|
Norepinephrine–dopamine Reuptake Inhibitor
A norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI) is a type of drug that inhibits the reuptake of the monoamine neurotransmitters norepinephrine and dopamine and thereby increases extracellular levels of these neurotransmitters and noradrenergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission. They work by competitively and/or noncompetitively inhibiting the norepinephrine transporter (NET) and dopamine transporter (DAT). NDRIs are used clinically in the treatment of conditions including attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and depression. Examples of well-known NDRIs include methylphenidate and bupropion. A closely related type of drug is a norepinephrine–dopamine releasing agent (NDRA). List of NDRIs Many NDRIs exist, including the following: Some NDRIs, such as methylphenidate, may not act as simple NDRIs but rather as DAT "inverse agonists" (and possibly also analogously at the NET as well). If this theory is correct, then methylphenidate a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depression (mood)
Depression is a mental state of low Mood (psychology), mood and aversion to activity. It affects about 3.5% of the global population, or about 280 million people worldwide, as of 2020. Depression affects a person's thoughts, behavior, feelings, and subjective well-being, sense of well-being. The pleasure or joy that a person gets from certain experiences is reduced, and the afflicted person often experiences a loss of motivation or interest in those activities. People with depression may experience sadness, feelings of dejection or hopelessness, difficulty in thinking and concentration, or a significant change in appetite or time spent sleeping; Suicidal ideation, suicidal thoughts can also be experienced. Depression can have multiple, sometimes overlapping, origins. Depression can be a symptom of some mood disorders, some of which are also commonly called ''depression'', such as major depressive disorder, bipolar disorder and dysthymia. Additionally, depression can be a norm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lefetamine
Lefetamine (Santenol) is a drug which is a stimulant and also an analgesic with effects comparable to codeine. Discovery The parent structure of lefetamine, 1,2-diphenylethylamine was first synthesized in the 1940s and showed weak analgesic activity. Lefetamine itself was first investigated in Japan in the 1950s. The L-isomer showed weak analgesic action comparable to codeine and antitussive action far weaker than codeine. The d-isomer showed no such activity but caused seizures in rats. Society and culture It was abused in Japan during the 1950s. In a small study in 1989 it showed some effect against opioid withdrawal symptoms without causing withdrawal symptoms itself. It was concluded that it may be an opioid partial agonist. It has been abused in Europe; in 1989 a small study of 15 abusers and some volunteers found that it had some partial similarity to opioids, that it produced withdrawal symptoms, and had dependence and abuse potential to a certain degree. In a sm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fencamine
Fencamine (Altimina, Sicoclor) is a psychostimulant drug of the amphetamine class. It is closely related to fenethylline Fenethylline (British Approved Name, BAN, United States Adopted Name, USAN) or fenetylline (International Nonproprietary Name, INN) is a codrug of amphetamine and theophylline and so a mutual prodrug of both. It is also spelled phenethylline; .... References Methamphetamines Norepinephrine-dopamine releasing agents Xanthines {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fencamfamine
Fencamfamin (INN), also known as fencamfamine or by the brand names Glucoenergan and Reactivan, is a stimulant which was developed by Merck in the 1960s. Medical uses Fencamfamin is still used, though rarely, for treating depressive day-time fatigue, lack of concentration and lethargy, particularly in individuals who have chronic medical conditions, as its favourable safety profile makes it the most suitable drug in some cases. Adverse effects Fencamfamin is well tolerated and causes minimal circulatory effects. Extended use may result in a dryness of the mouth. Contraindications Not to be used with heart diseases, angina pectoris and decompensated cardiac insufficiency, glaucoma, hyper-excitability and thyrotoxicosis or while treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Overdose Symptoms of overdose are nausea, agitation and restlessness, dryness of the mouth, dizziness and tremor. In gross overdosage also associated with dyspnoea, tachycardia, disorientation and convulsions. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylphenidate
Ethylphenidate (EPH) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and a close analog of methylphenidate. Ethylphenidate acts as a norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor, meaning it effectively boosts the levels of the norepinephrine and dopamine neurotransmitters in the brain, by binding to, and partially blocking the transporter proteins that normally remove those monoamines from the synaptic cleft. Ethylphenidate, being almost identical to methylphenidate in both structure and pharmacodynamics, likely also doesn't solely act as a "classical" reuptake inhibitor but primarily as an inverse agonist at the dopamine transporter (DAT), inducing dopamine transporter reversal and subsequent dopamine release from the axon terminal into the synaptic cleft in a manner similar to but distinct from amphetamines. Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics Ethylphenidate metabolizes into methylphenidate and ritalinic acid. Tiny amounts of ethylphenidate can be formed ''in vivo'' when ethanol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenylprolinol
Diphenylprolinol (D2PM), or (''R''/''S'')-(±)-diphenyl-2-pyrrolidinyl-methanol, is a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor which is used as a designer drug. Pharmacology The dextrorotary (''R'')-(+)-enantiomer is the more pharmacologically active, although a variety of related derivatives have been studied. Side effects including chest pain (suggestive of possible cardiovascular toxicity) have been seen following recreational use of diphenylprolinol, although it was combined with glaucine in a party pill product, thus making it impossible to say for certain which drug was responsible. Other uses Diphenylprolinol can be used to prepare the chiral CBS catalyst, which is used for enantioselective organic synthesis. See also * 2-Diphenylmethylpyrrolidine (Desoxy-diphenylprolinol) * Desoxypipradrol * Laballenic acid * Pipradrol * Prolinol Prolinol is a chiral amino-alcohol that is used as a chiral building block in organic synthesis. It exists as two enantiomers: t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Difemetorex
Difemetorex (INN) or diphemethoxidine (USAN) is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant drug introduced in France in 1966 by the pharmaceutical company, Ciba-Geigy; it was briefly used as an appetite suppressant and weight loss aid into the early 1970s, sold under the brand name Cleofil. A member of the piperidine chemical class, difemetorex was described as having such a disruptive and intolerable side effect of insomnia that patient drug compliance suffered and frequency of clinical use decreased, resulting in withdrawal from the market and cessation of production, availability, accessibility, and overall recognition among related substances. It is only known to have been marketed in France, and has remained virtually non-existent in the current era. Synthesis Alkylation of desoxypipradrol with ethylene oxide gives difemetorex. See also * Desoxypipradrol * Diphenylprolinol * SCH-5472 * Fenproporex * Mefenorex * Adrafinil * Ananxyl * Paroxetine * Pitolisant * Raloxife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dexmethylphenidate
Dexmethylphenidate, sold under the brand name Focalin among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant used in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in those over the age of five years. It is taken by mouth. The immediate-release formulation lasts up to five hours while the extended-release formulation lasts up to twelve hours. It is the more active enantiomer of methylphenidate. Common side effects include abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and fever. Serious side effects may include psychosis, sudden cardiac death, mania, anaphylaxis, seizures, and priapism. Safety during pregnancy and breastfeeding is unclear. Dexmethylphenidate was approved for medical use in the United States in 2001. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 109th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 5million prescriptions. Medical uses Dexmethylphenidate is used as a treatment for attention deficit hyperact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desoxypipradrol
Desoxypipradrol, also known as 2-diphenylmethylpiperidine (2-DPMP), is a drug developed by Ciba in the 1950s which acts as a norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NDRI). Chemistry Desoxypipradrol is closely related on a structural level to the compounds methylphenidate and pipradrol, all three of which share a similar pharmacological action. Of these three piperidines, desoxypipradrol has the longest elimination half-life, as it is a highly lipophilic molecule lacking polar functional groups that are typically targeted by metabolic enzymes, giving it an extremely long duration of action when compared to most psychostimulants. Methylphenidate, on the other hand, is a short-acting compound, as it possesses a methyl-ester moiety that is easily cleaved, forming a highly polar acid group, while pipradrol is intermediate in duration, possessing a hydroxyl group which can be conjugated (e.g. with glucuronide) to increase its hydrophilicity and facilitate excretion, but no eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
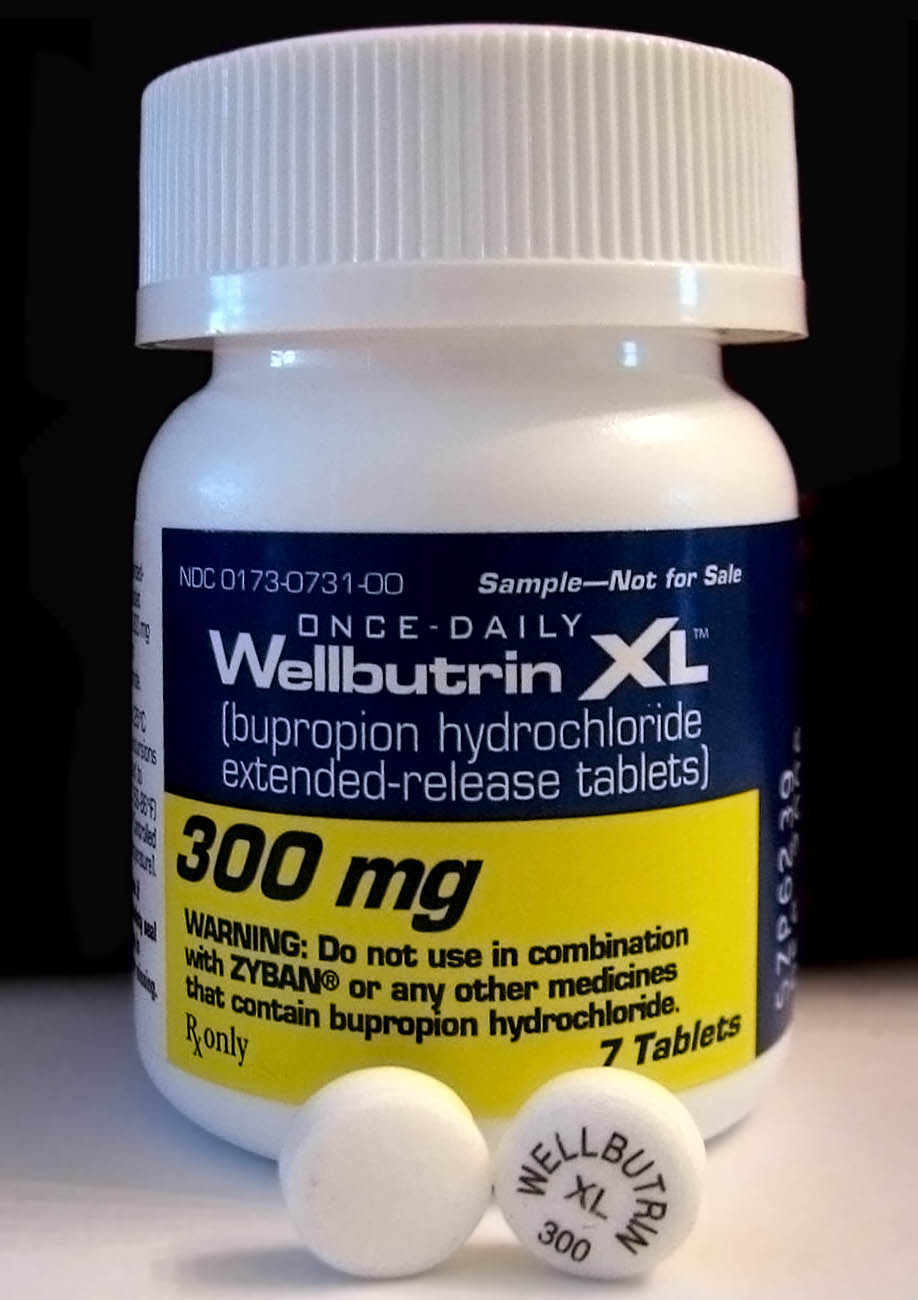
Bupropion
Bupropion, formerly called amfebutamone, and sold under the brand name Wellbutrin among others, is an atypical antidepressant that is indicated in the treatment of major depressive disorder, seasonal affective disorder, and to support smoking cessation. It is also popular as an add-on medication in the cases of "incomplete response" to the first-line selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant. Bupropion has several features that distinguish it from other antidepressants: it does not usually cause sexual dysfunction, it is not associated with weight gain and sleepiness, and it is more effective than SSRIs at improving symptoms of hypersomnia and fatigue. Bupropion, particularly the immediate-release formulation, carries a higher risk of seizure than many other antidepressants, hence caution is recommended in patients with a history of seizure disorder. The medication is taken by mouth. Common adverse effects of bupropion with the greatest difference fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amineptine
Amineptine, formerly sold under the brand name Survector among others, is an atypical antidepressant of the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) family. It acts as a selective and mixed dopamine reuptake inhibitor and releasing agent, and to a lesser extent as a norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. Amineptine was developed by the French Society of Medical research in the 1960s. Introduced in France in 1978 by the pharmaceutical company Servier, amineptine soon gained a reputation for abuse due to its short-lived, but pleasant, stimulant effect experienced by some patients. After widespread adoption of this drug, cases of hepatotoxicity emerged, some serious. This, along with the potential for abuse, led to the suspension of the French marketing authorization for Survector in 1999. Amineptine is illegal in both Germany and the United States. Medical uses Amineptine was approved in France for severe clinical depression of endogenous origin in 1978. Contraindications * Chorea * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |