|
Nastic Movement
Nastic movements are non-directional responses to stimuli (e.g. temperature, humidity, light irradiance), and are usually associated with plants. The movement can be due to changes in turgor. Decrease in turgor pressure causes shrinkage while increase in turgor pressure brings about swelling. Nastic movements differ from tropic movements in that the direction of tropic responses depends on the direction of the stimulus, whereas the direction of nastic movements is independent of the stimulus's position. The tropic movement is growth movement but nastic movement may or may not be growth movement. The rate or frequency of these responses increases as intensity of the stimulus increases. An example of such a response is the opening and closing of flowers (photonastic response), movement of euglena, chlamydomonas towards the source of light. They are named with the suffix "-nasty" and have prefixes that depend on the stimuli: * Epinasty: downward-bending from growth at the top, for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxalis Triangularis Photonasty Timelapse
''Oxalis'' ( (American English) or (British English)) is a large genus of flowering plants in the wood-sorrel family Oxalidaceae, comprising over 550 species. The genus occurs throughout most of the world, except for the polar areas; species diversity is particularly rich in tropical Brazil, Mexico, and South Africa. Many of the species are known as wood sorrels (sometimes written "woodsorrels" or "wood-sorrels") as they have an acidic taste reminiscent of the sorrel proper ('' Rumex acetosa''), which is only distantly related. Some species are called yellow sorrels or pink sorrels after the color of their flowers instead. Other species are colloquially known as false shamrocks, and some called sourgrasses. For the genus as a whole, the term oxalises is also used. Description and ecology These plants are annual or perennial. The leaves are divided into three to ten or more obovate and top-notched leaflets, arranged palmately with all the leaflets of roughly equal size. The maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyponastic Response
The hyponastic response is an upward bending of leaves or other plant parts, resulting from accelerated growth of the lower side of the petiole in comparison to its upper part. This can be observed in many terrestrial plants and is linked to the plant hormone ethylene Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds). Ethylene i .... The plant’s root senses the water excess and produces 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid which then is converted into ethylene, regulating this process.(Manual interactivo de fisiología vegetal;Facultad de Agronomía;Montevideo) Submerged plants often show the hyponastic response, where the upward bending of the leaves and the elongation of the petioles might help the plant to restore normal gas exchange with the atmosphere. Plants that are exposed to elevate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical and physical functions in a living system. According to the classes of organisms, the field can be divided into medical physiology, animal physiology, plant physiology, cell physiology, and comparative physiology. Central to physiological functioning are biophysical and biochemical processes, homeostatic control mechanisms, and communication between cells. ''Physiological state'' is the condition of normal function. In contrast, ''pathological state'' refers to abnormal conditions, including human diseases. The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine is awarded by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for exceptional scientific achievements in physiology related to the field of medicine. Foundations Cells Although there are differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinesis (biology)
Kinesis, like a taxis or tropism, is a movement or activity of a cell or an organism in response to a stimulus (such as gas exposure, light intensity or ambient temperature). Unlike taxis, the response to the stimulus provided is non-directional. The animal does not move toward or away from the stimulus but moves at either a slow or fast rate depending on its "comfort zone." In this case, a fast movement (non-random) means that the animal is searching for its comfort zone while a slow movement indicates that it has found it. Types There are two main types of kineses, both resulting in aggregations. However, the stimulus does not act to attract or repel individuals. Orthokinesis: in which the speed of movement of the individual is dependent upon the stimulus intensity. For example, the locomotion of the collembola, ''Orchesella cincta'', in relation to water. With increased water saturation in the soil there is an increase in the direction of its movement towards the aimed place. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxis
A taxis (; ) is the movement of an organism in response to a stimulus such as light or the presence of food. Taxes are innate behavioural responses. A taxis differs from a tropism (turning response, often growth towards or away from a stimulus) in that in the case of taxis, the organism has motility and demonstrates guided movement towards or away from the stimulus source. It is sometimes distinguished from a kinesis, a non-directional change in activity in response to a stimulus. Classification Taxes are classified based on the type of stimulus, and on whether the organism's response is to move towards or away from the stimulus. If the organism moves towards the stimulus the taxis are positive, while if it moves away the taxis are negative. For example, flagellate protozoans of the genus ''Euglena'' move towards a light source. This reaction or behavior is called ''positive phototaxis'' since phototaxis refers to a response to light and the organism is moving towards the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thigmonasty
Thigmonasty or seismonasty is the nastic movement, nastic response of a plant or fungus to touch or vibration. Conspicuous examples of thigmonasty include many species in the Fabaceae, leguminous family (biology), subfamily Mimosoideae, active carnivorous plants such as Dionaea (plant), Dionaea and a wide range of pollination mechanisms. Distinctive aspects Thigmonasty differs from thigmotropism in that nastic motion is independent of the direction of the stimulus. For example, tendrils from a climbing plant are thigmotropic because they twine around any support they touch, responding in whichever direction the stimulus came from. However, the shutting of a venus fly trap is thigmonastic; no matter what the direction of the stimulus, the trap simply shuts (and later possibly opens). The time scales of thigmonastic responses tend to be shorter than those of thigmotropic movements because many examples of thigmonasty depend on pre-accumulated turgor or on Bistability, bistable mec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermonasty
Thermonasty is a nondirectional response in plants to temperature. It is a form of nastic movement, not to be confused with thermotropism, which is a directional response in plants to temperature. A common example of this is in some ''Rhododendron'' species, but thermonasty has also been observed in other plants, such as ''Phryma leptostachya''. Flower opening in certain crocus and tulip species is also known to be thermonastic. These movements are thought to be regulated by having unequal cell elongation in certain plant tissues, causing different tissues to bend. In other processes, like in the temperature regulation of flower openings, movement has instead been shown to be a result of irreversible cell growth, a growth type not typically associated with plant movement. Furthermore, thermonasty has been shown to be independent of other environmental signals, such as light and gravity. Thermonasty is generally considered to be an adaptation for protection against colder temperatures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
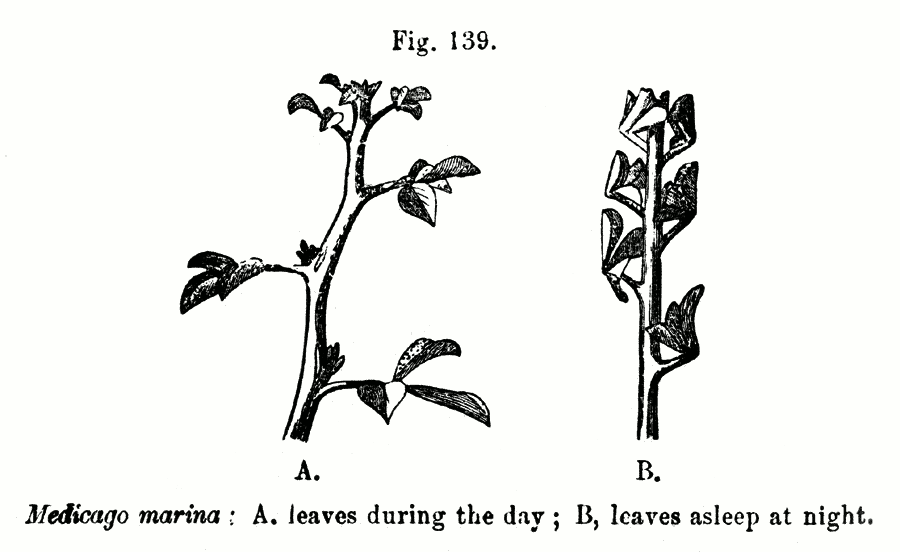
Nyctinasty
Nyctinasty is the circadian rhythmic nastic movement of higher plants in response to the onset of darkness, or a plant "sleeping". Nyctinastic movements are associated with diurnal light and temperature changes and controlled by the circadian clock. It has been argued that for plants that display foliar nyctinasty, it is a crucial mechanism for survival; however, most plants do not exhibit any nyctinastic movements. Nyctinasty is found in a range of plant species and across xeric, mesic, and aquatic environments, suggesting that this singular behavior may serve a variety of evolutionary benefits. Examples are the closing of the petals of a flower at dusk and the sleep movements of the leaves of many legumes. Physiology Plants use phytochrome to detect red and far red light. Depending on which kind of light is absorbed, the protein can switch between a Pr state that absorbs red light and a Pfr state that absorbs far red light. Red light converts Pr to Pfr and far red light convert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is equal to one event per second. The period is the interval of time between events, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency. For example, if a heart beats at a frequency of 120 times a minute (2 hertz), the period, —the interval at which the beats repeat—is half a second (60 seconds divided by 120 beats). Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio signals (sound), radio waves, and light. Definitions and units For cyclical phenomena such as oscillations, waves, or for examples of simple harmonic motion, the term ''frequency'' is defined as the number of cycles or vibrations per unit of time. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulus (psychology)
In psychology Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries betwe ..., a stimulus is any object or event that elicits a sensory or behavioral response in an organism. In this context, a distinction is made between the ''distal stimulus'' (the external, perceived object) and the ''proximal stimulus'' (the stimulation of sensory organs). *In perceptual psychology, a stimulus is an energy change (e.g., light or sound) which is registered by the senses (e.g., vision, hearing, taste, etc.) and constitutes the basis for perception. *In behavioral psychology (i.e., classical conditioning, classical and operant conditioning, operant conditioning), a stimulus constitutes the basis for behavior. The stimulus–response model emphasizes the relation between stimulus and behavior rather than an anim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropism
A tropism is a biological phenomenon, indicating growth or turning movement of a biological organism, usually a plant, in response to an environmental stimulus. In tropisms, this response is dependent on the direction of the stimulus (as opposed to nastic movements which are non-directional responses). Tropisms are usually named for the stimulus involved (for example, a phototropism is a reaction to sunlight). Tropisms occur in three sequential steps. First, there is a sensation to a stimulus. Next, signal transduction occurs. And finally, the directional growth response occurs. Tropisms are typically associated with plants (although not necessarily restricted to them). Where an organism is capable of directed physical movement (motility), movement or activity in response to a specific stimulus is more likely to be regarded by behaviorists as a ''taxis'' (directional response) or a '' kinesis'' (non-directional response). The Cholodny–Went model, proposed in 1927, is an ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turgor
Turgor pressure is the force within the cell that pushes the plasma membrane against the cell wall. It is also called ''hydrostatic pressure'', and is defined as the pressure in a fluid measured at a certain point within itself when at equilibrium. Generally, turgor pressure is caused by the osmotic flow of water and occurs in plants, fungi, and bacteria. The phenomenon is also observed in protists that have cell walls. This system is not seen in animal cells, as the absence of a cell wall would cause the cell to lyse when under too much pressure. The pressure exerted by the osmotic flow of water is called turgidity. It is caused by the osmotic flow of water through a selectively permeable membrane. Movement of water through a semipermeable membrane from a volume with a low solute concentration to one with a higher solute concentration is called osmotic flow. In plants, this entails the water moving from the low concentration solute outside the cell into the cell's vacuole. Mech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |