|
Nanofluidic Circuitry
Nanofluidic circuitry is a nanotechnology aiming for control of fluids in nanometer scale. Due to the effect of an electrical double layer within the fluid channel, the behavior of nanofluid is observed to be significantly different compared with its microfluidic counterparts. Its typical characteristic dimensions fall within the range of 1–100 nm. At least one dimension of the structure is in nanoscopic scale. Phenomena of fluids in nano-scale structure are discovered to be of different properties in electrochemistry and fluid dynamics. Background With the development of microfabrication and nanotechnology, the study of microfluidics and nanofluidics is drawing more attention. Research on microfluidic found its advantages in DNA analysis, lab-on-a-chip, and micro-TAS. Devices in a microfluidic system include channels, valves, mixers, and pumps. Integration of these microfluidic devices enables sorting, transporting, and mixing of substances within fluids. However, the failu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nernst–Planck Equation
The Nernst–Planck equation is a conservation of mass equation used to describe the motion of a charged chemical species in a fluid medium. It extends Fick's law of diffusion for the case where the diffusing particles are also moved with respect to the fluid by electrostatic forces. It is named after Walther Nernst and Max Planck. Equation The Nernst–Planck equation is a continuity equation for the time-dependent concentration c(t,) of a chemical species: : + \nabla \cdot = 0 where is the flux. It is assumed that the total flux is composed of three elements: diffusion, advection, and electromigration. This implies that the concentration is affected by an ionic concentration gradient \nabla c, flow velocity , and an electric field : : = -\underbrace_ + \underbrace_ +\underbrace_ where D is the diffusivity of the chemical species, z is the valence of ionic species, e is the elementary charge, k_\text is the Boltzmann constant, and T is the absolute temperature. The electric f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
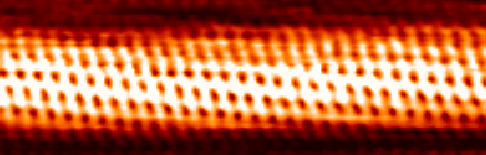
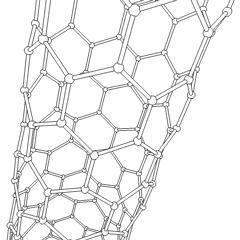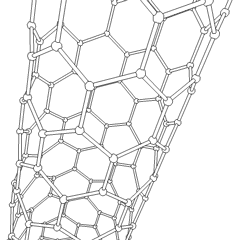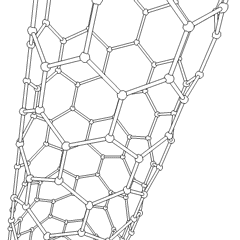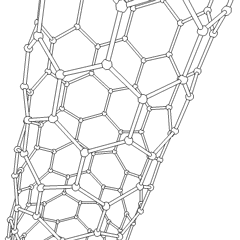
Carbon Nanotubes
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with a diameter in the nanometre range (nanoscale). They are one of the allotropes of carbon. Two broad classes of carbon nanotubes are recognized: * ''Single-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''SWCNTs'') have diameters around 0.5–2.0 nanometer, nanometres, about 100,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. They can be idealised as cutouts from a two-dimensional graphene sheet rolled up to form a hollow cylinder. * ''Multi-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''MWCNTs'') consist of nested single-wall carbon nanotubes in a nested, tube-in-tube structure. Double- and triple-walled carbon nanotubes are special cases of MWCNT. Carbon nanotubes can exhibit remarkable properties, such as exceptional tensile strength and thermal conductivity because of their nanostructure and bond strength, strength of the bonds between carbon atoms. Some SWCNT structures exhibit high electrical conductivity while others are semiconductors. In addition, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analytical Chemistry
Analytical skill, Analytical chemistry studies and uses instruments and methods to Separation process, separate, identify, and Quantification (science), quantify matter. In practice, separation, identification or quantification may constitute the entire analysis or be combined with another method. Separation isolates analytes. Qualitative inorganic analysis, Qualitative analysis identifies analytes, while Quantitative analysis (chemistry), quantitative analysis determines the numerical amount or concentration. Analytical chemistry consists of classical, wet chemistry, wet chemical methods and modern analytical techniques. Classical qualitative methods use separations such as Precipitation (chemistry), precipitation, Extraction (chemistry), extraction, and distillation. Identification may be based on differences in color, odor, melting point, boiling point, solubility, radioactivity or reactivity. Classical quantitative analysis uses mass or volume changes to quantify amount. Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Double Layer (interfacial)
Double layer may refer to: * Double layer (biospecific), the surface where two different phases of matter are in contact * Double layer (plasma physics), a structure in a plasma and consists of two parallel layers with opposite electrical charge * Double layer (surface science), a structure that appears on the surface of an object when it is placed into a liquid * Double layer forces, which occur between charged objects across liquids * Double layer potential In potential theory, an area of mathematics, a double layer potential is a solution of Laplace's equation corresponding to the electrostatic or magnetic potential associated to a dipole distribution on a closed surface ''S'' in three-dimensions. T ..., a solution of Laplace's equation * Double layer suturing, two layers of sutures, first in a deep level of a tissue and then at a more superficial level * DVD+R DL or Double layer, a DVD format {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatography
In chemical analysis, chromatography is a laboratory technique for the Separation process, separation of a mixture into its components. The mixture is dissolved in a fluid solvent (gas or liquid) called the ''mobile phase'', which carries it through a system (a column, a capillary tube, a plate, or a sheet) on which a material called the ''stationary phase'' is fixed. Because the different constituents of the mixture tend to have different affinities for the stationary phase and are retained for different lengths of time depending on their interactions with its surface sites, the constituents travel at different apparent velocities in the mobile fluid, causing them to separate. The separation is based on the differential partitioning between the mobile and the stationary phases. Subtle differences in a compound's partition coefficient result in differential retention on the stationary phase and thus affect the separation. Chromatography may be ''preparative'' or ''analytical' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrophoretic
Electrophoresis is the motion of charged dispersed particles or dissolved charged molecules relative to a fluid under the influence of a spatially uniform electric field. As a rule, these are zwitterions with a positive or negative net charge. Electrophoresis is used in laboratories to separate macromolecules based on their charges. The technique normally applies a negative charge called cathode so anionic protein molecules move towards a positive charge called anode. Therefore, electrophoresis of positively charged particles or molecules (cations) is sometimes called cataphoresis, while electrophoresis of negatively charged particles or molecules (anions) is sometimes called anaphoresis. Electrophoresis is the basis for analytical techniques used in biochemistry and molecular biology to separate particles, molecules, or ions by size, charge, or binding affinity, either freely or through a supportive medium using a one-directional flow of electrical charge. It is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Nanotubes
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with a diameter in the nanometre range (nanoscale). They are one of the allotropes of carbon. Two broad classes of carbon nanotubes are recognized: * ''Single-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''SWCNTs'') have diameters around 0.5–2.0 nanometer, nanometres, about 100,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair. They can be idealised as cutouts from a two-dimensional graphene sheet rolled up to form a hollow cylinder. * ''Multi-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''MWCNTs'') consist of nested single-wall carbon nanotubes in a nested, tube-in-tube structure. Double- and triple-walled carbon nanotubes are special cases of MWCNT. Carbon nanotubes can exhibit remarkable properties, such as exceptional tensile strength and thermal conductivity because of their nanostructure and bond strength, strength of the bonds between carbon atoms. Some SWCNT structures exhibit high electrical conductivity while others are semiconductors. In addition, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-assembled Monolayers
Self-assembled monolayers (SAM) are assemblies of organic molecules that form spontaneously on surfaces by adsorption and organize themselves into more or less distinct domains (head group, chain/backbone, and tail/end group). In some cases, molecules that form the monolayer do not interact strongly with the substrate. This is the case for porphyrins on highly oriented pyrolytic graphite, HOPG and two-dimensional supramolecular networks of perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride, PTCDA on gold. In other cases, the head group has a strong affinity for the substrate and anchors the molecule. Such an SAM consisting of a head group, chain (labeled "tail"), and functional end group is depicted in Figure 1. Common head groups include thiols, silanes, and phosphonates. SAMs are created by the chemisorption of head groups onto a substrate from either the vapor or liquid phase followed by a slower organization of "tail groups". Initially, at small molecular density on the surface, adsorbate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microelectromechanical Systems
MEMS (micro-electromechanical systems) is the technology of microscopic devices incorporating both electronic and moving parts. MEMS are made up of components between 1 and 100 micrometres in size (i.e., 0.001 to 0.1 mm), and MEMS devices generally range in size from 20 micrometres to a millimetre (i.e., 0.02 to 1.0 mm), although components arranged in arrays (e.g., digital micromirror devices) can be more than 1000 mm2. They usually consist of a central unit that processes data (an integrated circuit chip such as microprocessor) and several components that interact with the surroundings (such as microsensors). Because of the large surface area to volume ratio of MEMS, forces produced by ambient electromagnetism (e.g., electrostatic charges and magnetic moments), and fluid dynamics (e.g., surface tension and viscosity) are more important design considerations than with larger scale mechanical devices. MEMS technology is distinguished from molecular nanotechnol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gate Capacitance
In electronics, gate capacitance is the capacitance of the gate terminal of a field-effect transistor (FET). It can be expressed as the absolute capacitance of the gate of a transistor, or as the capacitance per unit area of an integrated circuit technology, or as the capacitance per unit width of minimum-length transistors in a technology. In generations of approximately Dennard scaling of metal-oxide-semiconductor FETs (MOSFETs), the capacitance per unit area has increased inversely with device dimensions. Since the gate area has gone down by the square of device dimensions, the gate capacitance of a transistor has gone down in direct proportion with device dimensions. With Dennard scaling, the capacitance per unit of gate width has remained approximately constant; this measurement can include gate–source and gate–drain overlap capacitances. Other scalings are not uncommon; the voltages and gate oxide thicknesses have not always decreased as rapidly as device dimensions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field-effect Transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the current through a semiconductor. It comes in two types: junction FET (JFET) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). FETs have three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by the Austr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |