|
Numenius Of Apamea
Numenius of Apamea (, ''Noumēnios ho ex Apameias''; ) was a Greek philosopher, who lived in Rome, and flourished during the latter half of the 2nd century AD. He was a Neopythagorean and forerunner of the Neoplatonists. Philosophy Statements and fragments of his apparently very numerous works have been preserved by Origen, Theodoret, and especially by Eusebius, and from them we may learn the nature of his Platonist-Pythagorean philosophy, and its approximation to the doctrines of Plato. Numenius was a Neopythagorean, but his object was to trace the doctrines of Plato up to Pythagoras, and at the same time to show that they were not at variance with the dogmas and mysteries of the Brahmins, Jews, Magi and Egyptians. His intention was to restore the philosophy of Plato, the genuine Pythagorean and mediator between Socrates and Pythagoras in its original purity, cleared from the Aristotelian and Stoic doctrines, and purified from the unsatisfactory and perverse explanations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2,746,984 residents in , Rome is the list of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, third most populous city in the European Union by population within city limits. The Metropolitan City of Rome Capital, with a population of 4,223,885 residents, is the most populous metropolitan cities of Italy, metropolitan city in Italy. Rome metropolitan area, Its metropolitan area is the third-most populous within Italy. Rome is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, within Lazio (Latium), along the shores of the Tiber Valley. Vatican City (the smallest country in the world and headquarters of the worldwide Catholic Church under the governance of the Holy See) is an independent country inside the city boun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenocrates
Xenocrates (; ; c. 396/5314/3 BC) of Chalcedon was a Greek philosopher, mathematician, and leader ( scholarch) of the Platonic Academy from 339/8 to 314/3 BC. His teachings followed those of Plato, which he attempted to define more closely, often with mathematical elements. He distinguished three forms of being: the sensible, the intelligible, and a third compounded of the two, to which correspond respectively, sense, intellect and opinion. He considered unity and duality to be gods which rule the universe, and the soul a self-moving number. God pervades all things, and there are daemonical powers, intermediate between the divine and the mortal, which consist in conditions of the soul. He held that mathematical objects and the Platonic Ideas are identical, unlike Plato who distinguished them. In ethics, he taught that virtue produces happiness, but external goods can minister to it and enable it to effect its purpose. Life Xenocrates was a native of Chalcedon. By the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic particles. In everyday as well as scientific usage, ''matter'' generally includes atoms and anything made up of them, and any particles (or combination of particles) that act as if they have both rest mass and volume. However it does not include massless particles such as photons, or other energy phenomena or waves such as light or heat. Matter exists in various states (also known as phases). These include classical everyday phases such as solid, liquid, and gas – for example water exists as ice, liquid water, and gaseous steam – but other states are possible, including plasma, Bose–Einstein condensates, fermionic condensates, and quark–gluon plasma. Usually atoms can be imagined as a nucleus of protons and neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
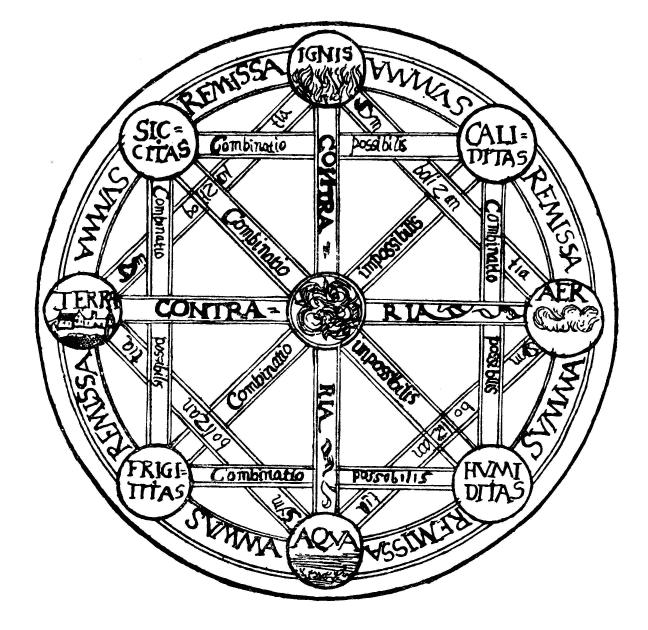
Classical Elements
The classical elements typically refer to earth, water, air, fire, and (later) aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler substances. Ancient cultures in Greece, Angola, Tibet, India, and Mali had similar lists which sometimes referred, in local languages, to "air" as "wind", and to "aether" as "space". These different cultures and even individual philosophers had widely varying explanations concerning their attributes and how they related to observable phenomena as well as cosmology. Sometimes these theories overlapped with mythology and were personified in deities. Some of these interpretations included atomism (the idea of very small, indivisible portions of matter), but other interpretations considered the elements to be divisible into infinitely small pieces without changing their nature. While the classification of the material world in ancient India, Hellenistic Egypt, and ancient Greece into air, earth, fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stoics
Stoicism is a school of Hellenistic philosophy that flourished in ancient Greece and Rome. The Stoics believed that the universe operated according to reason, ''i.e.'' by a God which is immersed in nature itself. Of all the schools of ancient philosophy, Stoicism made the greatest claim to being utterly systematic. The Stoics provided a unified account of the world, constructed from ideals of logic, monistic physics, and naturalistic ethics. These three ideals constitute virtue which is necessary for 'living a well reasoned life', seeing as they are all parts of a logos, or philosophical discourse, which includes the mind's rational dialogue with itself. Stoicism was founded in the ancient Agora of Athens by Zeno of Citium around 300 BC, and flourished throughout the Greco-Roman world until the 3rd century AD, and among its adherents was Roman Emperor Marcus Aurelius. Along with Aristotelian term logic, the system of propositional logic developed by the Stoics was one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eudorus Of Alexandria
Eudorus of Alexandria (; 1st century BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher, and a representative of Middle Platonism. He attempted to reconstruct Plato's philosophy in terms of Pythagoreanism. Life Little is known about Eudorus' life. Chronologically, he lived in the 1st century BC, and did his work prior to Strabo and Arius Didymus, both of whom quote him. He was involved in a plagiarism controversy with Aristo of Alexandria, one of Antiochus of Ascalon's students, as they had both written a work on the Nile. but he is not mentioned by Antiochus' contemporary Cicero, implying he was not one of Antiochus' students. Eudorus also wrote a survey of philosophy, at least one portion of which dealt with ethics, of which a summary by Arius Didymus is preserved in Stobaeus. He also wrote a commentary on Plato's '' Timaeus'' which is referred to by Plutarch, and may also have written a commentary on the '' Categories'' of Aristotle. Philosophy Eudorus combined Platonist, Pythagorean and S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moderatus Of Gades
Moderatus of Gades () was a Greek philosopher of the Neopythagorean school, who lived in the 1st century AD. He was a contemporary of Apollonius of Tyana. He wrote a great work on the doctrines of the Pythagoreans, and tried to show that the successors of Pythagoras had made no additions to the views of their founder, but had merely borrowed and altered the phraseology. Life Moderatus was from Gades, in Andalusia. He was probably a relative of the writer Columella (Lucius Junius Moderatus Columella), who shared the same cognomen and was also from Gades. Almost nothing is known about the life of Moderatus. The only concrete clue is provided by Plutarch, who reports that when he, Plutarch, returned to Rome after a long absence, Lucius, a disciple of Moderatus, who came from Etruria, was attending a banquet hosted by Sextius Sulla, a friend of Plutarch's. Since the banquet took place around 90 AD, it can be assumed that the teaching activity of Moderatus fell in the second half of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcidius
Calcidius (or Chalcidius) was a 4th-century philosopher who translated the first part (to 53c) of Plato's '' Timaeus'' from Greek into Latin around the year 321 and provided with it an extensive commentary. This was likely done for Bishop Hosius of Córdoba. Very little is otherwise known of him. His translation of the ''Timaeus'' was the only extensive text of Plato known to scholars in the Latin West for approximately 800 years.Edward Grant, (2004), ''Science and Religion, 400 B.C. to A.D. 1550'', pages 93–4. Greenwood Publishing Group His commentary also contained useful accounts of Greek astronomical knowledge. In the 12th century commentaries on this work were written by Christian scholars including Hisdosus and philosophers of the Chartres School, such as Thierry of Chartres and William of Conches. Interpreting it in the light of the Christian faith, the academics in the School of Chartres understood the dialogue to refer to '' creatio ex nihilo''. Calcidius' li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyry (philosopher)
Porphyry (; ; – ) was a Neoplatonic philosopher born in Tyre, Roman Phoenicia during Roman rule. He edited and published the '' Enneads'', the only collection of the work of Plotinus, his teacher. He wrote original works in the Greek language on a wide variety of topics, ranging from music theory to Homer to vegetarianism. His '' Isagoge'' or ''Introduction'', an introduction to logic and philosophy, was the standard textbook on logic throughout the Middle Ages in its Latin and Arabic translations. Porphyry was, and still is, also well-known for his anti-Christian polemics. Through works such as ''Philosophy from Oracles'' and '' Against the Christians'' (which was banned by Constantine the Great), he was involved in a controversy with early Christians. Life The ''Suda'' (a 10th-century Byzantine encyclopedia based on many sources now lost) reports that Porphyry was born in Tyre, however, other sources report that he was born in Batanaea, present-day Syria . His par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanford Encyclopedia Of Philosophy
The ''Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' (''SEP'') is a freely available online philosophy resource published and maintained by Stanford University, encompassing both an online encyclopedia of philosophy and peer-reviewed original publication. Each entry is written and maintained by an expert in the field, including professors from many academic institutions worldwide. Authors contributing to the encyclopedia give Stanford University the permission to publish the articles, but retain the copyright to those articles. Approach and history As of August 5, 2022, the ''SEP'' has 1,774 published entries. Apart from its online status, the encyclopedia uses the traditional academic approach of most encyclopedias and academic journals to achieve quality by means of specialist authors selected by an editor or an editorial committee that is competent (although not necessarily considered specialists) in the field covered by the encyclopedia and peer review. The encyclopedia was created i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platonic Academy
The Academy (), variously known as Plato's Academy, or the Platonic Academy, was founded in Classical Athens, Athens by Plato ''wikt:circa, circa'' 387 BC. The academy is regarded as the first institution of higher education in the west, where subjects as diverse as biology, geography, astronomy, mathematics, history, and many more were taught and investigated. Aristotle studied there for twenty years (367–347 BC) before founding his own school, the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum. The Academy persisted throughout the Hellenistic period as a Academic skepticism, skeptical school, until coming to an end after the death of Philo of Larissa in 83 BC. The Platonic Academy was destroyed by the Roman dictator Sulla in 86 BC. A neo-Platonic academy was later established in Athens that sought to continue the tradition of Plato's Academy. This academy was shut down by Justinian I, Justinian in 529 AD, when some of the scholars fled to Harran, where the study of classical texts continued. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apostasy
Apostasy (; ) is the formal religious disaffiliation, disaffiliation from, abandonment of, or renunciation of a religion by a person. It can also be defined within the broader context of embracing an opinion that is contrary to one's previous religious beliefs. One who undertakes apostasy is known as an apostate. Undertaking apostasy is called apostatizing (or apostasizing – also spelled apostacizing). The term ''apostasy'' is used by sociology, sociologists to mean the renunciation ''and'' criticism of, or opposition to, a person's former religion, in a technical sense, with no pejorative connotation. Occasionally, the term is also used metaphorically to refer to the renunciation of a non-religious belief or cause, such as a political party, social movement, or sports team. Apostasy is generally not a self-definition: few former believers call themselves apostates due to the term's negative connotation. Many religious groups and some states punish apostates; this may be the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |