|
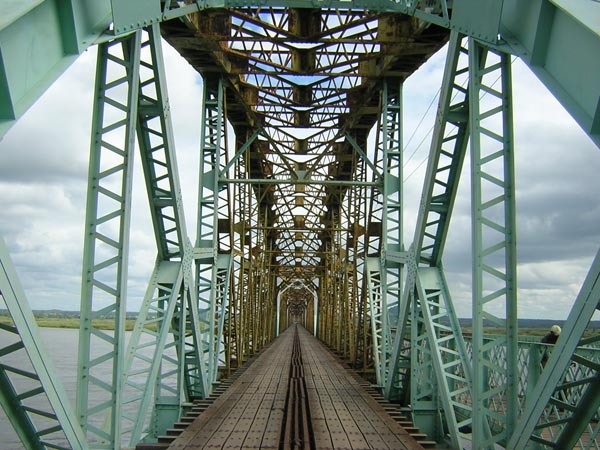
Neuquén–Cipolletti Bridges
The Neuquén-Cipolletti bridges are a series of four bridges that connect the cities of Neuquén, Argentina, Neuquén and Cipolletti by spanning the Neuquén River, in Argentina. Three parallel ones, two road bridges and a railway bridge, were built on a former herd wrangling path. The fourth one was built upstream. By 1899 the expansion of the Buenos Aires Great Southern Railway reached the station that later would become Cipolletti. To continue to the Neuquén Province, Neuquén Territory, a steel railway bridge was constructed in 1899–1902 to cross the Neuquén River. After the railroad connected Neuquén railway station, Neuquén Station on the Confluencia settlement, the capital of the Territory was moved to the area, and the city of Neuquén founded in 1904. Vehicular and pedestrian crossings of the river were made using boats and canoes at that time. By the 1930s, the service was overwhelmed by the growing population. The first road bridge opened 1937, while new road bridg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Vehicle
A motor vehicle, also known as a motorized vehicle, automotive vehicle, automobile, or road vehicle, is a self-propelled land vehicle, commonly wheeled, that does not operate on railway track, rails (such as trains or trams), does not fly (such as airplanes or helicopters), does not float on water (such as boats or ships), and is used for the transportation of people or cargo. The propulsion#Vehicular propulsion, vehicle propulsion is provided by an engine, engine or motor, usually a gasoline engine, gasoline/diesel engine, diesel internal combustion engine or an electric motor, electric traction motor, or some hybrid vehicle drivetrain, combination of the two as in hybrid electric vehicles and plug-in hybrid vehicles. For legal purpose, motor vehicles are often identified within a number of vehicle classes including cars, buses, motorcycles, off-road vehicles, light trucks and regular trucks. These classifications vary according to the legal codes of each country. Internationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limay River
The Limay River is an important river in the northwestern Argentine Patagonia (the region of Comahue). It originates at the eastern end of the Nahuel Huapi Lake and flows in a meandering path for about , collecting the waters of several tributaries, such as the Traful River, the Pichileufú and the Collón Curá. It then meets the Neuquén River and together they become the Río Negro. At this confluence lies the city of Neuquén. The river serves as natural border between the provinces of Río Negro and Neuquén. Its deep waters are clear, and carry a large flow, on average. Its drainage basin has an area of and includes almost all the rivers and streams of the Atlantic basin in the region, as well as an extensive network of lakes. The waters of the Limay are used to generate hydroelectricity at the five dams built on its course: Alicurá, Piedra del Águila, Pichi Picún Leufú, El Chocón, and Arroyito; together with the Cerros Colorados Complex on the Neuquén ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
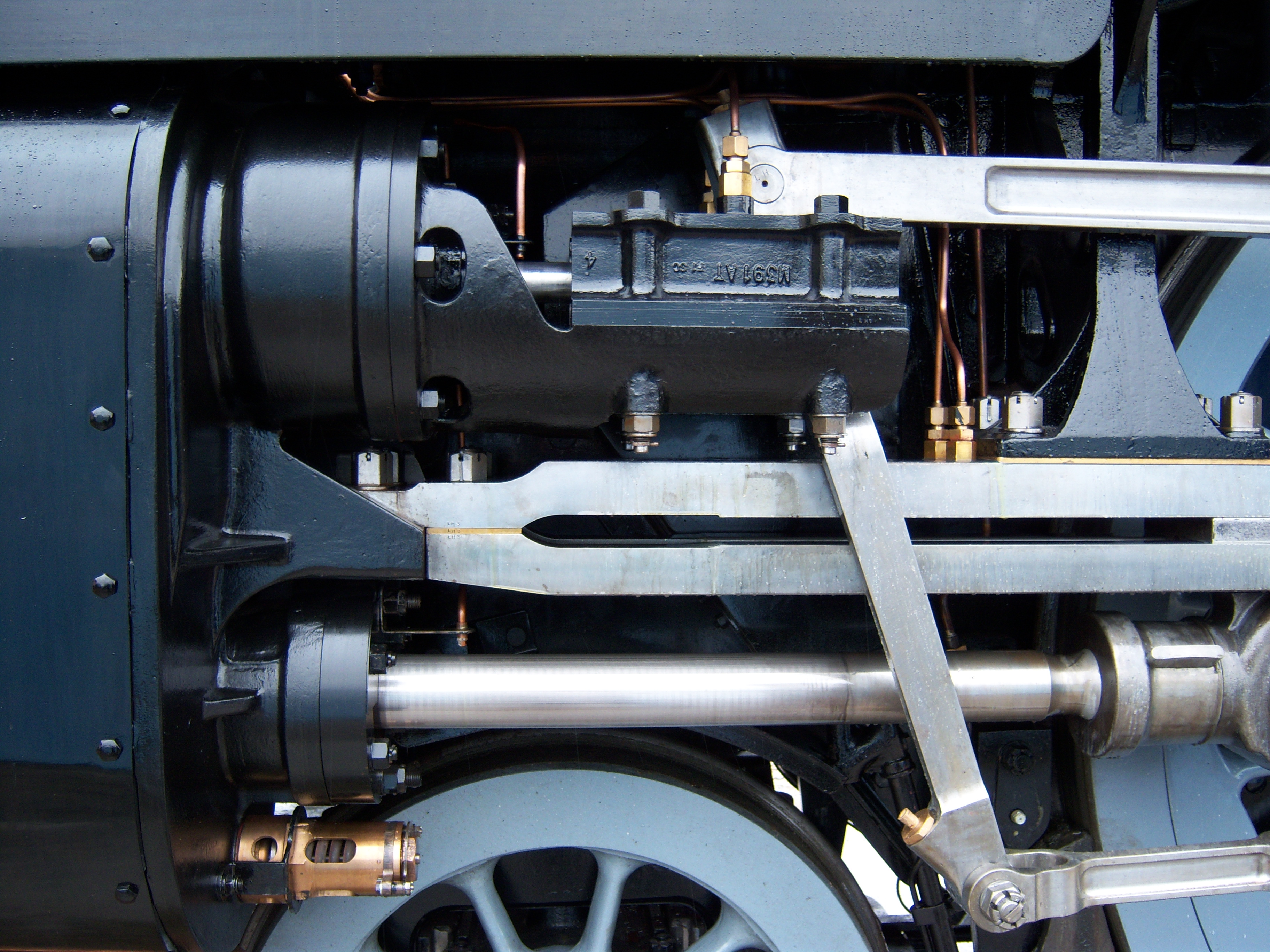
Cylinder (locomotive)
The cylinder is the power-producing element of the steam engine powering a steam locomotive. The cylinder (engine), cylinder is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were initially cast iron, but later made of steel. The cylinder casting includes other features such as (in the case of Stephenson's Rocket) valve ports and mounting feet. The last big American locomotives incorporated the cylinders as part of huge one-piece steel castings that were the Locomotive frame, main frame of the locomotive. Renewable wearing surfaces were needed inside the cylinders and provided by cast-iron bushings. The way the valve controlled the steam entering and leaving the cylinder was known as steam distribution and shown by the shape of the indicator diagram. What happened to the steam inside the cylinder was assessed separately from what happened in the boiler and how much friction the moving machinery had to cope wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingeniero White
{{Infobox settlement , name= Ingeniero White , settlement_type = Town , image_skyline = Elcastilloingenierowhite.jpg , image_size = 250px , image_caption = El Castillo museum , image_flag = , image_seal = , image_map = , map_caption = , pushpin_map = Argentina Buenos Aires Province , pushpin_mapsize = 260 , pushpin_label_position = right , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = {{flag, Argentina , subdivision_type1 = Province , subdivision_name1 = {{flag, Buenos Aires Province, name=Buenos Aires , subdivision_type2 = Partidos , subdivision_name2 = Bahía Blanca , subdivision_type3 = , subdivision_name3 = , leader_title = , leader_name = , established_title = Established , established_date = , area_magnitude = , area_total_km2 = , area_land_km2 = , area_water_km2 = , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caisson (engineering)
In geotechnical engineering, a caisson (; borrowed , , an augmentative of ) is a watertight retaining structure. It is used, for example, to work on the foundation (architecture), foundations of a bridge pier (architecture), pier, for the construction of a concrete dam, or for the repair of ships. Caissons are constructed in such a way that the water can be pumped out, keeping the work environment dry. When piers are being built using an open caisson, and it is not practical to reach suitable soil, Deep foundation, friction pilings may be driven to form a suitable sub-foundation. These piles are connected by a foundation pad upon which the column pier is erected. Caisson engineering has been used since at least the 19th century, with three prominent examples being the Royal Albert Bridge (completed in 1859), the Eads Bridge (completed in 1874), and the Brooklyn Bridge (completed in 1883). Types To install a caisson in place, it is brought down through soft mud until a suitable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
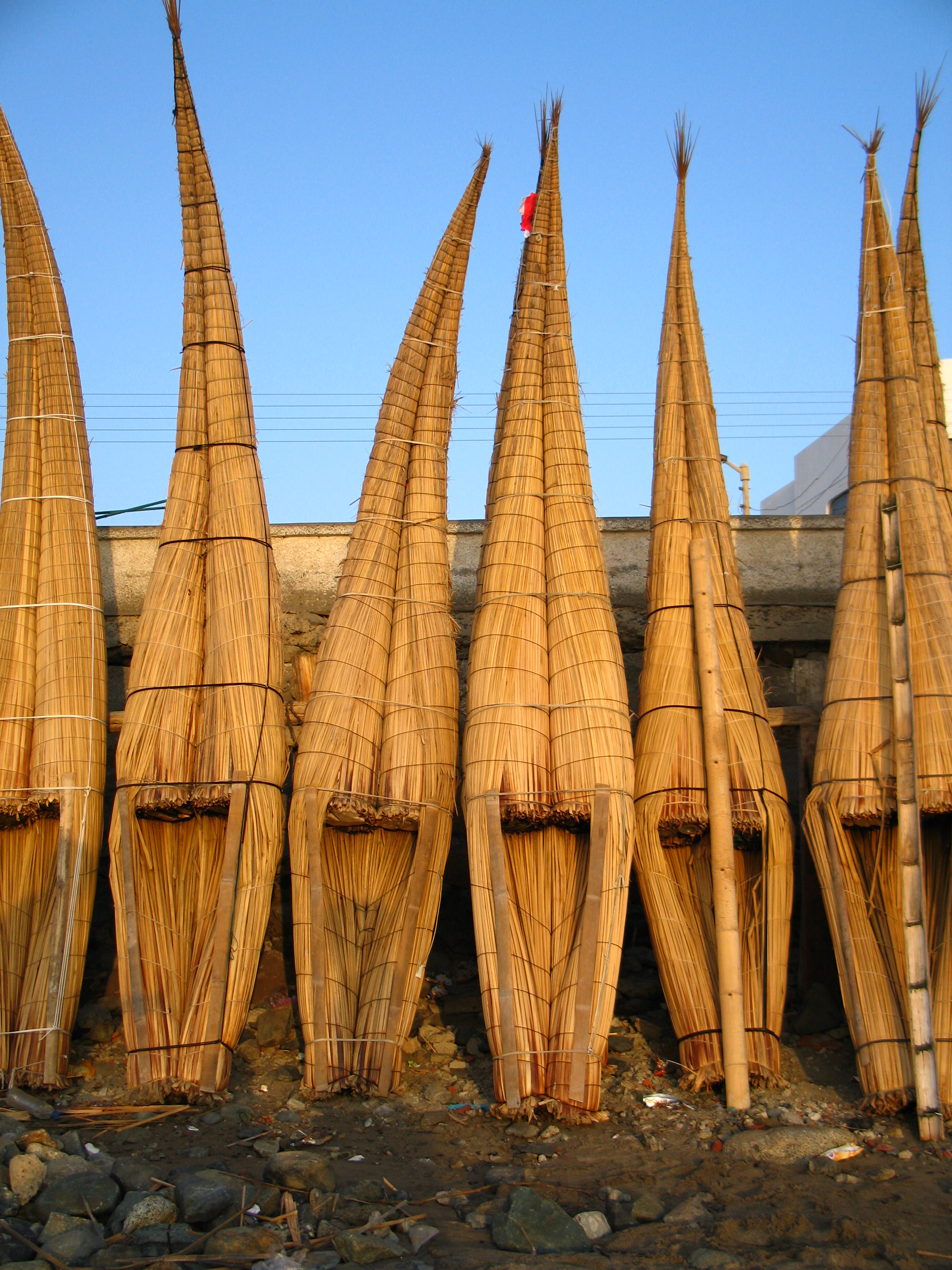
Schoenoplectus Californicus
''Schoeneoplectus californicus'' is a species of sedge known by the common names California bulrush, southern bulrush and giant bulrush. It is also sometimes called "tule", but the closely related ''Schoenoplectus acutus'' is the species most often referred to by that name. Description ''Schoenoplectus californicus'' is a rhizomed water plant found in marshy areas. It is native to the southern and western United States as well as Mexico, Central America, South America, Easter Island, and the Falkland Islands. It is naturalized on some Pacific islands including New Zealand, Hawaii and the Cook Islands. It has tall, thin, dark green stems which are usually triangular in cross-section and woolly, bristly tan or brown flowers in panicle inflorescences. Uses A notable subspecies is the totora, ''Schoenoplectus californicus'' subsp. ''tatora''. This is famous for making up the floating islands on which the Uros people of Lake Titicaca dwell, as well as occurring on isolated Eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lácar Department
Lácar is a department located in the south of Neuquén Province, Argentina. Geography The department is bounded by Huiliches Department to the north, Collón Cura Department to the northeast, Rio Negro Province to the southeast, Los Lagos Department to the south, and Chile to the east. {{DEFAULTSORT:Lacar Department Departments of Neuquén Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tide Gauge
A tide gauge is a device for measuring the change in sea level relative to a vertical datum. It is also known as a mareograph, marigraph, and sea-level recorder. When applied to freshwater continental water body, water bodies, the instrument may also be called a limnimeter. Operation Sensors continuously record the height of the water level with respect to a height reference surface close to the geoid. Water enters the device by the bottom pipe (far end of the tube, see picture), and electronic sensors measure its height and send the data to a tiny computer. Historical data are available for about 1,450 stations worldwide, of which about 950 have provided updates to the global data center since January 2010. At some places records cover centuries, for example in Amsterdam where data dating back to 1700 is available. When it comes to estimating the greater ocean picture, new modern tide gauges can often be improved upon by using satellite data. Tide gauges are used to measure t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pichi Mahuida
Pichi Mahuida is a village and municipality in Río Negro Province in Argentina Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt .... References {{coord, 38, 49, 53, S, 64, 56, 05, W, display=title, region:AR_type:city Populated places in Río Negro Province ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, within the wider West Midlands (region), West Midlands region, in England. It is the List of English districts by population, largest local authority district in England by population and the second-largest city in Britain – commonly referred to as the second city of the United Kingdom – with a population of million people in the city proper in . Birmingham borders the Black Country to its west and, together with the city of Wolverhampton and towns including Dudley and Solihull, forms the West Midlands conurbation. The royal town of Sutton Coldfield is incorporated within the city limits to the northeast. The urban area has a population of 2.65million. Located in the West Midlands (region), West Midlands region of England, Birmingham is considered to be the social, cultural, financial and commercial centre of the Midland ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brodie Henderson (engineer)
Sir Brodie Haldane Henderson, KCMG, CB (6 March 1869 – 28 September 1936) was a British civil engineer. Henderson was primarily a railway engineer who worked for many railroad corporations across South America, Australasia and Africa. He was the consultant for the Dona Ana Bridge which, when it was built in 1935, was the longest railway bridge in the world with a length of . He volunteered for service with the Royal Engineers at the outbreak of World War I and was put in charge of railway lines used to tranposrt Allied troops and supplies. In this capacity he held the rank of a Brigadier-General of the British Army and his success in this role resulted in him being decorated by the British, French and Belgian governments. After the war Henderson worked with the Imperial War Graves Commission, as High Sheriff of Hertfordshire in 1924 and as president of the Institution of Civil Engineers. He was an important patron of John William Waterhouse, the pre-Raphaelite painter, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |