|
New Frontiers Program
The New Frontiers program is a series of space exploration missions being conducted by NASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ... with the purpose of furthering the understanding of the Solar System. The program selects medium-class missions which can provide high science returns. NASA is encouraging both domestic and international scientists to submit mission proposals for the program. New Frontiers was built on the innovative approach used by the Discovery Program, Discovery and Explorer program, Explorer Programs of principal investigator-led missions. It is designed for medium-class missions that cannot be accomplished within the cost and time constraints of Discovery, but are not as large as Large Strategic Science Missions (Flagship missions). There are curren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Frontiers Program Website Header, 2016
New or NEW may refer to: Music * New, singer of K-pop group The Boyz * ''New'' (album), by Paul McCartney, 2013 ** "New" (Paul McCartney song), 2013 * ''New'' (EP), by Regurgitator, 1995 * "New" (Daya song), 2017 * "New" (No Doubt song), 1999 * "new", a song by Loona from the 2017 single album '' Yves'' * "The New", a song by Interpol from the 2002 album ''Turn On the Bright Lights'' Transportation * Lakefront Airport, New Orleans, U.S., IATA airport code NEW * Newcraighall railway station, Scotland, station code NEW Other uses * ''New'' (film), a 2004 Tamil movie * New (surname), an English family name * NEW (TV station), in Australia * new and delete (C++), in the computer programming language * Net economic welfare, a proposed macroeconomic indicator * Net explosive weight, also known as net explosive quantity * Network of enlightened Women, an American organization * Newar language, ISO 639-2/3 language code new * Next Entertainment World, a South Korean media company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planetary Science Decadal Survey
The Planetary Science Decadal Survey is a serial publication of the United States National Research Council produced for NASA and other United States Government Agencies such as the National Science Foundation.National Academy of Sciences, National Academies Press, http://www.nap.edu/download.php?record_id=13117 , ''Vision and Voyages for Planetary Science in the Decade 2013–2022'', 2011; . Retrieved February 23, 2015 The documents identify key questions facing planetary science and outlines recommendations for space and ground-based exploration ten years into the future. Missions to gather data to answer these big questions are described and prioritized, where appropriate. Similar decadal surveys cover astronomy and astrophysics, earth science, and heliophysics. As of 2022 there have been three "Decadals", one published in April 2002 for the decade from 2003 to 2013, one published on March 7, 2011 for the decade from 2013 to 2022, and one published on April 19, 2022 for the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
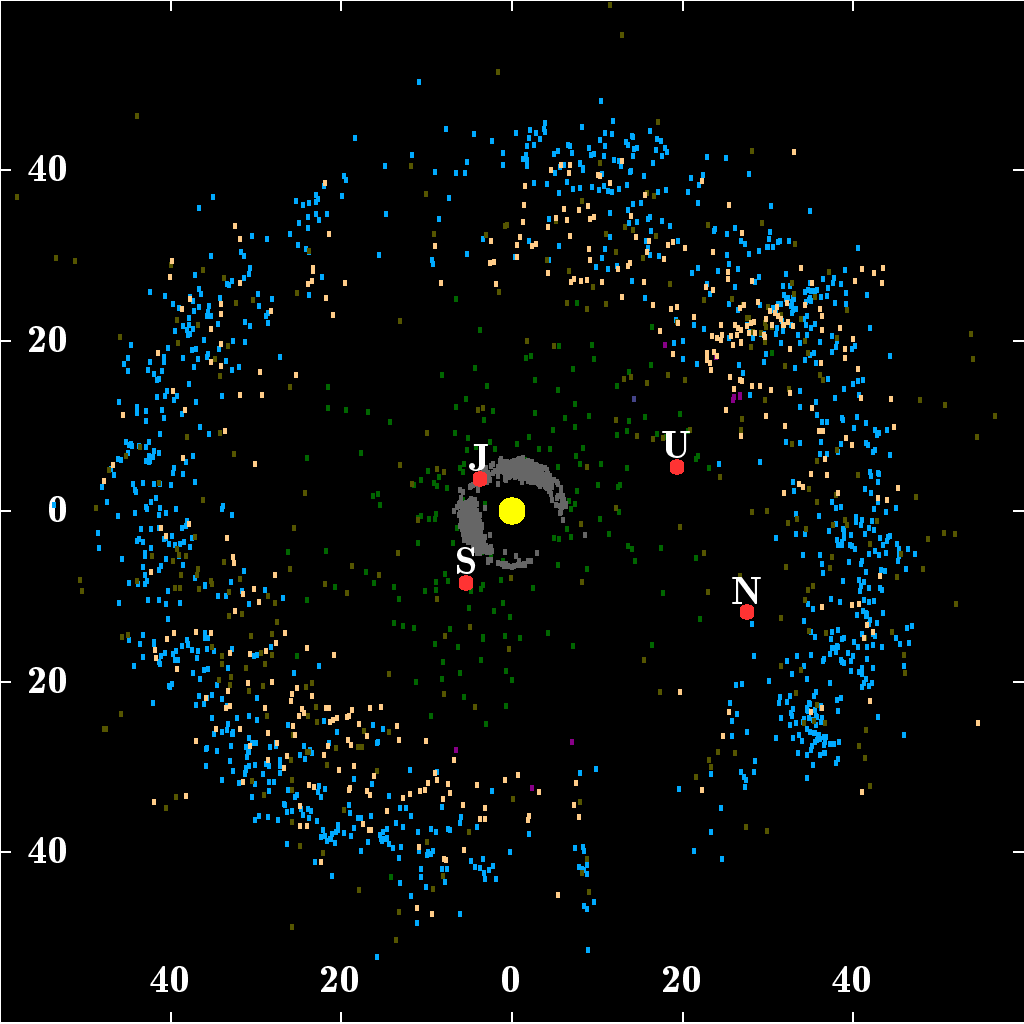
Kuiper Belt
The Kuiper belt ( ) is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small Solar System body, small bodies or remnants from when the Formation and evolution of the Solar System, Solar System formed. While many asteroids are composed primarily of rock (geology), rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen Volatile (astrogeology), volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane, ammonia, and water. The Kuiper belt is home to most of the objects that astronomers generally accept as dwarf planets: 90482 Orcus, Orcus, Pluto, Haumea, 50000 Quaoar, Quaoar, and Makemake. Some of the Solar System's natural satellite, moons, such as Neptune's Triton (moon), Triton and Saturn's Phoebe (moon), Phoebe, may ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
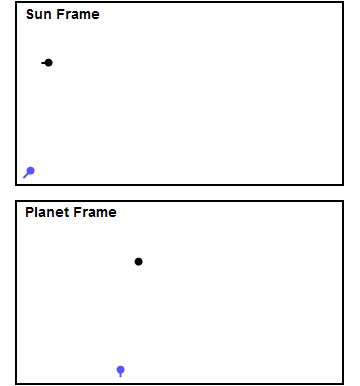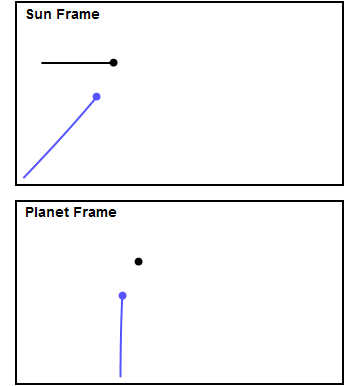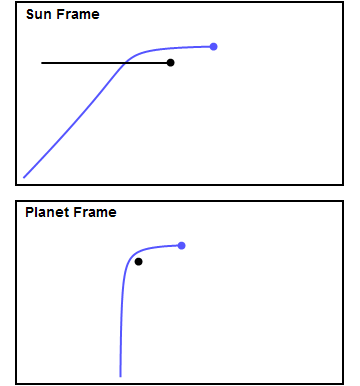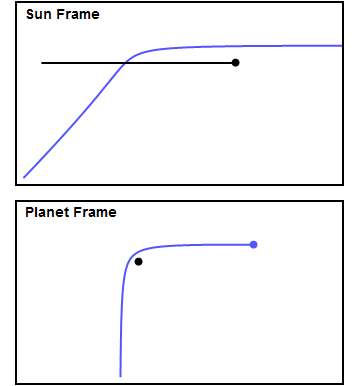
Gravity Assist
A gravity assist, gravity assist maneuver, swing-by, or generally a gravitational slingshot in orbital mechanics, is a type of spaceflight flyby (spaceflight), flyby which makes use of the relative movement (e.g. orbit around the Sun) and gravity of a planet or other astronomical object to alter the Course (navigation), path and speed of a spacecraft, typically to save propellant and reduce expense. Gravity assistance can be used to accelerate a spacecraft, that is, to increase or decrease its speed or redirect its path. The "assist" is provided by the motion of the gravitating body as it pulls on the spacecraft. Any gain or loss of kinetic energy and linear momentum by a passing spacecraft is correspondingly lost or gained by the gravitational body, in accordance with Newton's laws of motion#Newton's third law, Newton's Third Law. The gravity assist maneuver was first used in 1959 when the Soviet probe Luna 3 photographed the far side of Earth's Moon, and it was used by inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined and slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Its diameter is 11 times that of Earth and a tenth that of the Sun. Jupiter orbits the Sun at a distance of , with an orbital period of . It is the List of brightest natural objects in the sky, third-brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky, after the Moon and Venus, and has been observed since prehistoric times. Its name derives from that of Jupiter (god), Jupiter, the chief deity of ancient Roman religion. Jupiter was the first of the Sun's planets to form, and its inward migration during the primordial phase of the Solar System affected much of the formation history of the other planets. Jupiter's atmosphere consists of 76% hydrogen and 24% helium by mass, with a denser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charon (moon)
Charon ( or ), formal designation (134340) Pluto I, is the largest of the five known natural satellites of the dwarf planet Pluto. It has a mean radius of . Charon is the sixth-largest known trans-Neptunian object after Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, and Gonggong. It was discovered in 1978 at the United States Naval Observatory in Washington, D.C., using photographic plates taken at the United States Naval Observatory Flagstaff Station (NOFS). With half the diameter and one-eighth the mass of Pluto, Charon is a very large moon in comparison to its parent body. Its gravitational influence is such that the barycenter of the Plutonian system lies outside Pluto, and the two bodies are tidally locked to each other. The dwarf planet systems Pluto–Charon and Eris– Dysnomia are the only known examples of mutual tidal locking in the Solar System, though it is likely that – Vanth is another. The reddish-brown cap of the north pole of Charon is composed of tholins, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pluto
Pluto (minor-planet designation: 134340 Pluto) is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of Trans-Neptunian object, bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. It is the ninth-largest and tenth-most-massive known object to directly orbit the Sun. It is the largest known trans-Neptunian object by volume by a small margin, but is less massive than Eris (dwarf planet), Eris. Like other Kuiper belt objects, Pluto is made primarily of ice and rock and is much smaller than the inner planets. Pluto has roughly one-sixth the mass of the Moon and one-third its volume. Originally considered a planet, its classification was changed when astronomers adopted a new definition of planet, definition of ''planet''. Pluto has a moderately Orbital eccentricity, eccentric and Inclination, inclined orbit, ranging from from the Sun. Light from the Sun takes 5.5 hours to reach Pluto at its orbital distance of . Pluto's eccentric orbit periodically brings it closer to the Sun than Neptune, but a stabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
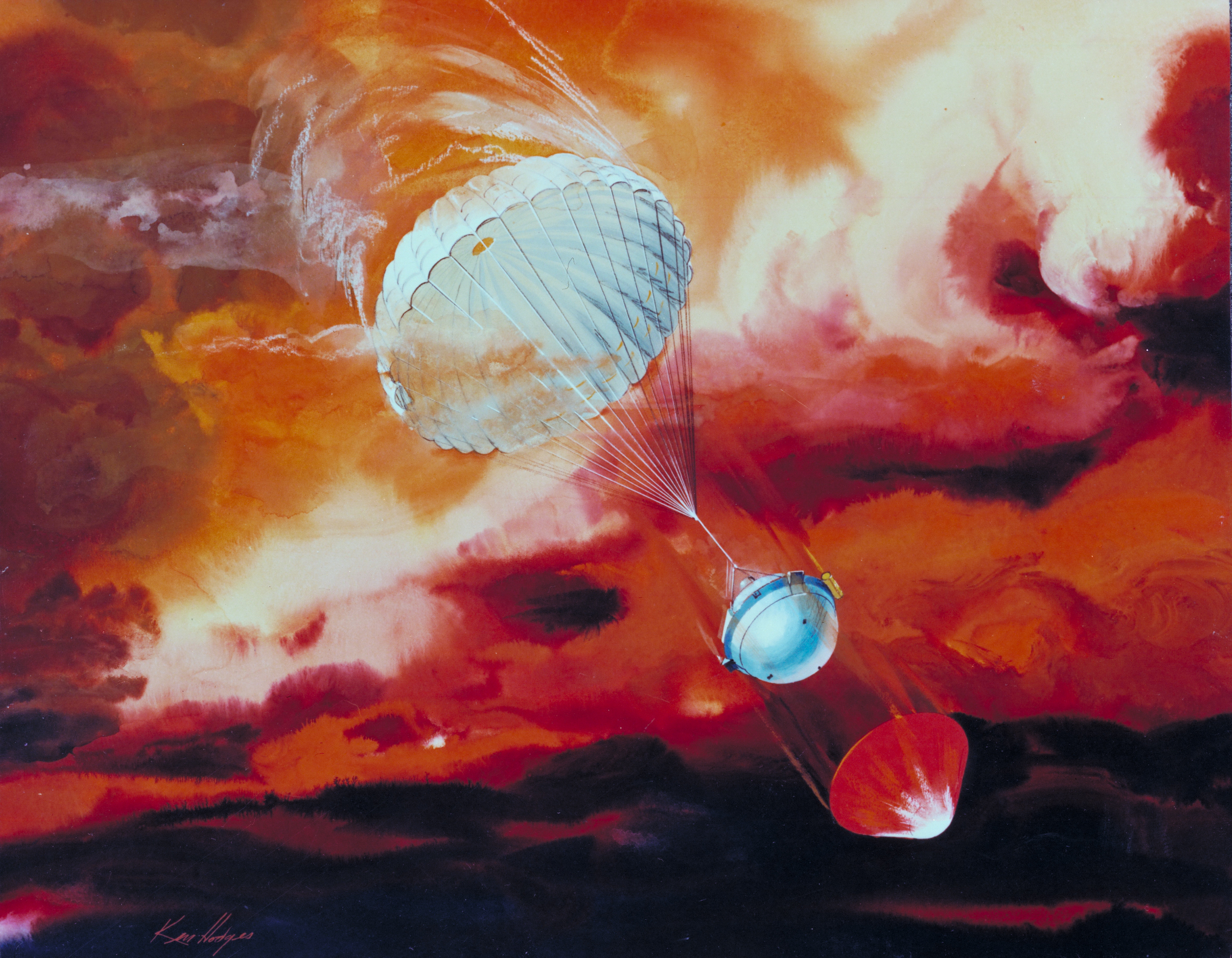
Saturn Atmospheric Entry Probe
The Saturn Atmospheric Entry Probe is a mission concept study for a robotic spacecraft to deliver a single probe into Saturn to study its atmosphere. The concept study was done to support the NASA 2010 Planetary Science Decadal Survey (Archived from the original). Due to the orbits and relative positions of Saturn and Earth, launch was proposed for 30 August 2027 for a 22 June 2034 arrival. The mission was studied for the NASA Planetary Science Decadal Survey as a possible NASA New Frontiers-class mission. Overview To unveil the processes of outer planet formation and Solar System evolution, detailed studies of the composition, structure, and dynamics of giant planet interiors and atmospheres would be necessary. To constrain the internal structure of gas giants, a combination of both ''in-situ'' entry-probe missions and remote-sensing studies of the giant planets would be needed. The Saturn Atmospheric Entry Probe mission would consist of a carrier-relay spacecraft and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Io Volcano Observer
Io Volcano Observer (IVO) is a proposed low-cost mission to explore Jupiter's moon Io (moon), Io to understand tidal heating as a fundamental planetary process. The main science goals are to understand (A) how and where tidal heat is generated inside Io, (B) how tidal heat is transported to the surface, and (C) how Io is evolving. These results are expected to have direct implications for the thermal history of Europa (moon), Europa and Ganymede (moon), Ganymede as well as provide insights into other tidally heated worlds such as Titan (moon), Titan and Enceladus. The IVO data may also improve our understanding of magma oceans and thus the early evolution of the Earth and Moon. IVO is similar to the Io Orbiter concept suggested for the New Frontiers program, New Frontiers Program by the 2013–2022 U. S. National Research Council Planetary Science Decadal Survey. The mission was proposed to NASA's Discovery Program by the University of Arizona and Johns Hopkins University's Appli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-Earth Object
A near-Earth object (NEO) is any small Solar System body orbiting the Sun whose closest approach to the Sun ( perihelion) is less than 1.3 times the Earth–Sun distance (astronomical unit, AU). This definition applies to the object's orbit around the Sun, rather than its current position, thus an object with such an orbit is considered an NEO even at times when it is far from making a close approach of Earth. If an NEO's orbit crosses the Earth's orbit, and the object is larger than across, it is considered a potentially hazardous object (PHO). Most known PHOs and NEOs are asteroids, but about a third of a percent are comets. There are over 37,000 known near-Earth asteroids (NEAs) and over 120 known short-period near-Earth comets (NECs). A number of solar-orbiting meteoroids were large enough to be tracked in space before striking Earth. It is now widely accepted that collisions in the past have had a significant role in shaping the geological and biological history of Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAESAR (spacecraft)
CAESAR (Comet Astrobiology Exploration Sample Return) is a sample-return mission concept to comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. The mission was proposed in 2017 to NASA's New Frontiers program mission 4, and on 20 December 2017 it was one of two finalists selected for further concept development. On 27 June 2019, the other finalist, the ''Dragonfly'' mission, was chosen instead. Had it been selected in June 2019, it would have launched between 2024 and 2025, with a capsule delivering a sample back to Earth in 2038. The Principal Investigator is Alexander Hayes of Cornell University in Ithaca, New York. ''CAESAR'' would be managed by NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Curation of the returned sample would take place at NASA's Astromaterials Research and Exploration Science Directorate, based at Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. The ''CAESAR'' team chose comet 67P over other cometary targets in part because the data collected by the ''Rosetta'' mis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MoonRise
Moonrise and moonset are times when the upper limb of the Moon appears above the horizon and disappears below it, respectively. The exact times depend on the lunar phase and declination, as well as the observer's location. As viewed from outside the polar circles, the Moon, like all other celestial objects outside the circumpolar circle, rises from the eastern half of the horizon and sets into the western half due to Earth's rotation. Direction and time Direction Since Earth rotates eastward, all celestial objects outside the circumpolar circle (including the Sun, Moon, and stars) rise in the east and set in the west for observers outside the polar circles. Seasonal variation means that they sometimes rise in the east-northeast or east-southeast, and sometimes set in the west-southwest or west-northwest. This north-south variation of the point along the horizon is bookended by two lunar standstills or turnarounds, the directions of which are sometimes depicted in arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |