|
Nogai Horde
The Nogai Horde was a confederation founded by the Nogais that occupied the Pontic–Caspian steppe from about 1500 until they were pushed west by the Kalmyks and south by the Russians in the 17th century. The Mongol tribe called the Manghuds constituted a core of the Nogai Horde. In the 13th century, the leader of the Golden Horde, Nogai Khan, a direct descendant of Genghis Khan through Jochi, formed an army of the Manghits joined by numerous Turkic tribes. A century later the Nogays were led by Edigu, a commander of Manghit paternal origin and Jochid maternal origin, who founded the Nogai dynasty. In 1557, Nogai ''Nur-al-Din'' Qazi Mirza quarreled with Ismael Beg and founded the Lesser Nogai Horde on the steppe of the North Caucasus. The Nogais north of the Caspian were thereafter called the Great Nogai Horde. In the early 17th century, the Horde broke down further under the onslaught of the Kalmyks. The Nogais north of the Black Sea were nominally subject to the Crimean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orda (organization)
An orda (also ordu, ordo, or ordon) or horde was a historical sociopolitical and military structure found on the Eurasian Steppe, usually associated with the Turkic and Mongol peoples. This form of entity can be seen as the regional equivalent of a clan or a tribe of nomads. Some successful ordas gave rise to khanates. The original term did not carry the meaning of a large khanate such as the Golden Horde. These structures were contemporarily referred to as ''ulus'' ("nation" or "tribe"). Etymology Etymologically, the word ''ordu'' ultimately comes from the Turkic ''ordu'' which means "army" in Turkic and Mongolian languages, as well as "seat of power" or "royal court". In English, it was directly or indirectly borrowed from Latin ''orda'', or from Polish ''horda''. Within the Liao Empire of the Khitans, the word ordo was used to refer to a nobleman's personal entourage or court, which included servants, retainers, and bodyguards. Emperors, empresses, and high ranking ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Tribes
The Turkic languages, Turkic term ''oğuz'' or ''oğur'' (in z-Turkic, z- and r-Turkic, respectively) is a historical term for "military division, clan, or tribe" among the Turkic peoples. With the Mongol invasions of 1206–21, the Turkic Khanate, khaganates were replaced by Mongolic peoples, Mongol or hybrid Turco-Mongol confederations, where the corresponding military division came to be known as ''Orda (organization), orda''. Background The 8th-century Orkhon inscriptions, Kul Tigin stela has the earliest instance of the term in Old Turkic epigraphy: ''Toquz Oghuz'', the "nine tribes". Later the word appears often for two largely separate groups of the Turkic migration in the early medieval period, namely: *Onogurs, Onogur ("ten tribes") *Utigurs *Kutrigurs *Uyghur Khaganate, Uyghur *Saragurs The stem ''uq-, oq-'' "kin, tribe" is from a Proto-Turkic ''*uk''. The Old Turkic word has often been connected with ''oq'' "arrow"; Pohl (2002) in explanation of this connection add ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuban
Kuban ( Russian and Ukrainian: Кубань; ) is a historical and geographical region in the North Caucasus region of southern Russia surrounding the Kuban River, on the Black Sea between the Don Steppe, the Volga Delta and separated from the Crimean Peninsula to the west by the Kerch Strait. Krasnodar Krai is often referred to as ''Kuban'', both officially and unofficially, although the term is not exclusive to the krai and also accommodates the republics of Adygea, Karachay-Cherkessia, and parts of Stavropol Krai. Cossack settlement The Cossack settlement of Kuban and of the adjacent Black Sea region occurred gradually for over a century, and was heavily influenced by the outcomes of the conflicts between Russia and Ottoman Empire.Azarenkova et al., pp. 8ff. In the mid-18th century, the area was predominantly inhabited by the Adyghe tribes. After the Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774, the population of the area started to show more pro-Russian tendencies. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukraine. To the east, the Crimean Bridge, constructed in 2018, spans the Strait of Kerch, linking the peninsula with Krasnodar Krai in Russia. The Arabat Spit, located to the northeast, is a narrow strip of land that separates the Syvash lagoons from the Sea of Azov. Across the Black Sea to the west lies Romania and to the south is Turkey. The population is 2.4 million, and the largest city is Sevastopol. The region, internationally recognized as part of Ukraine, has been under Russian occupation of Crimea, Russian occupation since 2014. Called the Tauric Peninsula until the early modern period, Crimea has historically been at the boundary between the Classical antiquity, classical world and the Pontic–Caspian steppe, steppe. Greeks in pre-Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Bug
The Southern Bug, also called Southern Buh (; ; ; or just ), and sometimes Boh River (; ), at the Encyclopedia of Ukraine is a navigable river located in Ukraine. It is the List of longest rivers of Ukraine, second-longest river flowing exclusively in Ukraine. While located in relatively close proximity, the river should not be confused with Western Bug or Bug which flows in opposite direction towards Baltics. The source of the Southern Bug is in the west of Ukraine, in the Volhynian-Podolian Upland, about from the Polish border, from where it flows southeasterly into the Bug Estuary (Black Sea basin) through the southern steppes (see Granite-steppe lands of Buh park). It is long and drains . [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
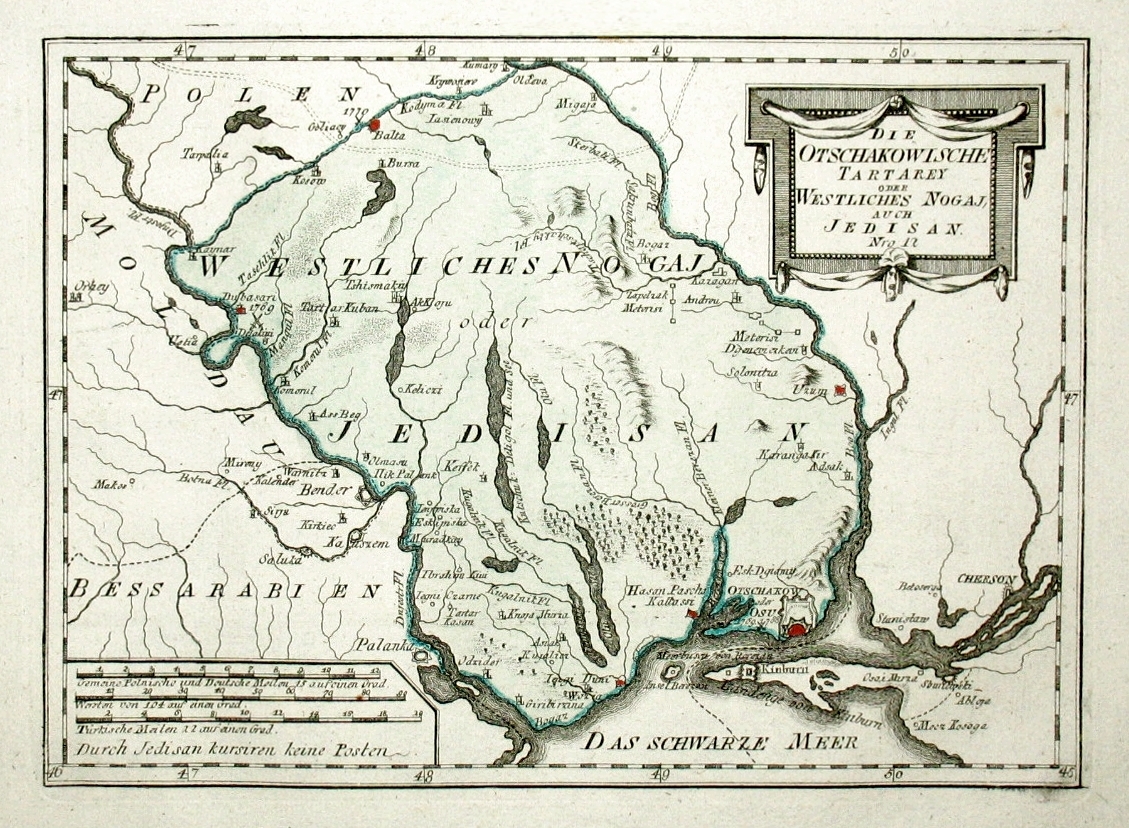
Yedisan
Yedisan (also ''Jedisan'' or ''Edisan''; , , , , , Dobrujan Tatar: ''Ğedísan'') was a conditional name for Özi aşaSancağı (Ochakiv Sanjak) of Silistra Eyalet, a territory located in today's Southern Ukraine between the Dniester and the Southern Bug (Boh), which was placed by the Ottomans under the control of the Nogai Horde in the 17th and 18th centuries and was named after one of the Nogai Hordes. In the Russian Empire, it was referred to as Ochakov Oblast, while the Ottoman Turks called it simply Özü after the city of Ochakiv which served as its administrative center. Another name used was Western Nogai. Geographically, it was the western part of the so-called Wild Fields that sprawled to the north of the Black Sea between the Dniester and Dnieper rivers. It lies east of Budjak and Bessarabia, south of Podolia and Zaporizhzhia, and west of Taurida. Since the mid-20th century, the territory has been divided between southwestern Ukraine and southeastern Moldova (sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dniester
The Dniester ( ) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and then through Moldova (from which it more or less separates the breakaway territory of Transnistria), finally discharging into the Black Sea on Ukrainian territory again. Names The name ''Dniester'' derives from Sarmatian ''dānu nazdya'' "the close river". (The Dnieper, also of Sarmatian origin, derives from the opposite meaning, "the river on the far side".) Alternatively, according to Vasily Abaev ''Dniester'' would be a blend of Scythian ''dānu'' "river" and Thracian ''Ister'', the previous name of the river, literally Dān-Ister (River Ister). The Ancient Greek name of Dniester, ''Tyras'' (Τύρας), is from Scythian ''tūra'', meaning "rapid". The names of the Don and Danube are also from the same Iranian word ''*dānu'' "river". Classical authors have also referred to it as ''Danaster.'' These early forms, without -''i''- but with -''a''-, contradict Abaev's hypoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danube
The Danube ( ; see also #Names and etymology, other names) is the List of rivers of Europe#Longest rivers, second-longest river in Europe, after the Volga in Russia. It flows through Central and Southeastern Europe, from the Black Forest south into the Black Sea. A large and historically important river, it was once a frontier of the Roman Empire. In the 21st century, it connects ten European countries, running through their territories or marking a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , passing through or bordering Austria, Slovakia, Hungary, Croatia, Serbia, Romania, Bulgaria, Moldova, and Ukraine. Among the many List of cities and towns on the river Danube, cities on the river are four national capitals: Vienna, Bratislava, Budapest, and Belgrade. Its drainage basin amounts to and extends into nine more countries. The Danube's longest headstream, the Breg (river), Breg, rises in Furtwangen im Schwarzwald, while the river carries its name from its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Budjak
Budjak, also known as Budzhak, is a historical region that was part of Bessarabia from 1812 to 1940. Situated along the Black Sea, between the Danube and Dniester rivers, this #Ethnic groups and demographics, multi-ethnic region covers an area of and is home to approximately 600,000 people. The majority of the region (former Izmail Oblast) is now located in Ukraine's Odesa Oblast, while the remaining part is found in the southern districts of Moldova. The region is bordered to the north by the rest of Moldova, to the west and south by Romania, and to the east by the Black Sea and the rest of Ukraine. Name and geography Historically, Budjak was the southeastern Bugeac Steppe, steppe region of Moldavia. Bordered by the northern Trajan's Wall at its north end, by the Danube, Danube river and Black Sea to its south, by Tigheci Hills (just east of the Prut, Prut River) to the west, and Dniester, Dniester River to the east, it was known as ''historic Bessarabia'' until 1812, when t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate, self-defined as the Throne of Crimea and Desht-i Kipchak, and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary, was a Crimean Tatars, Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the longest-lived of the Turkic peoples, Turkic khanates that succeeded the empire of the Golden Horde. Established by Hacı I Giray in 1441, it was regarded as the direct heir to the Golden Horde and to Cumania, Desht-i-Kipchak. In 1783, violating the 1774 Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca (which had guaranteed non-interference of both Russia and the Ottoman Empire in the affairs of the Crimean Khanate), the Annexation of the Crimean Khanate by the Russian Empire, Russian Empire annexed the khanate. Among the European powers, only France came out with an open protest against this act, due to the longstanding Franco-Ottoman alliance. Naming and geography The Crimean Khans, considering their state as the heir and legal successor of the Golden Horde and Desht-i Kipcha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia (country), Georgia, Romania, Russia, Turkey, and Ukraine. The Black Sea is Inflow (hydrology), supplied by major rivers, principally the Danube, Dnieper and Dniester. Consequently, while six countries have a coastline on the sea, its drainage basin includes parts of 24 countries in Europe. The Black Sea, not including the Sea of Azov, covers , has a maximum depth of , and a volume of . Most of its coasts ascend rapidly. These rises are the Pontic Mountains to the south, bar the southwest-facing peninsulas, the Caucasus Mountains to the east, and the Crimean Mountains to the mid-north. In the west, the coast is generally small floodplains below foothills such as the Strandzha; Cape Emine, a dwindling of the east end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Caucasus
The North Caucasus, or Ciscaucasia, is a subregion in Eastern Europe governed by Russia. It constitutes the northern part of the wider Caucasus region, which separates Europe and Asia. The North Caucasus is bordered by the Sea of Azov and the Black Sea to the west, the Caspian Sea to the east, and the Caucasus Mountains to the south. The region shares land borders with the countries of Georgia (country), Georgia and Azerbaijan in the South Caucasus. Located in the southern part of the region, Mount Elbrus is the List of European ultra-prominent peaks, tallest peak in Europe. Krasnodar is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, most populous among the urban area, urban centres in the region. The North Caucasus came under Russian control in the 19th century, following the Caucasian War between the Russian Empire and the various regional powers. The territory is the Southern Russia, southernmost portion of Russia and is divided between a number of Republics of Russia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |