|
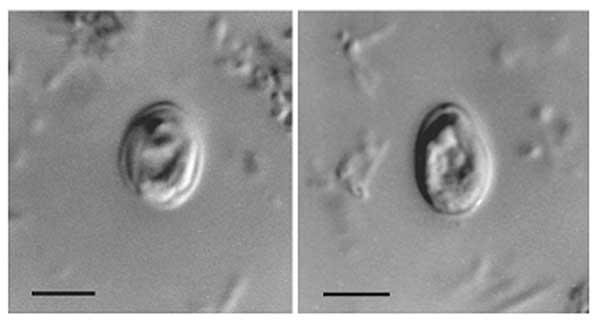
Nematocida Parisii
''Nematocida parisii'' is a parasitic species of Microsporidia fungi found in wild isolates of the common nematode, ''Caenorhabditis elegans''. The fungus forms spores and replicates in the intestines before leaving the host. Infection ''N. parisii'' is an intracellular parasite that is transmitted from one animal to another, most commonly through the fecal–oral route. Once it gets into the intestines, it forms small, ovoid microbes that become spores and leave holes in the intestinal wall. The spores are believed to exit cells by disrupting a conserved cytoskeletal structure in the intestine called the terminal web. None of the known immune pathways of ''C. elegans'' appear to be involved in mediating resistance against ''N. parisii''. Microsporidia have been found in several nematodes isolated from different locations, indicating that they are common natural parasites of ''C. elegans''. The ''N. parisii''–''C. elegans'' system is a useful tool for studying infection m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryota
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the Three-domain system, three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard (archaea), Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only Two-domain system, two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass (ecology), biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as Flagellated cell, flagellated phagotrophs. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminal Web
The terminal web is a filamentous structure found at the apical surface of epithelial cells that possess microvilli. It is composed primarily of actin filaments stabilized by spectrin, which also anchors the terminal web to the apical cell membrane. The presence of myosin II and tropomyosin Tropomyosin is a two-stranded alpha-helical, coiled coil protein found in actin-based cytoskeletons. Tropomyosin and the actin skeleton All organisms contain organelles that provide physical integrity to their cells. These type of organelles ar ... helps to explain the contractile ability of the terminal web. When contracted, the terminal web causes a decrease in diameter of the apex of the cell, causing the microvilli, which are anchored into the terminal web through their stiff actin fibers, to spread apart. This spreading apart of the microvilli aids cells in absorption.Ross, Michael H., and Wojciech Pawlina. "Chapter 5: Epithelial Tissue." Histology: a Text and Atlas : with Correlated Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestinal Parasite
An intestinal parasite infection is a condition in which a parasite infects the gastro-intestinal tract of humans and other animals. Such parasites can live anywhere in the body, but most prefer the intestinal wall. Routes of exposure and infection include ingestion of undercooked meat, drinking infected water, fecal-oral transmission and skin absorption. Some types of helminths and protozoa are classified as intestinal parasites that cause infection—those that reside in the intestines. These infections can damage or sicken the host (humans or other animals). If the intestinal parasite infection is caused by helminths, the infection is called helminthiasis. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms depend on the type of infection. Intestinal parasites produce a variety of symptoms in those affected, most of which manifest themselves in gastrointestinal complications and general weakness. Gastrointestinal conditions include inflammation of the small and/or large intestine, dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Host Microbe Interactions In Caenorhabditis Elegans
'' Caenorhabditis elegans''- microbe interactions are defined as any interaction that encompasses the association with microbes that temporarily or permanently live in or on the nematode ''C. elegans.'' The microbes can engage in a commensal, mutualistic or pathogenic interaction with the host. These include bacterial, viral, unicellular eukaryotic, and fungal interactions. In nature ''C. elegans'' harbours a diverse set of microbes. In contrast, ''C. elegans'' strains that are cultivated in laboratories for research purposes have lost the natural associated microbial communities and are commonly maintained on a single bacterial strain, ''Escherichia coli'' OP50. However, ''E. coli'' OP50 does not allow for reverse genetic screens because RNAi libraries have only been generated in strain HT115. This limits the ability to study bacterial effects on host phenotypes. The host microbe interactions of ''C. elegans'' are closely studied because of their orthologs in humans. Therefore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelomocyte
A coelomocyte () is a phagocytic leukocyte that appears in the bodies of animals that have a coelom. In most, it attacks and digests invading organisms such as bacteria and viruses through encapsulation and phagocytosis, though in some animals (e.g., the nematode worm ''Caenorhabditis elegans ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' (ro ...'') it does not seem capable of the phagocytosis. A coelomocyte may either be fixed to the body wall or may be free-floating within the coelom. The word comes from the Ancient Greek ''koílōma'', "cavity" or "hollow", and ''kýtos'', "receptacle" or "container". References {{reflist Leukocytes Mesoderm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidermis
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss. The epidermis is composed of multiple layers of flattened cells that overlie a base layer (stratum basale) composed of columnar cells arranged perpendicularly. The layers of cells develop from stem cells in the basal layer. The human epidermis is a familiar example of epithelium, particularly a stratified squamous epithelium. The word epidermis is derived through Latin , itself and . Something related to or part of the epidermis is termed epidermal. Structure Cellular components The epidermis primarily consists of keratinocytes ( proliferating basal and differentiated suprabasal), which comprise 90% of its cells, but also contains melanocytes, Langerhans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nematocida Displodere
''Nematocida'' is a genus of Microsporidia fungi. One species, '' N. parisii'', is found in wild isolates of ''Caenorhabditis elegans ''Caenorhabditis elegans'' () is a free-living transparent nematode about 1 mm in length that lives in temperate soil environments. It is the type species of its genus. The name is a blend of the Greek ''caeno-'' (recent), ''rhabditis'' (ro ...''. It has been nicknamed the nematode-killer from Paris. This species replicates in the intestines of ''C. elegans''. Nematode cuticle is a cuticle that includes fibers such as keratin, collagen, and some that run around in opposite directions from each other. This has a flexible extracellular exoskeleton structure that has many layers, (but is very stiff) and that has a barrier that helps prevent nematodes from natural and ecological harm that may happen. These may have powerful agents that are used to recognize, attach, penetrate and kill theses parasitic nematodes. References External links ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. Cell walls are absent in many eukaryotes, including animals, but are present in some other ones like fungi, algae and plants, and in most prokaryotes (except mollicute bacteria). A major function is to act as pressure vessels, preventing over-expansion of the cell when water enters. The composition of cell walls varies between taxonomic group and species and may depend on cell type and developmental stage. The primary cell wall of land plants is composed of the polysaccharides cellulose, hemicelluloses and pectin. Often, other polymers such as lignin, suberin or cutin are anchored to or embedded in plant cell walls. Algae possess cell walls made of glycoproteins and polysaccharides such as carrageenan and agar that are absent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoskeletal
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. It is composed of three main components, microfilaments, intermediate filaments and microtubules, and these are all capable of rapid growth or disassembly dependent on the cell's requirements. A multitude of functions can be performed by the cytoskeleton. Its primary function is to give the cell its shape and mechanical resistance to deformation, and through association with extracellular connective tissue and other cells it stabilizes entire tissues. The cytoskeleton can also contract, thereby deforming the cell and the cell's environment and allowing cells to migrate. Moreover, it is involved in many cell signaling pathways and in the uptake of extracellular material ( endocytosis), the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fecal–oral Route
The fecal–oral route (also called the oral–fecal route or orofecal route) describes a particular route of transmission of a disease wherein pathogens in fecal particles pass from one person to the mouth of another person. Main causes of fecal–oral disease transmission include lack of adequate sanitation (leading to open defecation), and poor hygiene practices. If soil or water bodies are polluted with fecal material, humans can be infected with waterborne diseases or soil-transmitted diseases. Fecal contamination of food is another form of fecal-oral transmission. Washing hands properly after changing a baby's diaper or after performing anal hygiene can prevent foodborne illness from spreading. The common factors in the fecal-oral route can be summarized as five Fs: fingers, flies, fields, fluids, and food. Diseases caused by fecal-oral transmission include typhoid, cholera, polio, hepatitis and many other infections, especially ones that cause diarrhea. Background Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracellular Parasite
Intracellular parasites are microparasites that are capable of growing and reproducing inside the cells of a host. Types of parasites There are two main types of intracellular parasites: Facultative and Obligate. Facultative intracellular parasites are capable of living and reproducing in or outside of host cells. Obligate intracellular parasites, on the other hand, need a host cell to live and reproduce. Many of these types of cells require specialized host types, and invasion of host cells occurs in different ways. Facultative Facultative intracellular parasites are capable of living and reproducing either inside or outside cells. Bacterial examples include: *''Bartonella henselae'' *''Francisella tularensis'' *''Listeria monocytogenes'' * ''Salmonella'' Typhi *''Brucella'' *''Legionella'' *''Mycobacterium'' *'' Nocardia'' *''Neisseria'' *''Rhodococcus equi'' *''Yersinia'' *''Staphylococcus aureus'' Fungal examples include: *''Histoplasma capsulatum''. *''Cryptococcus neofo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |