|
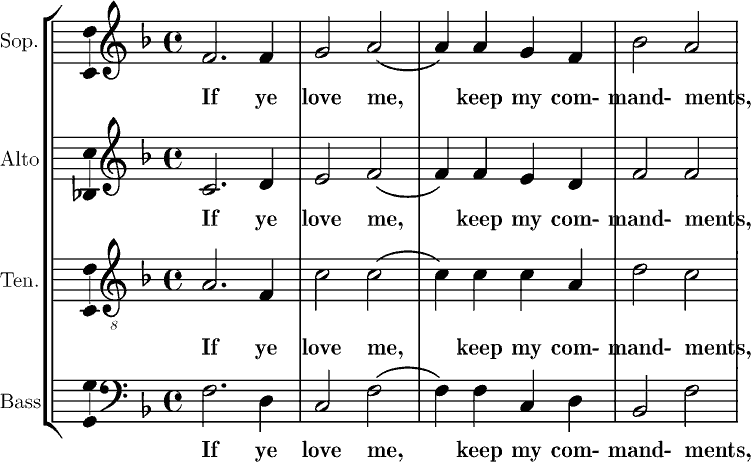
Neighbor Tone
A nonchord tone (NCT), nonharmonic tone, or embellishing tone is a note in a piece of music or song that is not part of the implied or expressed chord set out by the harmonic framework. In contrast, a chord tone is a note that is a part of the functional chord. Nonchord tones are most often discussed in the context of the common practice period of classical music, but the term can also be used in the analysis of other types of tonal music, such as Western popular music. Nonchord tones are often categorized as ''accented non-chord tones'' and ''unaccented non-chord tones'' depending on whether the dissonance occurs on an accented or unaccented beat (or part of a beat). Over time, some musical styles assimilated chord types outside of the common-practice style. In these chords, tones that might normally be considered nonchord tones are viewed as chord tones, such as the seventh of a minor seventh chord. For example, in 1940s-era bebop jazz, an F played with a C chord would be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Album For The Young
''Album for the Young'' ('), Op. 68, was composed by Robert Schumann in 1848 for his three daughters. The album consists of a collection of 43 short works. Unlike the ', they are suitable to be played by children or beginners. The second part, starting at Nr. 19 (""), is marked ' (For adults; For more grown-up ones) and contains more demanding pieces. List of pieces First part # Melodie (Melody), C major # Soldatenmarsch (Soldiers' march), G major # Trällerliedchen (Lilting song or Humming song), C major # Ein Choral (Chorale), G major. Harmonisation of "Selig sind, die aus Erbamen" or "Freu dich sehr, o meine Seele" found in number 7 of BWV 39 # Stückchen (A little piece), C major # Armes Waisenkind (The poor orphan), A minor # Jägerliedchen (Hunting song), F major # Wilder Reiter (The wild rider), A minor (This piece is more commonly known in English as "The Wild Horseman") # Volksliedchen (Folk song), D minor # Fröhlicher Landmann, von der Arbeit zurückkehrend ('The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleventh Chord
In music theory, an eleventh chord is a chord that contains the tertian extension of the eleventh. Typically found in jazz, an eleventh chord also usually includes the seventh and ninth, and elements of the basic triad structure. Variants include the dominant eleventh (C11, C–E–G–B–D–F), minor eleventh (Cm11, C–E–G–B–D–F), and major eleventh chord (Cmaj11, C–E–G–B–D–F).Smith, Johnny (1980). ''Mel Bay's Complete Johnny Smith Approach to Guitar'', p.231. . Using an augmented eleventh produces the dominant sharp eleventh (C911, C–E–G–B–D–F) and major ninth sharp eleventh (Cmaj911, C–E–G–B–D–F) chords. A perfect eleventh creates a highly dissonant minor ninth interval with the major third of major and dominant chords. To reduce this dissonance the third is often omitted (such as for example in the dominant eleventh chord that can be heard 52seconds into the song " Sun King" on The Beatles' ''Abbey Road ''Abbey Road'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equal Temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or Musical tuning#Tuning systems, tuning system that approximates Just intonation, just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into steps such that the ratio of the frequency, frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same. This system yields Pitch (music), pitch steps perceived as equal in size, due to the logarithmic changes in pitch frequency. In classical music and Western music in general, the most common tuning system since the 18th century has been 12 equal temperament (also known as ''12 tone equal temperament'', ' or ', informally abbreviated as ''12 equal''), which divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are equal on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the twelfth root of two, 12th root of 2, (\sqrt[12] ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. In Western world, Western countries the term ''equal temperamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Chord
In music, extended chords are certain Chord (music), chords (built from third (chord), thirds) or triad (music), triads with notes ''extended'', or added, beyond the seventh (chord), seventh. Ninth chord, Ninth, Eleventh chord, eleventh, and Thirteenth chord, thirteenth chords are extended chords. The thirteenth is the farthest extension diatonic and chromatic, diatonically possible as, by that point, all seven tonality, tonal degree (music), degrees are represented within the chord (the next extension, the fifteenth, is the same as the root of the chord). In practice however, extended chords do not typically use all the factor (chord), chord members; when it is not altered, the fifth is often omitted, as are notes between the seventh and the highest note (i.e., the ninth is often omitted in an eleventh chord; the ninth and eleventh are usually omitted in a thirteenth chord), unless they are altered to give a special texture. Chords extended beyond the seventh are rarely seen i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh Chord
A seventh chord is a chord (music), chord consisting of a triad (music), triad plus a note forming an interval (music), interval of a Interval (music), seventh above the chord's root (chord), root. When not otherwise specified, a "seventh chord" usually means a dominant seventh chord: a major triad together with a minor seventh. However, a variety of sevenths may be added to a variety of triads, resulting in many different types of seventh chords. In its earliest usage, the seventh was introduced solely as an nonchord tone, embellishing or nonchord tone. The seventh destabilized the triad, and allowed the composer to emphasize movement in a given direction. As time passed and the collective ear of the western world became more accustomed to Consonance and dissonance, dissonance, the seventh was allowed to become a part of the chord itself, and in some modern music, jazz in particular, . Additionally, the general acceptance of equal temperament during the 19th century reduced the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interval (music)
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or harmonic if it pertains to simultaneously sounding tones, such as in a chord. In Western music, intervals are most commonly differences between notes of a diatonic scale. Intervals between successive notes of a scale are also known as scale steps. The smallest of these intervals is a semitone. Intervals smaller than a semitone are called microtones. They can be formed using the notes of various kinds of non-diatonic scales. Some of the very smallest ones are called commas, and describe small discrepancies, observed in some tuning systems, between enharmonically equivalent notes such as C and D. Intervals can be arbitrarily small, and even imperceptible to the human ear. In physical terms, an interval is the ratio between two sonic fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consonance And Dissonance
In music, consonance and dissonance are categorizations of simultaneous or successive sounds. Within the Western tradition, some listeners associate consonance with sweetness, pleasantness, and acceptability, and dissonance with harshness, unpleasantness, or unacceptability, although there is broad acknowledgement that this depends also on familiarity and musical expertise. The terms form a structural dichotomy in which they define each other by mutual exclusion: a consonance is what is not dissonant, and a dissonance is what is not consonant. However, a finer consideration shows that the distinction forms a gradation, from the most consonant to the most dissonant. In casual discourse, as German composer and music theorist Paul Hindemith stressed, : "The two concepts have never been completely explained, and for a thousand years the definitions have varied". The term ''sonance'' has been proposed to encompass or refer indistinctly to the terms ''consonance'' and ''dissonance''. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counterpoint
In music theory, counterpoint is the relationship of two or more simultaneous musical lines (also called voices) that are harmonically dependent on each other, yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. The term originates from the Latin ''punctus contra punctum'' meaning "point against point", i.e. "note against note". John Rahn describes counterpoint as follows: Counterpoint has been most commonly identified in the European classical tradition, strongly developing during the Renaissance and in much of the common practice period, especially in the Baroque period. In Western pedagogy, counterpoint is taught through a system of species (see below). There are several different forms of counterpoint, including imitative counterpoint and free counterpoint. Imitative counterpoint involves the repetition of a main melodic idea across different vocal parts, with or without variation. Compositions written in free counterpoint often incorporate non-traditional harmonies and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homophony
In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a texture in which a primary part is supported by one or more additional strands that provide the harmony. One melody predominates while the other parts play either single notes or an elaborate accompaniment. This differentiation of roles contrasts with equal-voice polyphony (in which similar lines move with rhythmic and melodic independence to form an even texture) and monophony (in which all parts move in unison or octaves). Historically, homophony and its differentiated roles for parts emerged in tandem with tonality, which gave distinct harmonic functions to the soprano, bass and inner voices. A homophonic texture may be homorhythmic, which means that all parts have the same rhythm. Chorale texture is another variant of homophony. The most common type of homophony is melody-dominated homophony, in which one voice, often the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resolution (music)
Resolution in Western tonal music theory is the move of a Musical note, note or chord (music), chord from Consonance and dissonance, dissonance (an unstable sound) to a Consonance and dissonance, consonance (a more final or stable sounding one). Dissonance, resolution, and suspense can be used to create musical interest. Where a melody or chord progression, chordal pattern is expected to resolve to a certain note or chord, a different but similarly suitable note can be resolved to instead, creating an interesting and unexpected sound. For example, the deceptive cadence. Basis Resolution has a strong basis in Tonality, tonal music, since atonal music generally contains a more constant level of Consonance and dissonance, dissonance and lacks a tonal center to which to resolve. The concept of "resolution", and the degree to which resolution is "expected", is contextual as to culture and historical period. In a classical piece of the Baroque music, Baroque period, for example, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preparation (music)
In tonal music, a preparation is the consonant pitch or chord which precedes a dissonant nonharmonic tone. The move from a dissonance to a consonance constitutes a resolution. In the following example, the C major chord on the left is a preparation which precedes a nonharmonic tone that serves as an anticipation Anticipation is an emotion involving pleasure or anxiety in considering or awaiting an expected event. Anticipatory emotions include fear, anxiety, hope, and trust. When the anticipated event fails to occur, it results in disappointment (for ... (center, marked in red) to the G major harmony on the right. This harmony resolves the preceding dissonance: {{Consonance and dissonance Nonchord tones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orlando Di Lasso
Orlando di Lasso ( various other names; probably – 14 June 1594) was a composer of the late Renaissance. The chief representative of the mature polyphonic style in the Franco-Flemish school, Lassus stands with William Byrd, Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina, and Tomás Luis de Victoria as one of the leading composers of the later Renaissance. Immensely prolific, his music varies considerably in style and genres, which gave him unprecedented popularity throughout Europe. Name Lasso's name appears in many forms, often changed depending on the place in which his music was being performed or published. In addition to Orlando di Lasso, variations include Orlande de Lassus, Roland de Lassus, Orlandus Lassus, Orlande de Lattre and Roland de Lattre. Since these various spellings or translations of the same name have been known and accepted for centuries, and since there is no evidence that he stated a preference, none of them can be considered incorrect. Life and career Orlando ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |