|
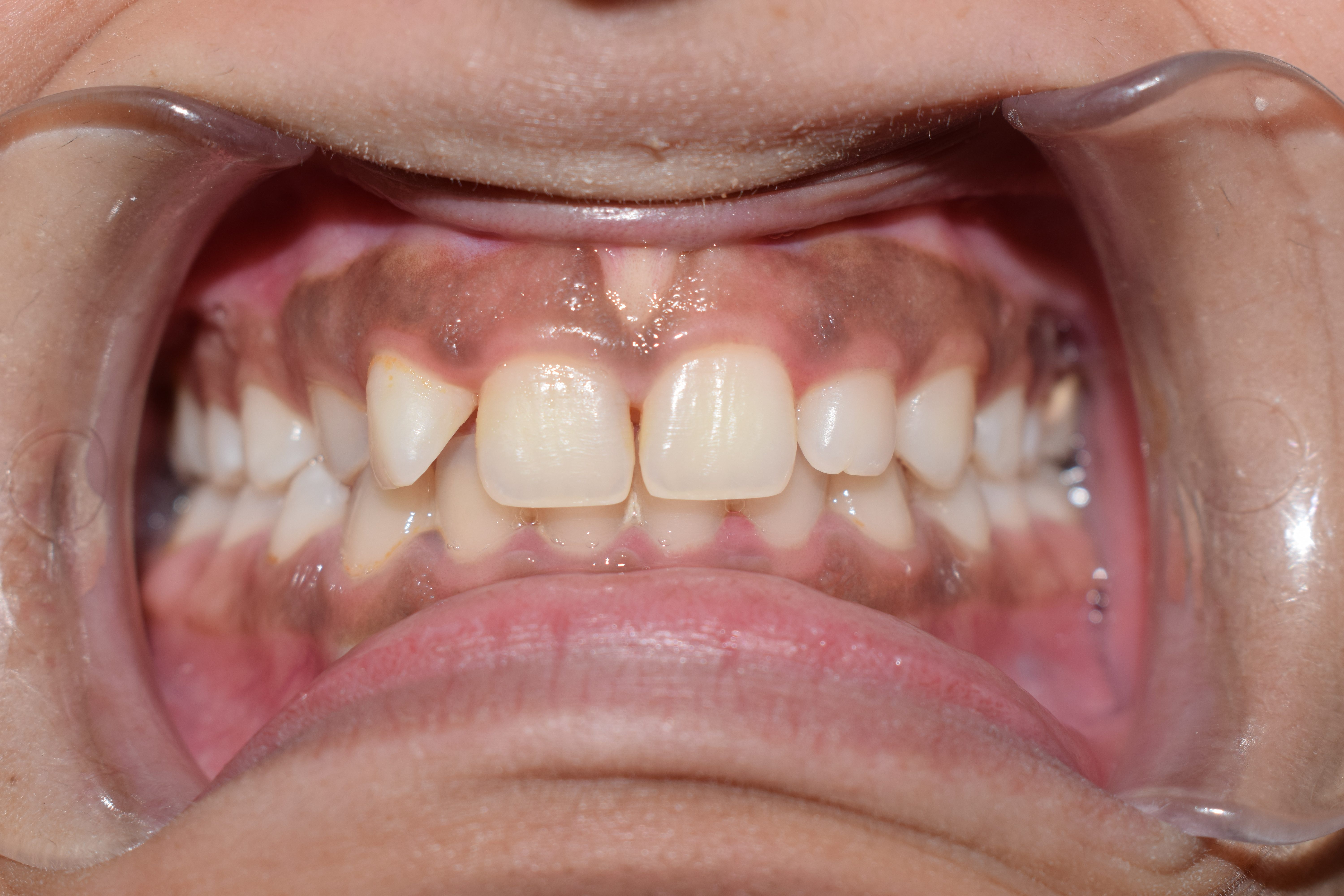
Mucogingival Junction
A mucogingival junction is an anatomical feature found on the intraoral mucosa. The mucosa of the cheeks and floor of the mouth are freely moveable and fragile, whereas the mucosa around the teeth and on the palate are firm and keratinized. Where the two tissue types meet is known as a mucogingival junction. There are three mucogingival junctions: on the facial of the maxilla and on both the facial and lingual of the mandible. The palatal gingiva of the maxilla is continuous with the tissue of the palate, which is bound down to the palatal bones. Because the palate is devoid of freely moveable alveolar mucosa, there is no mucogingival junction.Carranza's Clinical Periodontology, W.B. Saunders 2002, page 17. Clinical importance The clinical importance of the mucogingival junction is in measuring the width of attached gingiva. Attached gingiva is important because it is bound very tightly to the underlying alveolar bone and provides protection to the mucosa during functional u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucosa
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keratinized
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, horns, claws, hooves, and the outer layer of skin among vertebrates. Keratin also protects epithelial cells from damage or stress. Keratin is extremely insoluble in water and organic solvents. Keratin monomers assemble into bundles to form intermediate filaments, which are tough and form strong unmineralized epidermal appendages found in reptiles, birds, amphibians, and mammals. Excessive keratinization participate in fortification of certain tissues such as in horns of cattle and rhinos, and armadillos' osteoderm. The only other biological matter known to approximate the toughness of keratinized tissue is chitin. Keratin comes in two types, the primitive, softer forms found in all vertebrates and harder, derived forms found only among saurop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonly Used Terms Of Relationship And Comparison In Dentistry
This is a list of definitions of commonly used terms of location and direction in dentistry. This set of terms provides orientation within the oral cavity, much as anatomical terms of location provide orientation throughout the body. Terms Combining of terms Most of the principal terms can be combined using their corresponding combining forms (such as ''mesio-'' for ''mesial'' and ''disto-'' for ''distal''). They provide names for directions (vectors) and axes; for example, the coronoapical axis is the long axis of a tooth. Such combining yields terms such as those in the following list. The abbreviations should be used only in restricted contexts, where they are explicitly defined and help avoid extensive repetition (for example, a journal article that uses the term "mesiodistal" dozens of times might use the abbreviation "MD"). The abbreviations are ambiguous: (1) they are not spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Structure In humans, the maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla * Four processes ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process of maxilla ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process * three surfaces – anterior, posterior, medial * the Infraorbital foramen * the maxillary sinus * the incisive foramen Articulations Each maxilla articulates with nine bones: * two of the cranium: the frontal and ethmoid * seven of the face: the nasal, zygomatic, lacrimal, inferior n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Mandible
In anatomy, the mandible, lower jaw or jawbone is the largest, strongest and lowest bone in the human facial skeleton. It forms the lower jaw and holds the lower tooth, teeth in place. The mandible sits beneath the maxilla. It is the only movable bone of the skull (discounting the ossicles of the middle ear). It is connected to the temporal bones by the temporomandibular joints. The bone is formed prenatal development, in the fetus from a fusion of the left and right mandibular prominences, and the point where these sides join, the mandibular symphysis, is still visible as a faint ridge in the midline. Like other symphyses in the body, this is a midline articulation where the bones are joined by fibrocartilage, but this articulation fuses together in early childhood.Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, p. 59 The word "mandible" derives from the Latin word ''mandibula'', "jawbone" (literally "one used for chewing"), from ''wikt:mandere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separated. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior, bony hard palate and the posterior, fleshy soft palate (or velum). Structure Innervation The maxillary nerve branch of the trigeminal nerve supplies sensory innervation to the palate. Development The hard palate forms before birth. Variation If the fusion is incomplete, a cleft palate results. Function When functioning in conjunction with other parts of the mouth, the palate produces certain sounds, particularly velar, palatal, palatalized, postalveolar, alveolopalatal, and uvular consonants. History Etymology The English synonyms palate and palatum, and also the related adjective palatine (as in palatine bone), are all from the Latin ''palatum'' via Old French ''palat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolar Mucosa
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed ''lamina propria''. The oral cavity has sometimes been described as a mirror that reflects the health of the individual. Changes indicative of disease are seen as alterations in the oral mucosa lining the mouth, which can reveal systemic conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiency, or the local effects of chronic tobacco or alcohol use. The oral mucosa tends to heal faster and with less scar formation compared to the skin. The underlying mechanism remains unknown, but research suggests that extracellular vesicles might be involved. Classification Oral mucosa can be divided into three main categories based on function and histology: *Lining mucosa, nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, found almost everywhere else in the oral cavity, including the: **Alveolar mucosa, the lining between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gingiva
The gums or gingiva (plural: ''gingivae'') consist of the mucosal tissue that lies over the mandible and maxilla inside the mouth. Gum health and disease can have an effect on general health. Structure The gums are part of the soft tissue lining of the mouth. They surround the teeth and provide a seal around them. Unlike the soft tissue linings of the lips and cheeks, most of the gums are tightly bound to the underlying bone which helps resist the friction of food passing over them. Thus when healthy, it presents an effective barrier to the barrage of periodontal insults to deeper tissue. Healthy gums are usually coral pink in light skinned people, and may be naturally darker with melanin pigmentation. Changes in color, particularly increased redness, together with swelling and an increased tendency to bleed, suggest an inflammation that is possibly due to the accumulation of bacterial plaque. Overall, the clinical appearance of the tissue reflects the underlying histology, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolar Bone
The alveolar process () or alveolar bone is the thickened ridge of bone that contains the tooth sockets on the jaw bones (in humans, the maxilla and the mandible). The structures are covered by gums as part of the oral cavity. The synonymous terms ''alveolar ridge'' and ''alveolar margin'' are also sometimes used more specifically to refer to the ridges on the inside of the mouth which can be felt with the tongue, either on roof of the mouth between the upper teeth and the hard palate or on the bottom of the mouth behind the lower teeth. Terminology The term ''alveolar'' () ('hollow') refers to the cavities of the tooth sockets, known as dental alveoli. The alveolar process is also called the ''alveolar bone'' or ''alveolar ridge''. The curved portion is referred to as the alveolar arch. The alveolar bone proper, also called bundle bone, directly surrounds the teeth. The term alveolar crest describes the extreme rim of the bone nearest to the crowns of the teeth. The portion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastication
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, the food is positioned by the cheek and tongue between the teeth for grinding. The muscles of mastication move the jaws to bring the teeth into intermittent contact, repeatedly occluding and opening. As chewing continues, the food is made softer and warmer, and the enzymes in saliva begin to break down carbohydrates in the food. After chewing, the food (now called a bolus) is swallowed. It enters the esophagus and via peristalsis continues on to the stomach, where the next step of digestion occurs. Increasing the number of chews per bite increases relevant gut hormones. Studies suggest that chewing may decrease self-reported hunger and food intake. Chewing gum has been around for many centuries; there is evidence that northern Europeans c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toothbrush
A toothbrush is an oral hygiene tool used to clean the teeth, gums, and tongue. It consists of a head of tightly clustered bristles, atop of which toothpaste can be applied, mounted on a handle which facilitates the cleaning of hard-to-reach areas of the mouth. They should be used in conjunction with something to clean between the teeth where the bristles of the toothbrush cannot reach - for example floss, tape or interdental brushes. They are available with different bristle textures, sizes, and forms. Most dentists recommend using a soft toothbrush since hard-bristled toothbrushes can damage tooth enamel and irritate the gums. Because many common and effective ingredients in toothpaste are harmful if swallowed in large doses and instead should be spat out, the act of brushing teeth is most often done at a sink within the kitchen or bathroom, where the brush may be rinsed off afterwards to remove any debris remaining and then dried to reduce conditions ideal for germ growth (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teeth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)