|
Northern Sotho Language
Sepedi, also known as Northern Sotho, is one of South Africa’s twelve official languages and belongs to the Bantu language family, specifically the Sotho-Tswana group. The language is spoken mainly in Limpopo Province, and to a lesser extent in Gauteng, Mpumalanga, and North West''.'' Sepedi refers to the ''dialect'' spoken by the Pedi people. Northern Sotho is the umbrella term for a group of related dialects. The two terms are often used interchangeably, but technically Sepedi is one dialect of Northern Sotho. As of the 2022 South African Census, approximately 6.2 million people — or 10.0% of the national population speak Sepedi as their first language. Sepedi ranks as the fifth most spoken first language. Official language status Sepedi vs Northern Sotho According to Chapter 1, Section 6 of the South African Constitution, Sepedi is one of South Africa's 12 official languages. There has been significant debate about whether Northern Sotho should be used instead of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
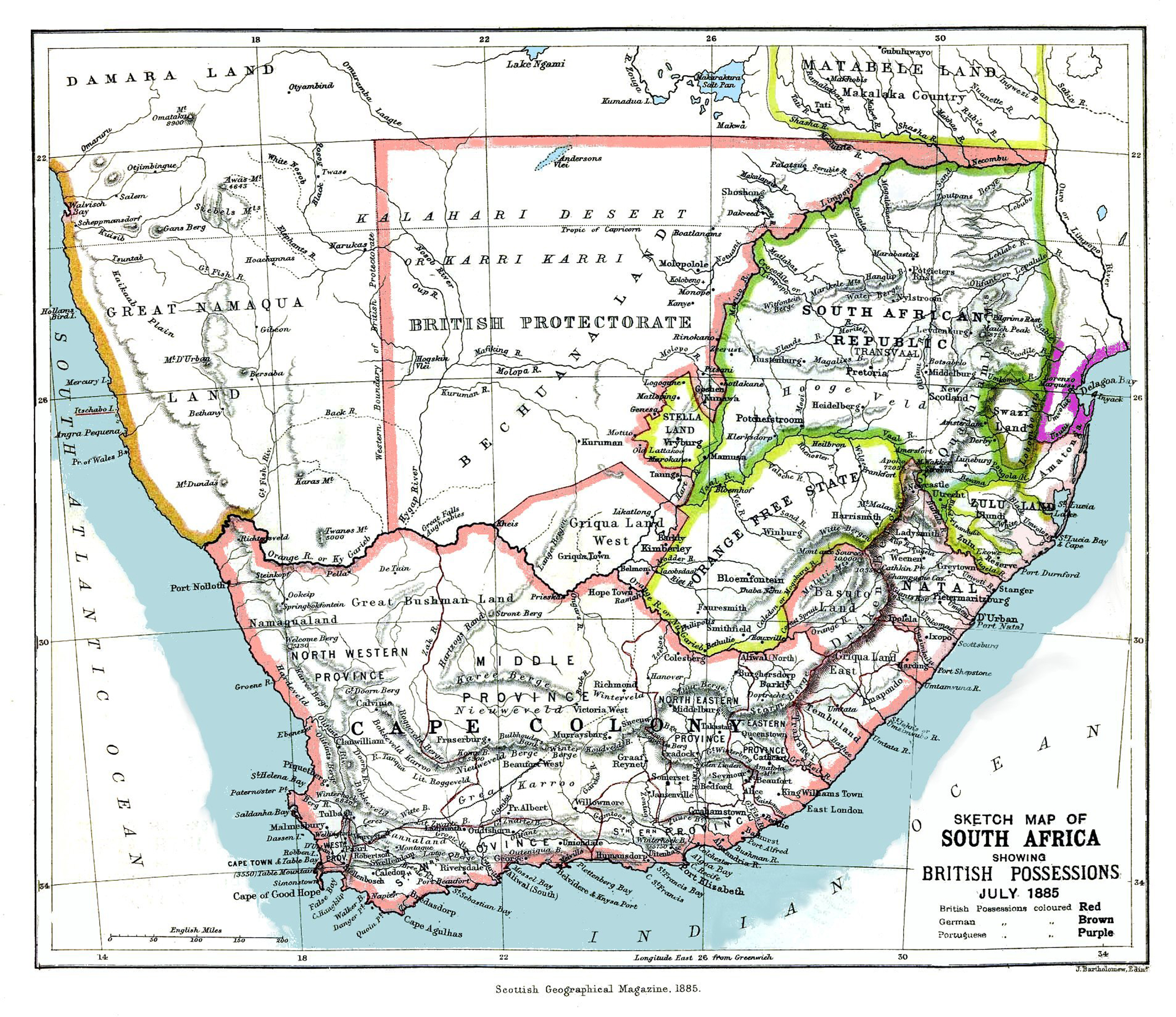
South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. Its Provinces of South Africa, nine provinces are bounded to the south by of coastline that stretches along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Ocean; to the north by the neighbouring countries of Namibia, Botswana, and Zimbabwe; to the east and northeast by Mozambique and Eswatini; and it encloses Lesotho. Covering an area of , the country has Demographics of South Africa, a population of over 64 million people. Pretoria is the administrative capital, while Cape Town, as the seat of Parliament of South Africa, Parliament, is the legislative capital, and Bloemfontein is regarded as the judicial capital. The largest, most populous city is Johannesburg, followed by Cape Town and Durban. Cradle of Humankind, Archaeological findings suggest that various hominid species existed in South Africa about 2.5 million years ago, and modern humans inhabited the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signed Northern Sotho
Signing or Signed may refer to: * Using sign language * Signature, placing one's name on a document * Signature (other) * Manual communication, signing as a form of communication using the hands in place of the voice * Digital signature, signing as a method of authenticating digital information * Traffic sign Traffic signs or road signs are signs erected at the side of or above roads to give instructions or provide information to road users. The earliest signs were simple wooden or stone milestones. Later, signs with directional arms were introduc ..., a road with a sign identifying is considered ''signed'' See also * Wikipedia:Sign your posts on talk pages, the Wikipedia policy of signing Talk pages {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MaPulana
The Mapulana or Pulana, are a low-veld ethnic group found in Bushbuckridge near Mpumalanga and Limpopo provinces. Their language is called Sepulana, it is erroneously considered a dialect of the Northern Sotho language group due to their proximity to the Bapedi people of Limpopo. Although it does share some similarities to Sepedi Northern Sotho, it is not a dialect of Sepedi - Sesotho Sa Lebowa). Sepulana forms part of the Eastern Sotho tribes, alongside Pai and Kutswe . Some of the Eastern Sotho tribes were settled in the Pilgrim's Rest district of the Former Transvaal Province. It is influenced by Swati, Xitsonga, Afrikaans, and English . The area where the Pulana live is called Bushbuckridge; it stretches from Crocodile River in the south to the Swazi border (Mapulana of Mashego) in the north, from the Crocodile to Olifants River (Limpopo) in the north, Lebombo Mountains in the east, and also includes the towns of Hazyview, White River, Mpumalanga ( Lepunama), Sabie, G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bapedi
The Pedi or - also known as the Northern Sotho, Basotho ba Lebowa, bakgatla ba dithebe, Transvaal Colony, Transvaal Sotho, Marota, or Dikgoshi - are a Sotho-Tswana peoples, Sotho-Tswana ethnic group native to South Africa, Botswana, and Lesotho that speak Pedi or ''Sepedi,'' which is one of the 12 official languages in South Africa. They are primarily situated in Limpopo, Gauteng and northern Mpumalanga. The Pedi people are part of the Bantu peoples of South Africa, Bantu ethnic group. Their common ancestors, along with the Sotho people, Sotho and Tswana people, Tswana, migrated from East Africa to South Africa no later than the 7th century CE. Over time, they emerged as a distinct people between the 15th and 18th centuries, with some settling in the northern region of the Transvaal. The Pedi maintained close ties with their relatives and neighboring tribes. Towards the end of the 18th century, the primary Pedi state was established, led by supreme leaders from the Maroteng ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veld
Veld ( or , Afrikaans language, Afrikaans and Dutch language, Dutch: ''veld'', field), also spelled veldt, is a type of wide-open, rural landscape in Southern Africa. Particularly, it is a flat area covered in grass or low scrubland, scrub, especially in the countries of South Africa, Namibia, Lesotho, Eswatini, Zimbabwe, and Botswana. A certain subtropical woodland ecoregion of Southern Africa has been officially defined as the Bushveld by the World Wide Fund for Nature. Trees are not abundant; frost, fire, and grazing animals allow grass to grow, but prevent the build-up of dense foliage. Etymology The word ''veld'' () comes from the Afrikaans language, Afrikaans word for "field". The etymological origin is older modern Dutch language, Dutch ''veldt'', a spelling that the History of Dutch orthography, Dutch abandoned in favour of ''veld'' during the 19th century, decades before the first Afrikaans dictionary.Eric Anderson Walker (ed). The Cambridge History of the British E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highveld
The Highveld (Afrikaans: ''Hoëveld,'' , ) is the portion of the South African inland plateau which has an altitude above roughly , but below , thus excluding the Lesotho mountain regions to the south-east of the Highveld. It is home to some of the country's most important commercial farming areas, as well as its largest concentration of metropolitan centres, especially the Gauteng conurbation, which accommodates one-third of South Africa's population. Location and description The Highveld constitutes almost all of the provinces of Free State and Gauteng and portions of the surrounding areas: the western rim of Lesotho and portions of the Eastern Cape, Northern Cape, North West, Limpopo, and Mpumalanga provinces of South Africa. The highest part of the Highveld, around , is its northeastern well-defined boundary, where the plateau escarpment (the Mpumalanga Drakensberg) separates it from the Mpumalanga Lowveld, (containing, amongst others, the Kruger National Park). Another we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modjadji
Queen Modjadji, or the Rain Queen, is the hereditary queen of Balobedu, a people of the Limpopo Province of South Africa. The Rain Queen is believed to have special powers, including the ability to control the clouds and rainfall. She is known as a mystical and historic figure who brought rain to her allies and drought to her enemies. She is not a ruler as such, but a powerful rainmaker and a traditional healer (ngaka). , the title is in dispute between two claimants. The traditional installation of Prince Lekukela Modjadji as the king of the Balobedu took place in October 2022 at Khetlhakoni Royal Palace in Modjadjiskloof outside Tzaneen in Limpopo. Princess Masalanabo, who was expected to be the next Rain Queen, is intended by the faction of the Modjadji Royal Council that installed him to now take a position reserved for her and become the Khadikholo (great aunt) of Balobedu. The other claimant is Lekukela's sister, who is known to loyalists as Masalanabo II Modjadji VII ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Merensky
Alexander Merensky (8 June 1837 in Panten near Liegnitz – 22 May 1918 in Berlin) was a German missionary, working in South Africa (Transvaal) from 1859 to 1892. Early life Alexander's mother, Pauline von Kessel, died during his birth, and his father, Conrad Albert Friedrich, seven years later, in 1844. He was therefore orphaned early in life and grew up in the well-known Schindler orphanage and among relatives. Encouraged by the well-known Rev. Gustav Knak, he entered the mission seminary of the Berlin Missionary Society in 1855 and was sent out on 23 November 1858. Together with a fellow missionary, Karl-Heinrich Theodor Grützner, he travelled by sailboat from Amsterdam to Cape Town and on to Natal. Mission stations On 14 August 1860, he and fellow missionary Heinrich Grützner co-founded the mission station Gerlachshoop, the first mission station of the Berlin Missionary Society north of the Vaal River. Merensky was ordained as missionary in Gerlachshoop on 11 Janu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedi Language
Sepedi, also known as Northern Sotho, is one of South Africa’s twelve official languages and belongs to the Bantu language family, specifically the Sotho-Tswana group. The language is spoken mainly in Limpopo Province, and to a lesser extent in Gauteng, Mpumalanga, and North West''.'' Sepedi refers to the ''dialect'' spoken by the Pedi people. Northern Sotho is the umbrella term for a group of related dialects. The two terms are often used interchangeably, but technically Sepedi is one dialect of Northern Sotho. As of the 2022 South African Census, approximately 6.2 million people — or 10.0% of the national population speak Sepedi as their first language. Sepedi ranks as the fifth most spoken first language. Official language status Sepedi vs Northern Sotho According to Chapter 1, Section 6 of the South African Constitution, Sepedi is one of South Africa's 12 official languages. There has been significant debate about whether Northern Sotho should be used instead of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlôkwa People
The term Batlôkwa (also Batlokoa, or Badogwa) refers to several Kgatla communities that reside in Botswana, Lesotho and South Africa. It comprises the followers of Tlôkwa kings and the members of clans identified as Tlôkwa, or individuals who identify themselves as of Tlôkwa descent. Most of the Batlôkwa clans trace their royal lineages to Kgwadi son of King Tabane, who was the father and founder of the Batlokwa nation. The Tlôkwa considers the Tlokwe-cat as their original totem which has since become extinct due to over-hunting for its fur, which was used by clan chiefs. Classification The Batlôkwa kingdom is part of the larger group of Bakgatla people, which is one of sub-divisions of the Bantu-speaking Tswana peoples. These different groups are often classified for convenience as 'Sotho-Tswana'. This is because, from an early stage of their history, they shared a number of linguistic and cultural characteristics that distinguished them from other Bantu-speakers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |