|
Nickel Carbonyl
Nickel carbonyl (IUPAC name: tetracarbonylnickel) is a Organonickel chemistry, nickel(0) organometallic compound with the chemical formula, formula Ni(CO)4. This colorless liquid is the principal metal carbonyl, carbonyl of nickel. It is an Reaction intermediate, intermediate in the Mond process for producing very high-purity nickel and a reagent in organometallic chemistry, although the Mond Process has fallen out of common usage due to the health hazards in working with the compound. Nickel carbonyl is one of the most dangerous substances yet encountered in nickel chemistry due to its very high toxicity, compounded with high volatility and rapid skin absorption. Structure and bonding In nickel tetracarbonyl, the oxidation state for nickel is assigned as zero, because the Ni−C bonding electrons come from the C atom and are still assigned to C in the hypothetical ionic bond which determines the oxidation states. The formula conforms to the 18-electron rule. The molecule is tetra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Solvents
A solvent (from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:solvo#Latin, solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a Solution (chemistry), solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for Chemical polarity#Polarity of molecules, polar molecules, and the most common solvent used by living things; all the ions and proteins in a Cell (biology), cell are dissolved in water within the cell. Major uses of solvents are in paints, paint removers, inks, and dry cleaning. Specific uses for Organic compound, organic solvents are in dry cleaning (e.g. tetrachloroethylene); as paint thinners (toluene, turpentine); as nail polish removers and solvents of glue (acetone, methyl acetate, ethyl acetate); in spot removers (hexane, petrol ether); in detergents (D-limonene, citrus terpenes); and in perfumes (ethanol). Solvents find various applications in chemical, pharmaceutical, oil, and gas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Carbonyl
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. These properties are all associated with having electrons available at the Fermi level, as against nonmetallic materials which do not. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into a wire) and malleable (can be shaped via hammering or pressing). A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polymeric sulfur nitride. The general science of metals is called metallurgy, a subtopic of materials science; aspects of the electronic and thermal properties are also within the scope of condensed matter physics and solid-state chemistry, it is a multidisciplinary topic. In colloquial use materials such as steel alloys are referred to as metals, while others such as polymers, wood or ceramics are nonmetallic materials. A metal conducts electricity at a temperature of absolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahedral
In geometry, a tetrahedron (: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular Face (geometry), faces, six straight Edge (geometry), edges, and four vertex (geometry), vertices. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the ordinary convex polytope, convex polyhedra. The tetrahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a Euclidean geometry, Euclidean simplex, and may thus also be called a 3-simplex. The tetrahedron is one kind of pyramid (geometry), pyramid, which is a polyhedron with a flat polygon base and triangular faces connecting the base to a common point. In the case of a tetrahedron, the base is a triangle (any of the four faces can be considered the base), so a tetrahedron is also known as a "triangular pyramid". Like all convex polyhedra, a tetrahedron can be folded from a single sheet of paper. It has two such net (polyhedron), nets. For any tetrahedron there exists a sphere (called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation State
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical Electrical charge, charge of an atom if all of its Chemical bond, bonds to other atoms are fully Ionic bond, ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state may be positive, negative or zero. Beside nearly-pure ionic bonding, many covalent bonds exhibit a strong ionicity, making oxidation state a useful predictor of charge. The oxidation state of an atom does not represent the "real" charge on that atom, or any other actual atomic property. This is particularly true of high oxidation states, where the ionization energy required to produce a multiply positive ion is far greater than the energies available in chemical reactions. Additionally, the oxidation states of atoms in a given compound may vary depending on Electronegativities of the elements (data page), the choice of electronegativity scale used in their calculation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merck & Co
Merck & Co., Inc. is an American Multinational corporation, multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Rahway, New Jersey. The company does business as Merck Sharp & Dohme or MSD outside the United States and Canada. It is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world, generally ranking in the global top five by revenue. Merck & Co. was originally established as the American affiliate of Merck Group in 1891. Merck develops and produces medicines, vaccines, biologic therapies and animal health products. It has several blockbuster products, including cancer immunotherapy, anti-diabetic medications, and vaccines for HPV and chickenpox, each generating significant revenue as of 2020. The company is ranked 71st on the 2022 Fortune 500, ''Fortune'' 500 and 87th on the 2022 Forbes Global 2000, ''Forbes'' Global 2000, both based on 2021 revenues. In 2023, the company’s seat in the ''Forbes'' Global 2000 was 73. Products The company develops medicines, vaccines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacteria, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a substructure of the organism, such as a cell (biology), cell (cytotoxicity) or an organ such as the liver (hepatotoxicity). Sometimes the word is more or less synonymous with poison#Poisoning, poisoning in everyday usage. A central concept of toxicology is that the effects of a toxicant are Dose (biochemistry), dose-dependent; even water can lead to water intoxication when taken in too high a dose, whereas for even a very toxic substance such as snake venom there is a dose below which there is no detectable toxic effect. Toxicity is species-specific, making cross-species analysis problematic. Newer paradigms and metrics are evolving to bypass animal testing, while maintaining the concept of toxicity endpoints. Etymology In Ancient G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic Chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (Metal carbonyl, metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganics, metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reagent
In chemistry, a reagent ( ) or analytical reagent is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or test if one occurs. The terms ''reactant'' and ''reagent'' are often used interchangeably, but reactant specifies a substance ''consumed'' in the course of a chemical reaction. ''Solvents'', though involved in the reaction mechanism, are usually not called reactants. Similarly, ''catalysts'' are not consumed by the reaction, so they are not reactants. In biochemistry, especially in connection with enzyme-catalyzed reactions, the reactants are commonly called substrates. Definitions Organic chemistry In organic chemistry, the term "reagent" denotes a chemical ingredient (a compound or mixture, typically of inorganic or small organic molecules) introduced to cause the desired transformation of an organic substance. Examples include the Collins reagent, Fenton's reagent, and Grignard reagents. Analytical chemistry In analytical chemistry, a reag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mond Process
The Mond process, sometimes known as the carbonyl process, is a technique created by Ludwig Mond in 1890, to extract and purify nickel. The process was used commercially before the end of the 19th century, and particularly by the International Nickel Company in the Sudbury Basin. This process converts nickel oxides into nickel metal with very high purity being attainable in just a single step. Synopsis This process involves the fact that carbon monoxide combines with nickel readily and reversibly to give nickel carbonyl. No other element forms a carbonyl compound under the mild conditions used in the process. This process has three steps: 1. Nickel oxide reacts with syngas at 200 °C to give nickel, together with impurities including iron and cobalt. :NiO(s) + H2(g) → Ni(s) + H2O(g) 2. The impure nickel reacts with carbon monoxide at 50–60 °C to form the gas nickel carbonyl, leaving the impurities as solids. :Ni(s) + 4 CO(g) → Ni(CO)4(g) 3. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Intermediate
In chemistry, a reaction intermediate, or intermediate, is a molecular entity arising within the sequence of a stepwise chemical reaction. It is formed as the reaction product of an elementary step, from the reactants and/or preceding intermediates, but is consumed in a later step. It does not appear in the chemical equation for the overall reaction. For example, consider this hypothetical reaction: :A + B → C + D If this overall reaction comprises two elementary steps thus: :A + B → X :X → C + D then X is a reaction intermediate. The phrase ''reaction intermediate'' is often abbreviated to the single word ''intermediate'', and this is IUPAC's preferred form of the term. But this shorter form has other uses. It often refers to reactive intermediates. It is also used more widely for chemicals such as cumene which are traded within the chemical industry but are not generally of value outside it. IUPAC definition The IUPAC Gold Book defines an ''intermediate'' as a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
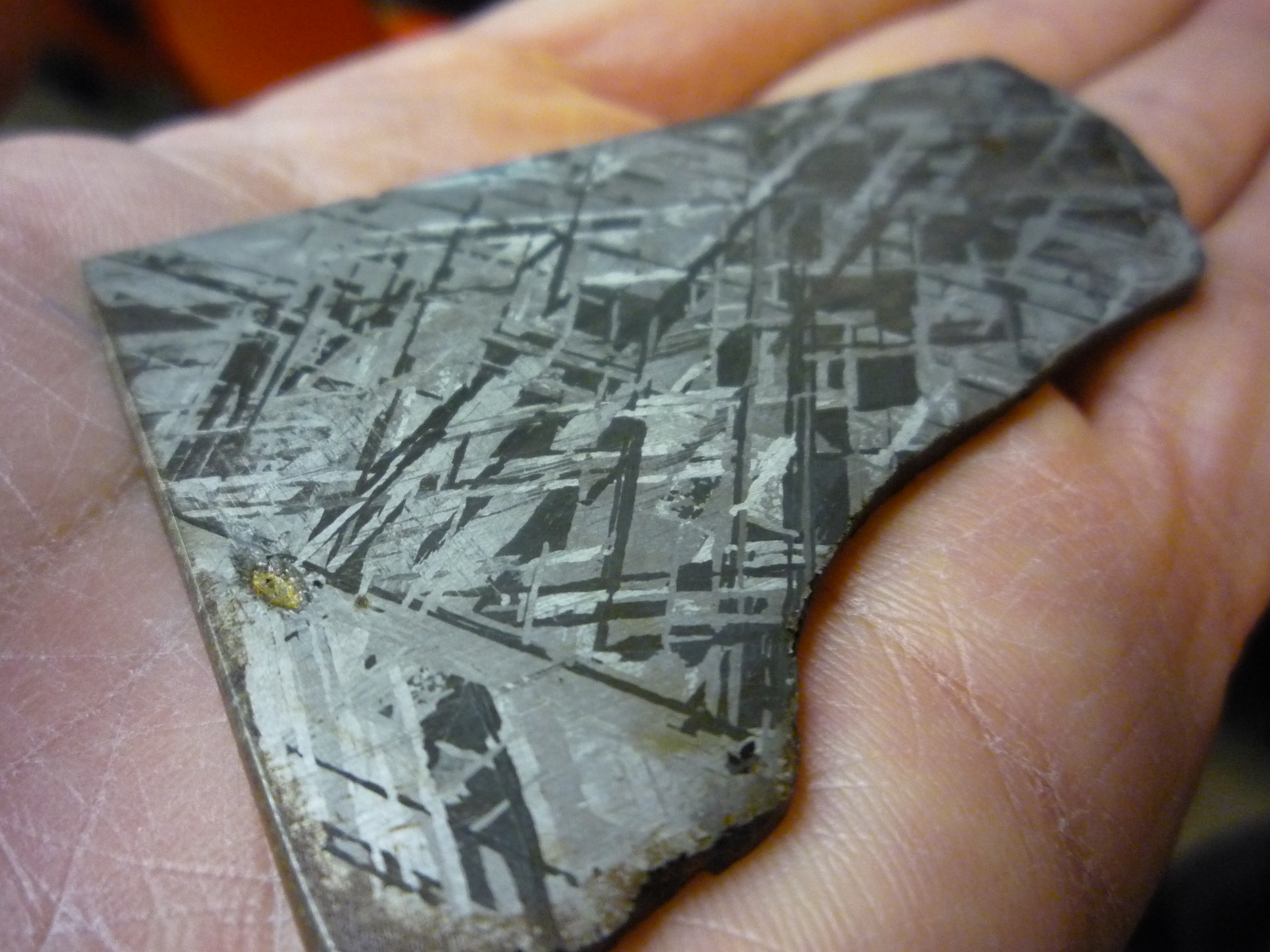
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slow to react with air under standard conditions because a passivation layer of nickel oxide forms on the surface that prevents further corrosion. Even so, pure native nickel is found in Earth's crust only in tiny amounts, usually in ultramafic rocks, and in the interiors of larger nickel–iron meteorites that were not exposed to oxygen when outside Earth's atmosphere. Meteoric nickel is found in combination with iron, a reflection of the origin of those elements as major end products of supernova nucleosynthesis. An iron–nickel mixture is thought to compose Earth's outer and inner cores. Use of nickel (as natural meteoric nickel–iron alloy) has been traced as far back as 3500 BCE. Nickel was first isolated and classifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |