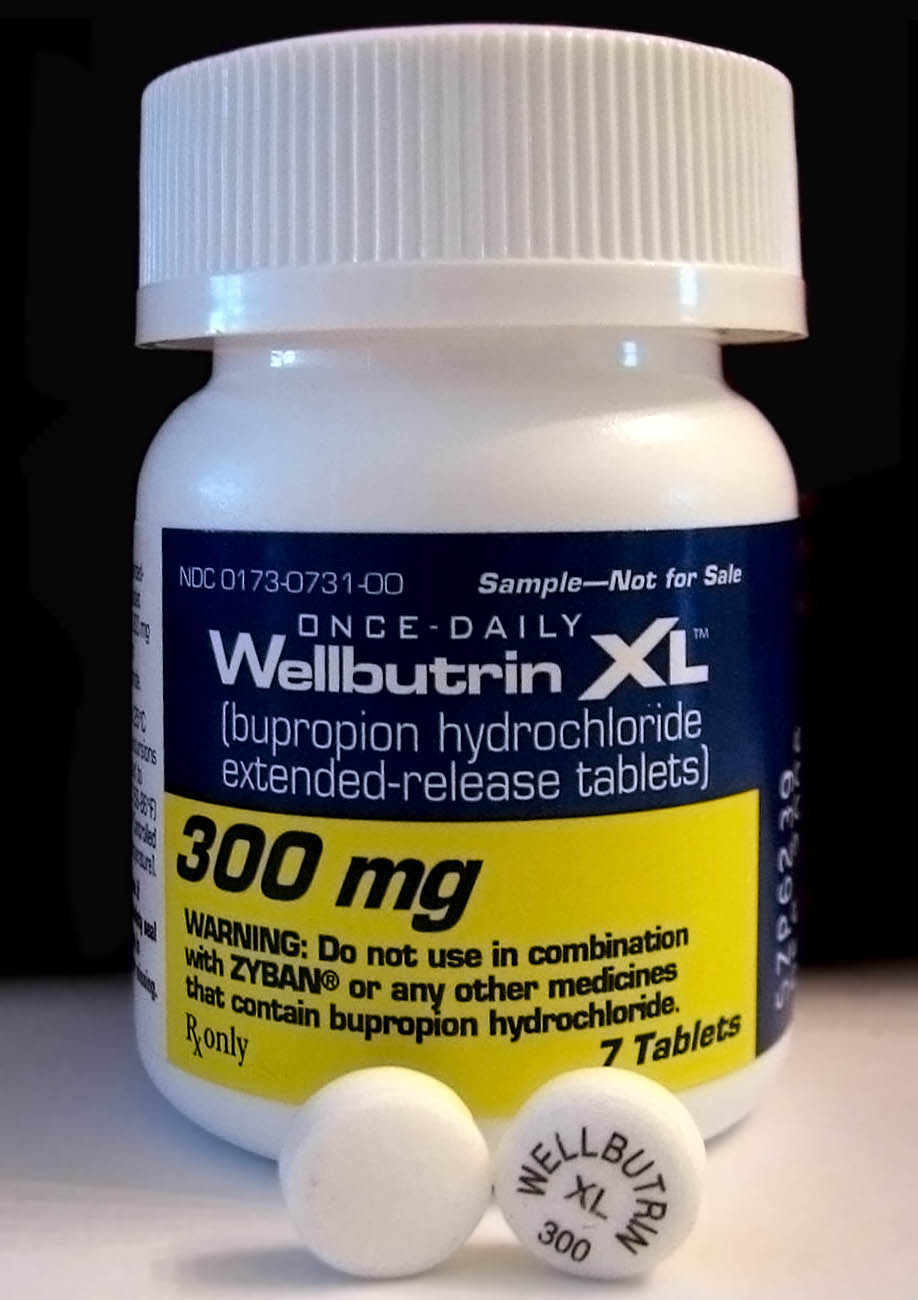
Bupropion
Bupropion, sold under the brand names Wellbutrin and Zyban among others, is an atypical antidepressant primarily used to treat major depressive disorder and to support smoking cessation. It is also popular as an add-on medication in the cases of "incomplete response" to the first-line selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant. Bupropion has several features that distinguish it from other antidepressants: it does not usually cause sexual dysfunction; it is not associated with weight gain and sleepiness, and it is more effective than SSRIs at improving symptoms of hypersomnia and fatigue. Bupropion does, however, carry a much higher risk of seizure than many other antidepressants and extreme caution must be taken in patients with a history of seizure disorder. Common adverse effects of bupropion with the greatest difference from placebo are dry mouth, nausea, constipation, insomnia, anxiety, tremor, and excessive sweating. Raised blood pressure is notable. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotine Replacement Therapy
Nicotine replacement therapy (NRT) is a medically approved way to treat people with tobacco use disorder by taking nicotine through means other than tobacco. It is used to help with quitting smoking or stopping chewing tobacco. It increases the chance of quitting tobacco smoking by about 55%. Often it is used along with other behavioral techniques. NRT has also been used to treat ulcerative colitis. Types of NRT include the adhesive patch, chewing gum, lozenges, nose spray, and inhaler. The use of multiple types of NRT at a time may increase effectiveness. Common side effects depend on the formulation of nicotine. Common side effects with the gum include nausea, hiccups, and irritation of the mouth. Common side effects with the patch include skin irritation and a dry mouth while the inhaler commonly results in a cough, runny nose, or headaches. Serious risks include nicotine poisoning and continued addiction. They do not appear to increase the risk of heart attacks. There are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striatum
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs from different sources; and serves as the primary input to the rest of the basal ganglia. Functionally, the striatum coordinates multiple aspects of cognition, including both motor and action planning, decision-making, motivation, reinforcement, and reward perception. The striatum is made up of the caudate nucleus and the lentiform nucleus. The lentiform nucleus is made up of the larger putamen, and the smaller globus pallidus. Strictly speaking the globus pallidus is part of the striatum. It is common practice, however, to implicitly exclude the globus pallidus when referring to striatal structures. In primates, the striatum is divided into a ventral striatum, and a dorsal striatum, subdivisions that are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Dependence
Physical dependence is a physical condition caused by chronic use of a tolerance-forming drug, in which abrupt or gradual drug withdrawal causes unpleasant physical symptoms. Physical dependence can develop from low-dose therapeutic use of certain medications such as benzodiazepines, opioids, antiepileptics and antidepressants, as well as the recreational misuse of drugs such as alcohol, opioids and benzodiazepines. The higher the dose used, the greater the duration of use, and the earlier age use began are predictive of worsened physical dependence and thus more severe withdrawal syndromes. Acute withdrawal syndromes can last days, weeks or months. Protracted withdrawal syndrome, also known as post-acute-withdrawal syndrome or "PAWS", is a low-grade continuation of some of the symptoms of acute withdrawal, typically in a remitting-relapsing pattern, often resulting in relapse and prolonged disability of a degree to preclude the possibility of lawful employment. Protracted withdra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor (chemistry), precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is biosynthesis, synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons (nerve cells) to send signals to other nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in specific regions of the brain, but affect many regions systemically. The brain includes several distinct dopaminergic pathway, dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward system, reward-motivated behavior. The anticipa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |