|
Murrays' Mills
Murrays' Mills is a complex of former cotton mills on land between Jersey Street and the Rochdale Canal in the district of Ancoats, Manchester, England. The mills were built for brothers Adam and George Murray. The first mill on the site, Old Mill, was begun in 1797, and is the world's oldest surviving urban steam-powered cotton spinning factory. After Old Mill opened, the company continued to expand and prosper, and by 1806 the complex was the largest in the world, employing about 1,000 people at its peak: Decker Mill was opened in 1802, New Mill in 1804, Little Mill in 1822, and Doubling and Fireproof Mill in 1842. The main complex formed a quadrangle surrounding a private canal basin linked under the road to the Rochdale Canal, which opened in 1804. The canal basin was used to deliver raw cotton and coal and to transport spun cotton away from the complex. In 1898, A & G Murray became part of the Fine Cotton Spinners' and Doublers' Association Limited (FCSDA). The mill com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cotton Mill
A cotton mill is a building that houses spinning (textiles), spinning or weaving machinery for the production of yarn or cloth from cotton, an important product during the Industrial Revolution in the development of the factory system. Although some were driven by animal power, most early mills were built in rural areas at fast-flowing rivers and streams using water wheels for power. The development of viable Watt steam engine, steam engines by Boulton and Watt from 1781 led to the growth of larger, steam-powered mills allowing them to be concentrated in urban mill towns, like Manchester, which with neighbouring Salford, Greater Manchester, Salford had more than 50 mills by 1802. The mechanisation of the spinning process in the early factories was instrumental in the growth of the machine tool industry, enabling the construction of larger cotton mills. Joint stock company, Limited companies were developed to construct mills, and the trading floors of the Manchester Royal Excha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulton And Watt
Boulton & Watt was an early British engineering and manufacturing firm in the business of designing and making marine and stationary steam engines. Founded in the English West Midlands around Birmingham in 1775 as a partnership between the English manufacturer Matthew Boulton and the Scottish engineer James Watt, the firm had a major role in the Industrial Revolution and grew to be a major producer of steam engines in the 19th century. The engine partnership The partnership was formed in 1775 to exploit Watt's patent for a steam engine with a separate condenser. This made much more efficient use of its fuel than the older Newcomen engine. Initially the business was based at the Soho Manufactory near Boulton's Soho House on the southern edge of the then-rural parish of Handsworth. However most of the components for their engines were made by others, for example the cylinders by John Wilkinson. In 1795, they began to make steam engines themselves at their Soho Foundry in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doubling (yarn)
Doubling may refer to: Mathematics * Arithmetical doubling of a count or a measure, expressed as: ** Multiplication by 2 ** Increase by 100%, i.e. one-hundred percent ** Doubling the cube (i. e., hypothetical geometric construction of a cube with twice the volume of a given cube) * Doubling time, the length of time required for a quantity to double in size or value * Doubling map, a particular infinite two-dimensional geometrical construction * ''see also:'' Period-doubling bifurcation Music * The composition or performance of a melody with itself or itself transposed at a constant interval such as the octave, third, or sixth, Voicing (music)#Doubling * The assignment of a melody to two instruments in an arrangement * The playing of two (or more) instruments alternately by a single player, e.g. ''Flute, doubling piccolo'' ** Musicians who play more than one woodwind instrument are called woodwind doublers or reed players * Doubletracking, a recording technique in which a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beam Engine
A beam engine is a type of steam engine where a pivoted overhead beam is used to apply the force from a vertical piston to a vertical connecting rod. This configuration, with the engine directly driving a pump, was first used by Thomas Newcomen around 1705 to remove water from mines in Cornwall. The efficiency of the engines was improved by engineers including James Watt, who added a separate condenser; Jonathan Hornblower and Arthur Woolf, who compounded the cylinders; and William McNaught, who devised a method of compounding an existing engine. Beam engines were first used to pump water out of mines or into canals but could be used to pump water to supplement the flow for a waterwheel powering a mill. The rotative beam engine is a later design of beam engine where the connecting rod drives a flywheel by means of a crank (or, historically, by means of a sun and planet gear). These beam engines could be used to directly power the line-shafting in a mill. They also c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doubling And Fireproof Mill
Doubling may refer to: Mathematics * Arithmetical doubling of a count or a measure, expressed as: ** Multiplication by 2 ** Increase by 100%, i.e. one-hundred percent ** Doubling the cube (i. e., hypothetical geometric construction of a cube with twice the volume of a given cube) * Doubling time, the length of time required for a quantity to double in size or value * Doubling map, a particular infinite two-dimensional geometrical construction * ''see also:'' Period-doubling bifurcation Music * The composition or performance of a melody with itself or itself transposed at a constant interval such as the octave, third, or sixth, Voicing (music)#Doubling * The assignment of a melody to two instruments in an arrangement * The playing of two (or more) instruments alternately by a single player, e.g. ''Flute, doubling piccolo'' ** Musicians who play more than one woodwind instrument are called Woodwind Doublers or Reed Players * Doubletracking, a recording technique in which a mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joshua Field (engineer)
Joshua Field FRS (1786 – 11 August 1863) was a British civil engineer and mechanical engineer. Field was born in Hackney in 1786, his father was John Field a corn and seed merchant who was later to become Master of the Worshipful Company of Merchant Taylors. Field was a pupil of dockyard engineer Simon Goodrich from 1803 to 1805. Commissioned by Samuel Bentham, the Inspector-general of naval works, he worked with Samuel Goodrich to develop tools for mass-producing ships' blocks at Portsmouth Dockyard. The block mills they designed required ten unskilled men to take the place of 110 skilled craftsmen, and have been recognised as the first use of machine tools for mass production. They were built by Henry Maudslay between 1802 and 1806, and represented the first steam-powered manufactory in any dockyard. He then joined Maudslay to form the firm of Messrs. Maudslay, Sons and Field of Lambeth. One of their projects was to build engines for the SS Great Western's Atlantic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gasometer
A gas holder or gasholder, also known as a gasometer, is a large container in which natural gas or town gas is stored near atmospheric pressure at ambient temperatures. The volume of the container follows the quantity of stored gas, with pressure coming from the weight of a movable cap. Typical volumes for large gas holders are about , with diameter structures. Gas holders now tend to be used for balancing purposes to ensure that gas pipes can be operated within a safe range of pressures, rather than for actually storing gas for later use. Etymology Antoine Lavoisier devised the first gas holder, which he called a ''gazomètre'', to assist his work in pneumatic chemistry. It enabled him to weigh the gas in a pneumatic trough with the precision he required. He published his ''Traité Élémentaire de Chimie'' in 1789. James Watt Junior collaborated with Thomas Beddoes in constructing the pneumatic apparatus, a shortlived piece of medical equipment that incorporated a ''gaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line Shafting
A line shaft is a power-driven rotating shaft for power transmission that was used extensively from the Industrial Revolution until the early 20th century. Prior to the widespread use of electric motors small enough to be connected directly to each piece of machinery, line shafting was used to distribute power from a large central power source to machinery throughout a workshop or an industrial complex. The central power source could be a water wheel, turbine, windmill, animal power or a steam engine. Power was distributed from the shaft to the machinery by a system of belts, pulleys and gears known as ''millwork''. Operation A typical line shaft would be suspended from the ceiling of one area and would run the length of that area. One pulley on the shaft would receive the power from a parent line shaft elsewhere in the building. The other pulleys would supply power to pulleys on each individual machine or to subsequent line shafts. In manufacturing where there were a lar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Fairbairn
Sir William Fairbairn, 1st Baronet of Ardwick (19 February 1789 – 18 August 1874) was a Scottish civil engineer, structural engineer Structural engineers analyze, design, plan, and research structural components and structural systems to achieve design goals and ensure the safety and comfort of users or occupants. Their work takes account mainly of safety, technical, economic ... and shipbuilder. In 1854 he succeeded George Stephenson and Robert Stephenson to become the third president of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers. Early career Born in Kelso, Scotland, Kelso to a local farmer, Fairbairn showed an early mechanical aptitude and served as an apprentice millwright in Newcastle upon Tyne where he befriended the young George Stephenson. He moved to Manchester in 1813 to work for Adam Parkinson and Thomas Hewes. In 1817, he launched his mill-machinery business with James Lillie as William Fairbairn & Sons, Fairbairn and Lillie Engine Makers. Structural studies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
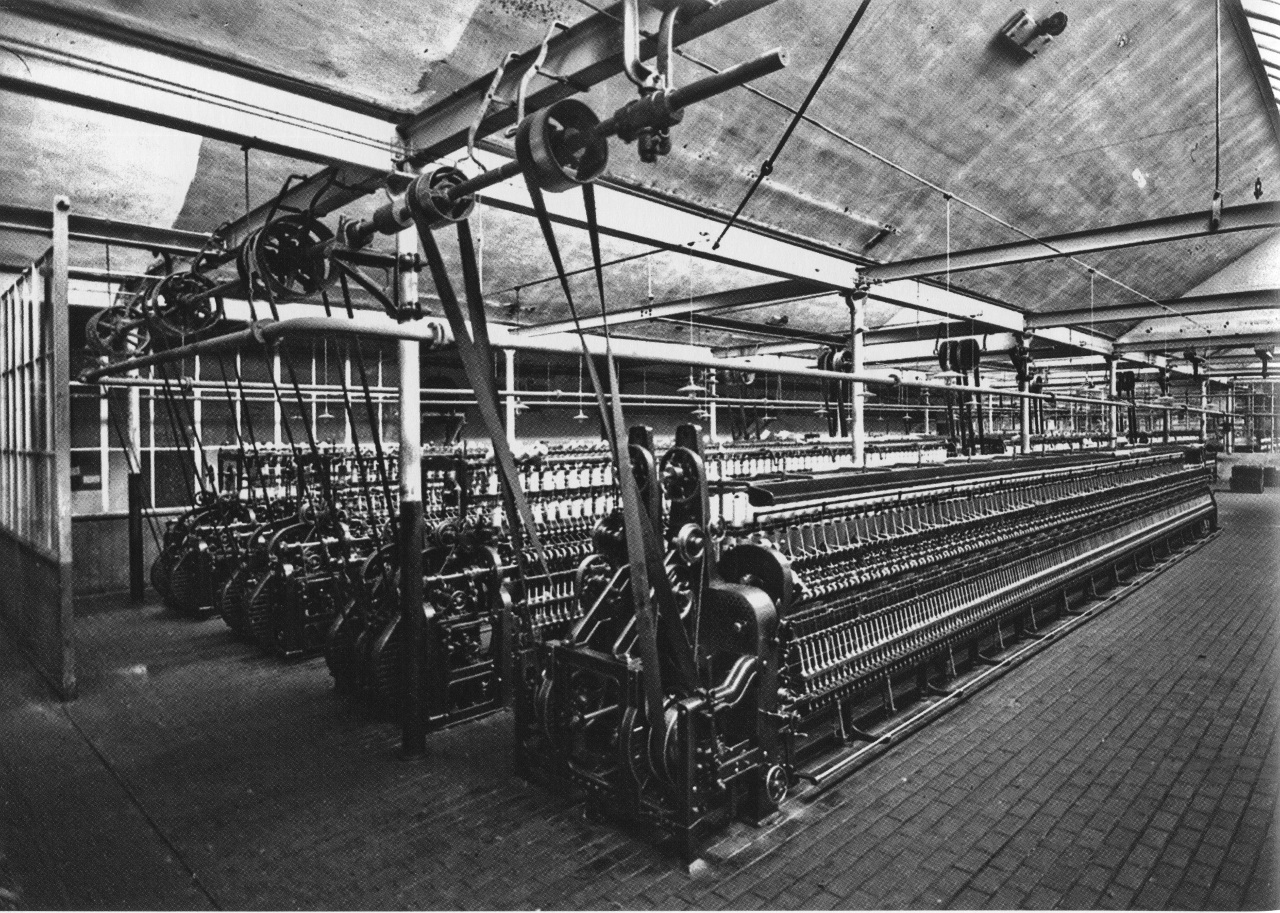
Murrays Mill Quadrangle Interior 2008
Murrays Coaches is an Australian express and coach charter company. History Murrays was founded by Bill Murray in the early 1950s as a school bus operator in Canberra. The operation was taken over by Ron Murray in 1970 by which time it was operating services to Captains Flat, Kowen Forest, Naas, Tidbinbilla, Uriarra and Williamsdale with 10 buses. Murrays were operating seven school buses when the services were taken over by Deane's Buslines in November 1997. At some point Murrays diversified into coach operation, initially to the Snowy Mountains. By the mid-1980s Murrays were operating interstate services from Canberra to Sydney, Wollongong and Narooma. These services continue today. In May 1979, Murrays purchased Sydney bus routes 6 Arncliffe to Earlwood and 49 Carlton to Rockdale. These were sold in October 1982 to Brighton Bus Lines after the laws requiring tourist vehicle licences to be attached to route service operators were relaxed. In late 1988, an operation c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
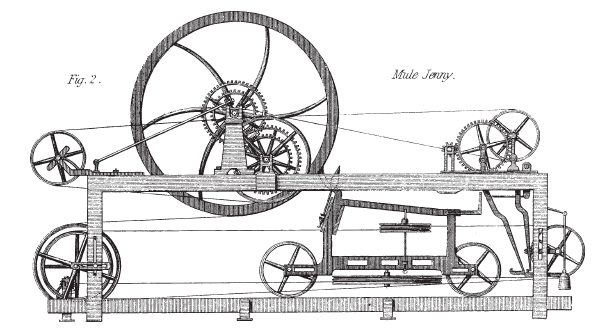
Spinning Mule
The spinning mule is a machine used to spin cotton and other fibres. They were used extensively from the late 18th to the early 20th century in the mills of Lancashire and elsewhere. Mules were worked in pairs by a minder, with the help of two boys: the little piecer and the big or side piecer. The carriage carried up to 1,320 spindles and could be long, and would move forward and back a distance of four times a minute. It was invented between 1775 and 1779 by Samuel Crompton. The self-acting (automatic) mule was patented by Richard Roberts in 1825. At its peak there were 50,000,000 mule spindles in Lancashire alone. Modern versions are still in niche production and are used to spin woollen yarns from noble fibres such as cashmere, ultra-fine merino and alpaca for the knitware market. The spinning mule spins textile fibres into yarn by an intermittent process. In the draw stroke, the roving is pulled through rollers and twisted; on the return it is wrapped onto the spindle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |