|
National Health Interview Survey
The National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) is an annual, cross-sectional survey intended to provide nationally representative estimates on a wide range of health status and utilization measures among the nonmilitary, noninstitutionalized population of the United States. Each annual data set can be used to examine the disease burden and access to care that individuals and families are currently experiencing in the United States. NHIS is designed by the CDC's National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) – the government agency tasked to monitor the population's health status and behavior – and administered by the U.S. Census Bureau. NHIS has been administered since 1957, although the core content and questionnaires undergo major revisions every 10–15 years. NHIS allows both governmental and outside researchers to obtain estimates on a variety of health-related topics among either the entire nation or specific demographic groups of the population. Also, since the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-sectional Study
In statistics and econometrics, cross-sectional data is a type of data collected by observing many subjects (such as individuals, firms, countries, or regions) at a single point or period of time. Analysis of cross-sectional data usually consists of comparing the differences among selected subjects, typically with no regard to differences in time. For example, if we want to measure current obesity levels in a population, we could draw a sample of 1,000 people randomly from that population (also known as a cross section of that population), measure their weight and height, and calculate what percentage of that sample is categorized as obese. This cross-sectional sample provides us with a snapshot of that population, at that one point in time. Note that we do not know based on one cross-sectional sample if obesity is increasing or decreasing; we can only describe the current proportion. Cross-sectional data differs from ''time series'' data, in which the same small-scale or aggreg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
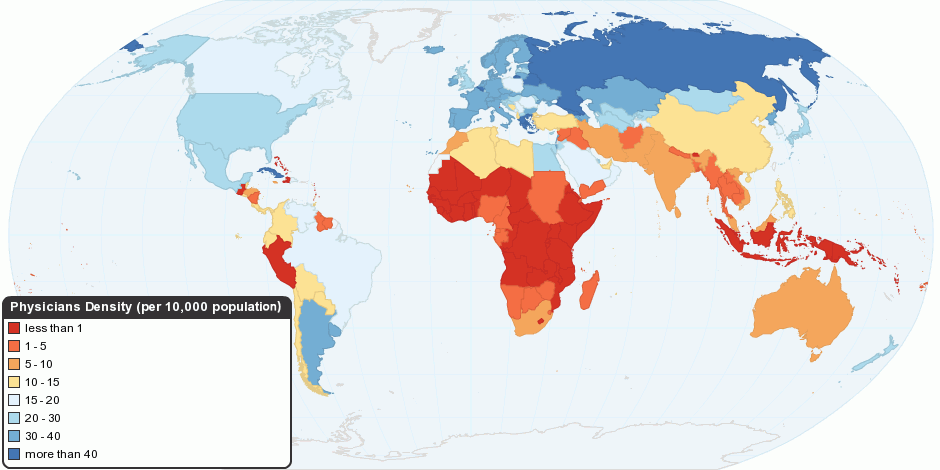
Medical Facility
A health facility is, in general, any location where healthcare is provided. Health facilities range from small clinics and doctor's offices to urgent care centers and large hospitals with elaborate emergency rooms and trauma centers. The number and quality of health facilities in a country or region is one common measure of that area's prosperity and quality of life. In many countries, health facilities are regulated to some extent by law; licensing by a regulatory agency is often required before a facility may open for business. Health facilities may be owned and operated by for-profit businesses, non-profit organizations, governments, and, in some cases, individuals, with proportions varying by country. See also the recent review paper, Health facility workload The workload of a health facility is often used to indicate its size. Large health facilities are those with a greater patient load. In Australia the workload of a health facility is used to determine the level of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
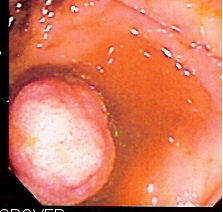
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving Cell growth#Disorders, abnormal cell growth with the potential to Invasion (cancer), invade or Metastasis, spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible Signs and symptoms of cancer, signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in defecation, bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. List of cancer types, Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor Diet (nutrition), diet, sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical activity or Alcohol abuse, excessive alcohol consumption. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. infectious causes of cancer, Infection with specific viruses, bacteria and parasites is an environmental factor cau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Screening
The objective of cancer screening is to detect cancer before symptoms appear, involving various methods such as blood tests, urine tests, DNA tests, and medical imaging. The purpose of screening is early cancer detection, to make the cancer easier to treat and extending life expectancy. In 2019, cancer was the second leading cause of death globally; more recent data is pending due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Universal screening, also known as mass screening or population screening, involves the screening of individuals within certain age and gender groups, aiming to screen the population for particular cancers or cancer risk factors. Selective screening, also known as targeted screening, identifies individuals with a higher risk of developing cancer, including individuals with a family history (genetic risk) of cancer or individuals engaging in high-risk behaviors such as smoking. The act of cancer screening plays a pivotal role in both preventing cancer and providing early diagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupational Health
Occupational safety and health (OSH) or occupational health and safety (OHS) is a multidisciplinary field concerned with the safety, health, and welfare of people at work (i.e., while performing duties required by one's occupation). OSH is related to the fields of occupational medicine and occupational hygiene and aligns with workplace health promotion initiatives. OSH also protects all the general public who may be affected by the occupational environment. According to the official estimates of the United Nations, the '' WHO/ ILO'' ''Joint Estimate of the Work-related Burden of Disease and Injury'', almost 2 million people die each year due to exposure to occupational risk factors. Globally, more than 2.78 million people die annually as a result of workplace-related accidents or diseases, corresponding to one death every fifteen seconds. There are an additional 374 million non-fatal work-related injuries annually. It is estimated that the economic burden of o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Injuries
Injury is physiological damage to the living tissue of any organism, whether in humans, in other animals, or in plants. Injuries can be caused in many ways, including mechanically with penetration by sharp objects such as teeth or with blunt objects, by heat or cold, or by venoms and biotoxins. Injury prompts an inflammatory response in many taxa of animals; this prompts wound healing. In both plants and animals, substances are often released to help to occlude the wound, limiting loss of fluids and the entry of pathogens such as bacteria. Many organisms secrete antimicrobial chemicals which limit wound infection; in addition, animals have a variety of immune responses for the same purpose. Both plants and animals have regrowth mechanisms which may result in complete or partial healing over the injury. Cells too can repair damage to a certain degree. Taxonomic range Animals Injury in animals is sometimes defined as mechanical damage to anatomical structure, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunizations
Immunization, or immunisation, is the process by which an individual's immune system becomes fortified against an infectious agent (known as the immunogen). When this system is exposed to molecules that are foreign to the body, called ''non-self'', it will orchestrate an immune response, and it will also develop the ability to quickly respond to a subsequent encounter because of immunological memory. This is a function of the adaptive immune system. Therefore, by exposing a human, or an animal, to an immunogen in a controlled way, its body can learn to protect itself: this is called active immunization. The most important elements of the immune system that are improved by immunization are the T cells, B cells, and the antibodies B cells produce. Memory B cells and memory T cells are responsible for a swift response to a second encounter with a foreign molecule. Passive immunization is direct introduction of these elements into the body, instead of production of these elements b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Medicine
Alternative medicine refers to practices that aim to achieve the healing effects of conventional medicine, but that typically lack biological plausibility, testability, repeatability, or supporting evidence of effectiveness. Such practices are generally not part of evidence-based medicine. Unlike modern medicine, which employs the scientific method to test plausible therapies by way of Guidelines for human subject research, responsible and ethical clinical trials, producing repeatable evidence of either effect or of no effect, alternative therapies reside outside of mainstream medicine and do not originate from using the scientific method, but instead rely on testimonials, anecdotes, religion, tradition, superstition, belief in supernatural "Energy (esotericism), energies", pseudoscience, fallacy, errors in reasoning, propaganda, fraud, or other unscientific sources. Frequently used terms for relevant practices are New Age medicine, wikt:pseudo-medicine, pseudo-medicine, unortho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
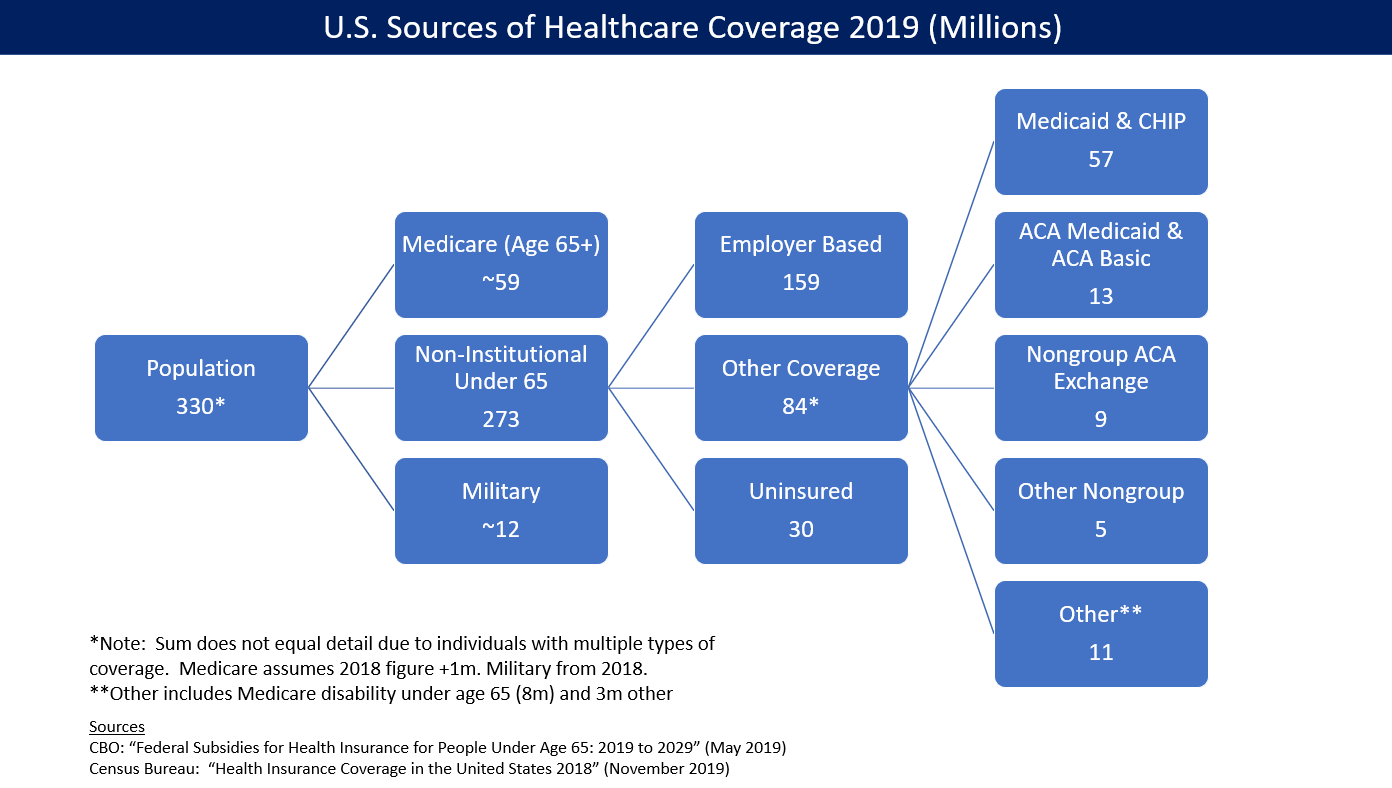
Health Insurance Coverage In The United States
In the United States, health insurance coverage is provided by several public and private sources. During 2019, the U.S. population was approximately 330 million, with 59 million people 65 years of age and over covered by the federal Medicare program. The 273 million non-institutionalized persons under age 65 either obtained their coverage from employer-based (159 million) or non-employer based (84 million) sources, or were uninsured (30 million). During the year 2019, 89% of the non-institutionalized population had health insurance coverage. Separately, approximately 12 million military personnel (considered part of the "institutional" population) received coverage through the Veteran's Administration and Military Health System. Despite being among the world's top economic powers, the US remains the sole industrialized nation in the world without universal health care coverage. The United States healthcare system is ranked 29th compared to other nations, due to the lack o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Disparities
Health equity arises from access to the social determinants of health, specifically from wealth, power and prestige. Individuals who have consistently been deprived of these three determinants are significantly disadvantaged from health inequities, and face worse health outcomes than those who are able to access certain resources. It is not equity to simply provide every individual with the same resources; that would be equality. In order to achieve health equity, resources must be allocated based on an individual need-based principle. According to the World Health Organization, "Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity". The quality of health and how health is distributed among economic and social status in a society can provide insight into the level of development within that society. Health is a basic human right and human need, and all human rights are interconnected. Thus, health must be discuss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Risk Factors
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection. Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often used as a synonym. The main difference lies in the realm of practice: medicine ( clinical practice) versus public health. As an example from clinical practice, low ingestion of dietary sources of vitamin C is a known risk factor for developing scurvy. Specific to public health policy, a determinant is a health risk that is general, abstract, related to inequalities, and difficult for an individual to control. For example, poverty is known to be a determinant of an individual's standard of health Health has a variety of definitions, which have been used for different purposes over time. In general, it refers to physical and emotional well-being, especially that associated with normal functioning of the human body, absent of disease, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outcomes Research
Outcomes research is a branch of public health research which studies the end results (wikt:outcome#Noun, outcomes) of the structure and processes of the health care system on the health and well-being of patients and populations. According to one medical outcomes and guidelines source book - 1996, ''Outcomes research'' includes health services research that focuses on identifying variations in medical procedures and associated health outcomes. Though listed as a synonym for the National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings, MeSH term "Outcome Assessment (Health Care)", outcomes research may refer to both health services research and healthcare outcomes assessment, which aims at health technology assessment, decision making, and policy analysis through systematic evaluation of quality of care, access, and effectiveness. Description Outcomes research is applied to clinical and population based research that seeks to study and optimize the end results of healthcare in terms o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |