|
Neurofibromatosis
Neurofibromatosis (NF) refers to a group of three distinct genetic conditions in which tumors grow in the nervous system. The tumors are non-cancerous (benign) and often involve the skin or surrounding bone. Although symptoms are often mild, each condition presents differently. neurofibromatosis type I, Neurofibromatosis type I (NF1) is typically characterized by Café au lait spot, café au lait spots (light-brown flat patches of skin), Neurofibroma, neurofibromas (small bumps in or under the skin), scoliosis (side-way curvature of the back), and Headache, headaches. neurofibromatosis type II, Neurofibromatosis type II (NF2), on the other hand, may present with early-onset hearing loss, cataracts, tinnitus, difficulty walking or maintaining balance, and muscle atrophy. The third type is called schwannomatosis and often presents in early adulthood with widespread pain, numbness, or tingling due to nerve compression. The cause is a genetic mutation in certain oncogenes. These c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurofibromatosis Type I
Neurofibromatosis type I (NF-1), or von Recklinghausen syndrome, is a complex multi-system neurocutaneous disorder caused by a subset of genetic mutations at the neurofibromin 1 (''NF1'') locus. Other conditions associated with mutation of the ''NF1'' gene include Watson syndrome. NF-1 is a gene on chromosome 17 that is responsible for production of a protein (neurofibromin) which is needed for normal function in many human cell types. causes tumors along the nervous system that can grow anywhere on the body. is one of the most common genetic disorders and is not limited to any person's race or sex. NF-1 is an autosomal dominant disorder, which means that mutation or deletion of one copy (or allele) of the is sufficient for the development of , although presentation varies widely and is often different even between relatives affected by . , there are at least 100,000 people in the U.S. and about 25,000 people in the UK who have been diagnosed with NF. Common symptoms of inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurofibromatosis Type 2
Neurofibromatosis type II (also known as MISME syndrome – multiple inherited schwannomas, meningiomas, and ependymomas) is a genetic condition that may be inherited or may arise spontaneously, and causes benign tumors of the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves. The types of tumors frequently associated with NF2 include vestibular schwannomas, meningiomas, and ependymomas. The main manifestation of the condition is the development of bilateral benign brain tumors in the nerve sheath of the cranial nerve VIII, which is the "auditory-vestibular nerve" that transmits sensory information from the inner ear to the brain. Besides, other benign brain and spinal tumors occur. Symptoms depend on the presence, localisation and growth of the tumor(s). Many people with this condition also experience vision problems. Neurofibromatosis type II (NF2 ''or'' NF II) is caused by mutations of the "Merlin" gene, which seems to influence the form and movement of cells. The principal treatment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurofibroma
A neurofibroma is a benign nerve-sheath tumor in the peripheral nervous system. In 90% of cases, they are found as stand-alone tumors (solitary neurofibroma, solitary nerve sheath tumor or sporadic neurofibroma), while the remainder are found in persons with neurofibromatosis type I (NF1), an autosomal-dominant genetically inherited disease. They can result in a range of symptoms from physical disfiguration and pain to cognitive disability. Neurofibromas arise from nonmyelinating-type Schwann cells that exhibit biallelic inactivation of the ''NF1'' gene that codes for the protein neurofibromin. This protein is responsible for regulating the RAS-mediated cell growth signaling pathway. In contrast to schwannomas, another type of tumor arising from Schwann cells, neurofibromas incorporate many additional types of cells and structural elements in addition to Schwann cells, making it difficult to identify and understand all the mechanisms through which they originate and develop. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
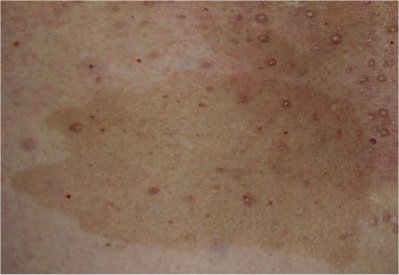
Café Au Lait Spot
''Café au lait'' spots, or ''café au lait'' macules, are flat, hyperpigmented birthmarks. The name ''café au lait'' is French for "coffee with milk" and refers to their light-brown color. They are caused by a collection of pigment-producing melanocytes in the epidermis of the skin. These spots are typically permanent and may grow or increase in number over time. Café au lait spots are often harmless but may be associated with syndromes such as neurofibromatosis type 1 and McCune–Albright syndrome. Café au lait lesions with rough borders ("coast of Maine") may be seen in McCune–Albright syndrome. In contrast, café au lait lesions of neurofibromatosis type 1 have smooth borders ("coast of California"). Cause Café au lait spots can arise from diverse and unrelated causes: *Ataxia–telangiectasia * Basal cell nevus syndrome * Benign congenital skin lesion * Bloom syndrome * Chédiak–Higashi syndrome * Congenital melanocytic naevus * Fanconi anemia * Fibrous dyspl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwannomatosis
Schwannomatosis is an extremely rare genetic disorder closely related to the more-common disorder neurofibromatosis (NF). Originally described in Japanese patients, it consists of multiple cutaneous schwannomas, central nervous system tumors, and other neurological complications, excluding hallmark signs of NF. The exact frequency of schwannomatosis cases is unknown, although some populations have noted frequencies as few as 1 case per 1.7 million people. Schwannomas are mostly benign tumors that commonly occur in individuals with NF2 and schwannomatosis (sometimes called neurofibromatosis type III). Schwann cells are glial cells that myelinate the axons of nerve cells. Myelin is a lipid covering that speeds the conduction of action potentials. When Schwann cells proliferate out of control in an encapsulation it is called a schwannoma. Although schwannomas are benign they become detrimental when the growing tumor compresses the nerve. Schwannomas on sensory nerve axons cause c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scoliosis
Scoliosis (: scolioses) is a condition in which a person's Vertebral column, spine has an irregular curve in the coronal plane. The curve is usually S- or C-shaped over three dimensions. In some, the degree of curve is stable, while in others, it increases over time. Mild scoliosis does not typically cause problems, but more severe cases can affect breathing and movement. Pain is usually present in adults, and can worsen with age. As the condition progresses, it may alter a person's life, and hence can also be considered a disability. It can be compared to kyphosis and lordosis, other abnormal curvatures of the spine which are in the sagittal plane (front-back) rather than the coronal (left-right). The cause of most cases is unknown, but it is believed to involve a combination of Genetics, genetic and environmental factors. Scoliosis most often occurs during growth spurts right before puberty. Risk factors include other affected family members. It can also occur due to anoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutation is the ult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tinnitus
Tinnitus is a condition when a person hears a ringing sound or a different variety of sound when no corresponding external sound is present and other people cannot hear it. Nearly everyone experiences faint "normal tinnitus" in a completely quiet room; but this is of concern only if it is bothersome, interferes with normal hearing, or is associated with other problems. The word ''tinnitus'' comes from the Latin language, Latin ''wikt:en:tinnitus#Latin, tinnire'', "to ring." In some people, it interferes with concentration, and can be associated with anxiety and Depression (mood), depression. Tinnitus is usually associated with hearing loss and decreased comprehension of speech in noisy environments. It is common, affecting about 10–15% of people. Most tolerate it well, and it is a significant (severe) problem in only 1–2% of people. It can trigger a fight-or-flight response, as the brain may perceive it as dangerous and important. Rather than a disease, tinnitus is a sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Atrophy
Muscle atrophy is the loss of skeletal muscle mass. It can be caused by immobility, aging, malnutrition, medications, or a wide range of injuries or diseases that impact the musculoskeletal or nervous system. Muscle atrophy leads to muscle weakness and causes disability. Disuse causes rapid muscle atrophy and often occurs during injury or illness that requires immobilization of a limb or bed rest. Depending on the duration of disuse and the health of the individual, this may be fully reversed with activity. Malnutrition first causes fat loss but may progress to muscle atrophy in prolonged starvation and can be reversed with nutritional therapy. In contrast, cachexia is a wasting syndrome caused by an underlying disease such as cancer that causes dramatic muscle atrophy and cannot be completely reversed with nutritional therapy. Sarcopenia is age-related muscle atrophy and can be slowed by exercise. Finally, diseases of the muscles such as muscular dystrophy or myopathies can caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |