|
Non-finite Clause
In linguistics, a non-finite clause is a dependent or embedded clause that represents a state or event in the same way no matter whether it takes place before, during, or after text production. In this sense, a non-finite dependent clause represents one process as a circumstance for another without specifying the time when it takes place as in the following examples: ;Non-Finite Dependent Clauses * ''I'm going to Broadway to watch a play''. * ''I went to Broadway to watch a play''. ;Finite Dependent Clauses * ''I'm going to Broadway so I can watch a play''. * ''I went to Broadway so I could watch a play''. Similarly, a non-finite embedded clause represents a qualification for something that is being represented as in the following examples: ;Non-Finite Embedded Clauses * ''I'm on a street called Bellevue Avenue''. * ''I was on a street called Bellevue Avenue''. ;Finite Embedded Clauses * ''I'm on a street that is called Bellevue Avenue''. * ''I'm on a street that used to be ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperative Mood
The imperative mood is a grammatical mood that forms a command or request. The imperative mood is used to demand or require that an action be performed. It is usually found only in the present tense, second person. They are sometimes called ''directives'', as they include a feature that encodes directive force, and another feature that encodes modality of unrealized interpretation. An example of a verb used in the imperative mood is the English phrase "Go." Such imperatives imply a second-person subject (''you''), but some other languages also have first- and third-person imperatives, with the meaning of "let's (do something)" or "let them (do something)" (the forms may alternatively be called cohortative and jussive). Imperative mood can be denoted by the glossing abbreviation . It is one of the irrealis moods. Formation Imperative mood is often expressed using special conjugated verb forms. Like other finite verb forms, imperatives often inflect for person and nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
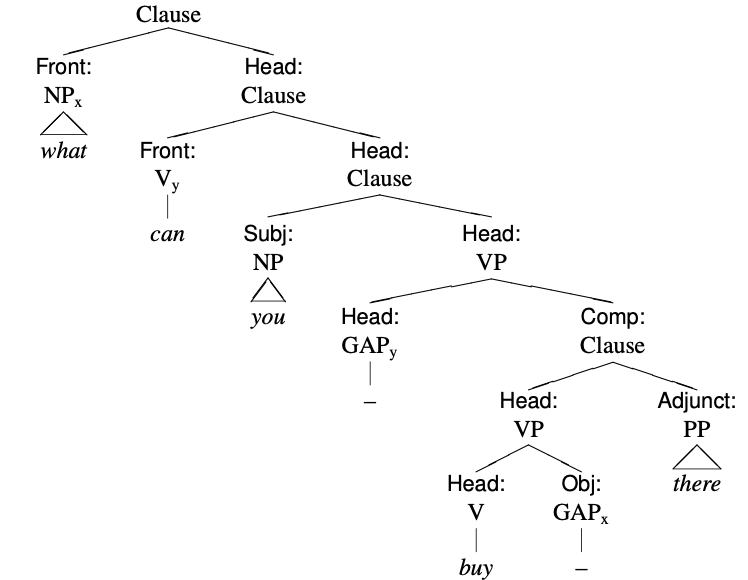
English Clause Syntax
This article describes the syntax of clauses in the English language, chiefly in Modern English. A clause is often said to be the smallest grammatical unit that can express a Proposition, complete proposition. But this Semantics, semantic idea of a clause leaves out much of English clause syntax. For example, clauses can be questions, but questions are not propositions. A syntactic description of an English clause is that it is a Subject (grammar), subject and a English verbs, verb. But this too fails, as a clause need not have a subject, as with the imperative, and, in many theories, an English clause may be verbless. The idea of what qualifies varies between theories and has changed over time. History of the concept The earliest use of the word ''clause'' in Middle English is non-technical and similar to the current everyday meaning of ''phrase'': "A sentence or clause, a brief statement, a short passage, a short text or quotation; in a ~, briefly, in short; (b) a written message ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carthago Delenda Est
("Furthermore, I think that Carthage must be destroyed"), often abbreviated to or ("Carthage must be destroyed"), is a Latin oratorical phrase attributed to Cato the Elder, a politician of the Roman Republic. The phrase originates from debates held in the Roman Senate prior to the Third Punic War (149–146 BC) between Rome and Carthage. Cato is said to have used the phrase as the conclusion to all of his speeches to push for the war, even when the speech was otherwise unrelated to Carthage or foreign affairs. Historical background Although Rome was successful in the first two Punic Wars, as it vied for dominance with the seafaring Punic city-state of Carthage in North Africa (now Tunisia), it suffered several humiliations and damaging reverses in the course of these engagements, especially at the Battle of Cannae in 216 BC. Rome nonetheless managed to win the Second Punic War thanks to Scipio Africanus in 201 BC. After its defeat, Carthage ceased to be a threat to Rome an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nominative Absolute
In English grammar, a nominative absolute is an absolute, the term coming from Latin for "loosened from" or "separated", part of a sentence, functioning as a sentence modifier (usually at the beginning or end of the sentence). It provides an additional information about the main subject and verb. Its analogues are the ablative absolute in Latin, the genitive absolute in Greek, or the locative absolute in Sanskrit. A noun in the common case or a pronoun in the nominative case is joined with a predicate that does not include a finite verb A finite verb is a verb that contextually complements a subject, which can be either explicit (like in the English indicative) or implicit (like in null subject languages or the English imperative). A finite transitive verb or a finite intra .... One way to identify a nominative absolute is to add a conjunction and a verb: one can often (though not always) create a subordinate clause out of a nominative absolute by adding a subordina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Progressive Aspect
The continuous and progressive aspects (abbreviated and ) are grammatical aspects that express incomplete action ("to do") or state ("to be") in progress at a specific time: they are non-habitual, imperfective aspects. In the grammars of many languages the two terms are used interchangeably. This is also the case with English: a construction such as ''"He is washing"'' may be described either as ''present continuous'' or as ''present progressive''. However, there are certain languages for which two different aspects are distinguished. In Chinese, for example, ''progressive'' aspect denotes a current action, as in "he is getting dressed", while ''continuous'' aspect denotes a current state, as in "he is wearing fine clothes". As with other grammatical categories, the precise semantics of the aspects vary from language to language, and from grammarian to grammarian. For example, some grammars of Turkish count the -iyor form as a present tense; some as a progressive tense; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adverbial
In English grammar, an adverbial ( abbreviated ) is a word (an adverb) or a group of words (an adverbial clause or adverbial phrase) that modifies or more closely defines the sentence or the verb. (The word ''adverbial'' itself is also used as an adjective, meaning "having the same function as an adverb".) Look at the examples below: :''Danny speaks fluently.'' (telling more about the verb) :''Lorna ate breakfast yesterday morning''. (telling when the verb's action occurred) The form of adverbials Adverbials most commonly take the form of adverbs, adverb phrases, temporal noun phrases or prepositional phrases. Many types of adverbials (for instance: reason and condition) are often expressed by clauses In language, a clause is a Constituent (linguistics), constituent or Phrase (grammar), phrase that comprises a semantic predicand (expressed or not) and a semantic Predicate (grammar), predicate. A typical clause consists of a subject (grammar), .... :''James answered immedi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Predicative Expression
A predicative expression (or just predicative) is part of a clause predicate, and is an expression that typically follows a copula or linking verb, e.g. ''be'', ''seem'', ''appear'', or that appears as a second complement (object complement) of a certain type of verb, e.g. ''call'', ''make'', ''name'', etc. The most frequently acknowledged types of predicative expressions are predicative adjectives (also predicate adjectives) and predicative nominals (also predicate nominals). The main trait of all predicative expressions is that they serve to express a property that is assigned to a "subject", whereby this subject is usually the clause subject, but at times it can be the clause object. A primary distinction is drawn between predicative (also ''predicate'') and attributive expressions. Further, predicative expressions are typically ''not'' clause arguments, and they are also typically ''not'' clause adjuncts. There is hence a three-way distinction between predicative expressi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subject (grammar)
A subject is one of the two main parts of a Sentence (linguistics), sentence (the other being the Predicate (grammar), predicate, which modifies the subject). For the simple Sentence (linguistics), sentence ''John runs'', ''John'' is the subject, a person or thing about whom the statement is made. Traditionally the subject is the word or phrase which controls the verb in the clause, that is to say with which the verb Agreement (linguistics), agrees (''John is'' but ''John and Mary are''). If there is no verb, as in ''Nicola what an idiot!'', or if the verb has a different subject, as in ''John I can't stand him!'', then 'John' is not considered to be the grammatical subject, but can be described as the ''Topic and comment, topic'' of the sentence. While these definitions apply to simple English sentences, defining the subject is more difficult in more complex sentences and languages. For example, in the sentence ''It is difficult to learn French'', the subject seems to be the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar
In linguistics, grammar is the set of rules for how a natural language is structured, as demonstrated by its speakers or writers. Grammar rules may concern the use of clauses, phrases, and words. The term may also refer to the study of such rules, a subject that includes phonology, morphology (linguistics), morphology, and syntax, together with phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are, broadly speaking, two different ways to study grammar: traditional grammar and #Theoretical frameworks, theoretical grammar. Fluency in a particular language variety involves a speaker internalizing these rules, many or most of which are language acquisition, acquired by observing other speakers, as opposed to intentional study or language teaching, instruction. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later in life usually involves more direct instruction. The term ''grammar'' can also describe the linguistic behaviour of groups of speakers and writer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Passive Voice
In English, the passive voice is marked by a subject that is followed by a stative verb complemented by a past participle. For example: The recipient of a sentence's action is referred to as the patient. In sentences using the active voice, the subject is the of the action—referred to as the agent. Above, the agent is omitted entirely, but it may also be included adjunctively while maintaining the passive voice: The initial examples rewritten in the active voice yield: The English passive voice typically involves forms of the verbs ''to be'' or ''to get'' followed by a passive participle as the subject complement—sometimes referred to as a ''passive verb''. English allows a number of additional passive constructions that are not possible in many other languages with analogous passive formations to the above. A sentence's indirect object may be promoted to the subject position—e.g. ''Tom was given a bag''. Similarly, the complement of a preposition may be promoted, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press was the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted a letters patent by King Henry VIII in 1534, it was the oldest university press in the world. Cambridge University Press merged with Cambridge Assessment to form Cambridge University Press and Assessment under Queen Elizabeth II's approval in August 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 countries, it published over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publications include more than 420 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and university textbooks, and English language teaching and learning publications. It also published Bibles, runs a bookshop in Cambridge, sells through Amazon, and has a conference venues business in Cambridge at the Pitt Building and the Sir Geoffrey Cass Sports and Social Centre. It also served as the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press, as part of the University of Cambridge, was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |