|
Myocardial Scarring
Myocardial scarring is the accumulation of fibrous tissue resulting after some form of trauma to the cardiac tissue. Fibrosis is the formation of excess tissue in replacement of necrotic or extensively damaged tissue. Fibrosis in the heart is often hard to detect because fibromas, scar tissue or small tumors formed in one cell line, are often formed. Because they are so small, they can be hard to detect by methods such as magnetic resonance imaging. A cell line is a path of fibrosis that follow only a line of cells. Causes Myocardial infarction A myocardial infarction, also known as a heart attack, often result in the formation of fibrosis. A myocardial infarction is an ischemic event, or a restriction of blood flow to body tissue, such as by atherothrombosis. Without blood flow to the myocardium, it is deprived of oxygen, causing tissue death and irreversible damage. The tissue destroyed by the infarction is replaced with non-functioning fibrosis, restoring some of the struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Inferior Wall Scar
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the chest. In humans, other mammals, and birds, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right atria and lower left and right ventricles. Commonly the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. Fish, in contrast, have two chambers, an atrium and a ventricle, while most reptiles have three chambers. In a healthy heart blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a small amount of fluid. The wall of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laparoscopy
Laparoscopy () is an operation performed in the abdomen or pelvis using small incisions (usually 0.5–1.5 cm) with the aid of a camera. The laparoscope aids diagnosis or therapeutic interventions with a few small cuts in the abdomen.MedlinePlus > Laparoscopy Update Date: 21 August 2009. Updated by: James Lee, MD // No longer valid Laparoscopic surgery, also called minimally invasive procedure, bandaid surgery, or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique. There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery versus an exploratory laparotomy. These include reduced pain due to smaller incisions, reduced hemorrhaging, and shorter recovery time. The key element is the use of a laparoscope, a long fiber optic cable system that allows viewing of the affected area by snaking the cable from a more distant, but more easily accessible location. Laparoscopic surgery includes operations within the abdominal or pelvic cavities, whereas keyhole surgery per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
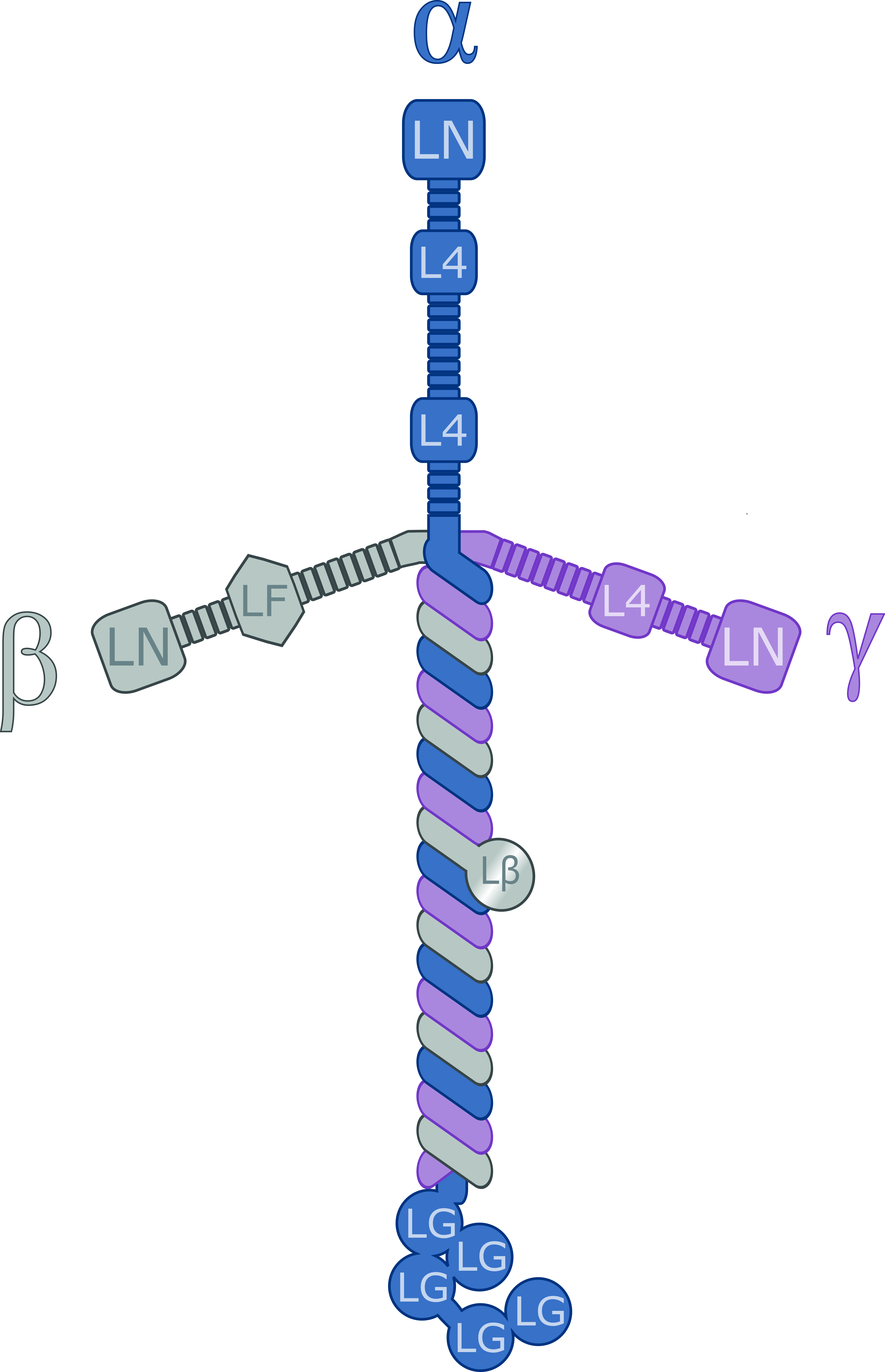
Laminin
Laminins are a family of glycoproteins of the extracellular matrix of all animals. They are major components of the basal lamina (one of the layers of the basement membrane), the protein network foundation for most cells and organs. The laminins are an important and biologically active part of the basal lamina, influencing cell differentiation, migration, and adhesion. Laminins are heterotrimeric proteins with a high molecular mass (~400 to ~900 kDa). They contain three different chains (α, β and γ) encoded by five, four, and three paralogous genes in humans, respectively. The laminin molecules are named according to their chain composition. Thus, laminin-511 contains α5, β1, and γ1 chains. Fourteen other chain combinations have been identified ''in vivo''. The trimeric proteins intersect to form a cross-like structure that can bind to other cell membrane and extracellular matrix molecules. The three shorter arms are particularly good at binding to other laminin molecules, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
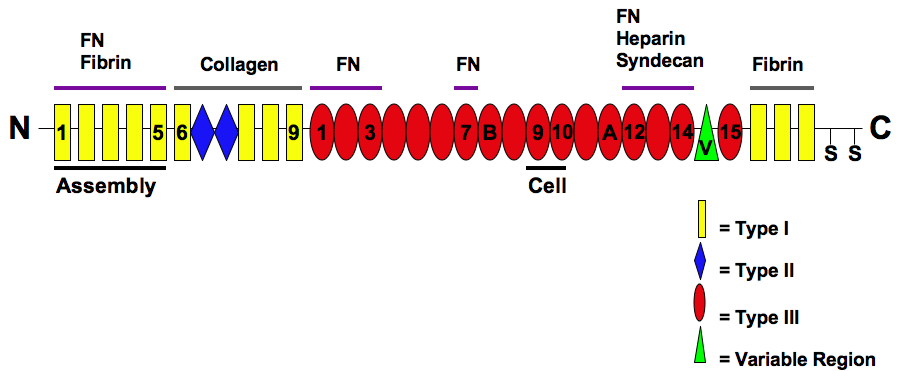
Fibronectin
Fibronectin is a high- molecular weight (~500-~600 kDa) glycoprotein of the extracellular matrix that binds to membrane-spanning receptor proteins called integrins. Fibronectin also binds to other extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen, fibrin, and heparan sulfate proteoglycans (e.g. syndecans). Fibronectin exists as a protein dimer, consisting of two nearly identical monomers linked by a pair of disulfide bonds. The fibronectin protein is produced from a single gene, but alternative splicing of its pre-mRNA leads to the creation of several isoforms. Two types of fibronectin are present in vertebrates: * soluble plasma fibronectin (formerly called "cold-insoluble globulin", or CIg) is a major protein component of blood plasma (300 μg/ml) and is produced in the liver by hepatocytes. * insoluble cellular fibronectin is a major component of the extracellular matrix. It is secreted by various cells, primarily fibroblasts, as a soluble protein dimer and is then ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrin
Fibrin (also called Factor Ia) is a fibrous, non-globular protein involved in the clotting of blood. It is formed by the action of the protease thrombin on fibrinogen, which causes it to polymerize. The polymerized fibrin, together with platelets, forms a hemostatic plug or clot over a wound site. When the lining of a blood vessel is broken, platelets are attracted, forming a platelet plug. These platelets have thrombin receptors on their surfaces that bind serum thrombin molecules, which in turn convert soluble fibrinogen in the serum into fibrin at the wound site. Fibrin forms long strands of tough insoluble protein that are bound to the platelets. Factor XIII completes the cross-linking of fibrin so that it hardens and contracts. The cross-linked fibrin forms a mesh atop the platelet plug that completes the clot. Fibrin was discovered by Marcello Malpighi in 1666. Role in disease Excessive generation of fibrin due to activation of the coagulation cascade leads to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix, is a three-dimensional network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest. Each type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collagen
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole-body protein content. Collagen consists of amino acids bound together to form a triple helix of elongated fibril known as a collagen helix. It is mostly found in connective tissue such as cartilage, bones, tendons, ligaments, and skin. Depending upon the degree of mineralization, collagen tissues may be rigid (bone) or compliant (tendon) or have a gradient from rigid to compliant (cartilage). Collagen is also abundant in corneas, blood vessels, the gut, intervertebral discs, and the dentin in teeth. In muscle tissue, it serves as a major component of the endomysium. Collagen constitutes one to two percent of muscle tissue and accounts for 6% of the weight of the skeletal muscle tissue. The fibroblast is the most common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metalloproteinase
A metalloproteinase, or metalloprotease, is any protease enzyme whose catalytic mechanism involves a metal. An example is ADAM12 which plays a significant role in the fusion of muscle cells during embryo development, in a process known as myogenesis. Most metalloproteases require zinc, but some use cobalt. The metal ion is coordinated to the protein via three ligands. The ligands coordinating the metal ion can vary with histidine, glutamate, aspartate, lysine, and arginine. The fourth coordination position is taken up by a labile water molecule. Treatment with chelating agents such as EDTA leads to complete inactivation. EDTA is a metal chelator that removes zinc, which is essential for activity. They are also inhibited by the chelator orthophenanthroline. Classification There are two subgroups of metalloproteinases: * Exopeptidases, metalloexopeptidases ( EC number: 3.4.17). * Endopeptidases, metalloendopeptidases (3.4.24). Well known metalloendopeptidases include ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity), and B cells (for humoral immunity, humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity). They are the main type of cell found in lymph, which prompted the name "lymphocyte". Lymphocytes make up between 18% and 42% of circulating white blood cells. Types The three major types of lymphocyte are T cell A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...s, B cells and Natural killer cell, natural killer (NK) cells. Lymphocytes can be identified by their large nucleus. T cells and B cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense ( innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrophil
Neutrophils (also known as neutrocytes or heterophils) are the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. They form an essential part of the innate immune system, with their functions varying in different animals. They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and differentiated into subpopulations of neutrophil-killers and neutrophil-cagers. They are short-lived and highly mobile, as they can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot. Neutrophils may be subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils (or bands). They form part of the polymorphonuclear cells family (PMNs) together with basophils and eosinophils. The name ''neutrophil'' derives from staining characteristics on hematoxylin and eosin ( H&E) histological or cytological preparations. Whereas basophilic white blood cells stain dark blue and eosinophilic white blood cells stain bright red, neutrophils stain a neutral pink. Norm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Heart Defect
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular disease. Signs and symptoms depend on the specific type of defect. Symptoms can vary from none to life-threatening. When present, symptoms may include rapid breathing, bluish skin ( cyanosis), poor weight gain, and feeling tired. CHD does not cause chest pain. Most congenital heart defects are not associated with other diseases. A complication of CHD is heart failure. The cause of a congenital heart defect is often unknown. Risk factors include certain infections during pregnancy such as rubella, use of certain medications or drugs such as alcohol or tobacco, parents being closely related, or poor nutritional status or obesity in the mother. Having a parent with a congenital heart defect is also a risk factor. A number of genetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |