|
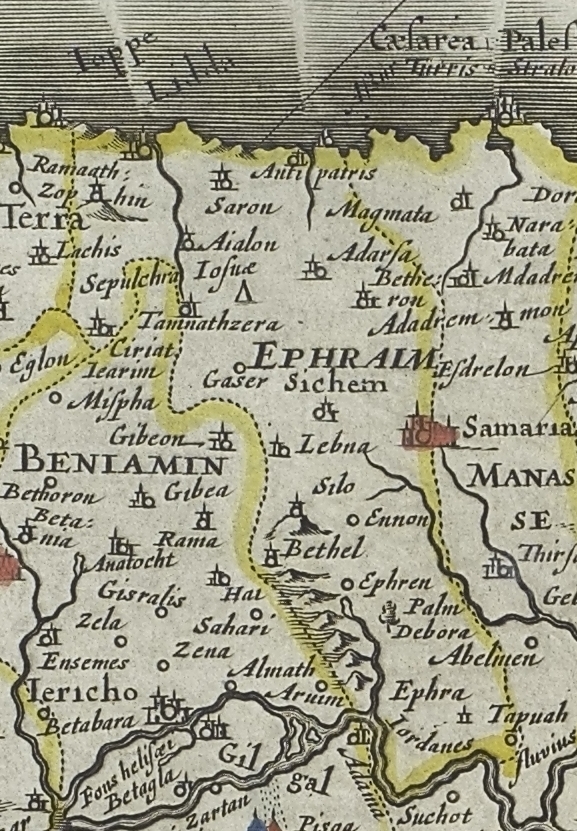
Mount Of Ephraim
Mount Ephraim ( he, הר אפרים), or alternately Mount of Ephraim, was the historical name for the central mountainous district of Israel once occupied by the Tribe of Ephraim (), extending from Bethel to the plain of Jezreel. In Joshua's time (), approximately sometime between the 18th century BCE and the 13th century BCE, these hills were densely wooded. They were intersected by well-watered, fertile valleys, referred to in . Later, the region became known as Samaria, after the capital city of the northern Kingdom of Israel which was centered in the area. Notable persons Joshua was buried at Timnath-heres among the mountains of Ephraim, on the north side of the hill of Gaash (). This region is also called the "mountains of Israel" () and the "mountains of Samaria" (: ). Israel's fourth judge and prophetess Deborah lived in this region. Her home was called "the palm tree of Deborah", and was between Bethel and Ramah in Benjamin (). 'Then Jeroboam built Shechem in mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southeastern shore of the Mediterranean Sea and the northern shore of the Red Sea, and shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the northeast, Jordan to the east, and Egypt to the southwest. Israel also is bordered by the Palestinian territories of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip to the east and west, respectively. Tel Aviv is the economic and technological center of the country, while its seat of government is in its proclaimed capital of Jerusalem, although Israeli sovereignty over East Jerusalem is unrecognized internationally. The land held by present-day Israel witnessed some of the earliest human occupations outside Africa and was among the earliest known sites of agriculture. It was inhabited by the Canaanites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribe Of Ephraim
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim ( he, אֶפְרַיִם, ''ʾEp̄rayīm,'' in pausa: אֶפְרָיִם, ''ʾEp̄rāyīm'') was one of the tribes of Israel. The Tribe of Manasseh together with Ephraim formed the ''House of Joseph''. It is one of the ten lost tribes. The etymology of the name is disputed.For the etymology, see Ephraim as portrayed in biblical narrative According to the Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim is descended from a man named Ephraim, who is recorded as the son of Joseph, the son of Jacob, and Asenath, the daughter of Potiphera. The descendants of Joseph formed two of the tribes of Israel, whereas the other sons of Jacob were the founders of one tribe each. The Bible records that the Tribe of Ephraim entered the land of Canaan during its conquest by Joshua, a descendant of Ephraim himself. However, many archeologists have abandoned the idea that Joshua carried out a conquest of Canaan similar to that described in the Book of Joshua, seein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bethel
Bethel ( he, בֵּית אֵל, translit=Bēṯ 'Ēl, "House of El" or "House of God",Bleeker and Widegren, 1988, p. 257. also transliterated ''Beth El'', ''Beth-El'', ''Beit El''; el, Βαιθήλ; la, Bethel) was an ancient Israelite sanctuary frequently mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. Bethel is first referred to in the bible as being near where Abram pitched his tent. Later, Bethel is mentioned as the location where Jacob dreams of a ladder leading to heaven, and which he therefore named Bethel, "House of God". The name is further used for a border city located between the territory of the Israelite tribe of Benjamin and that of the tribe of Ephraim, which first belonged to the Benjaminites and was later conquered by the Ephraimites. In the 4th century CE, Eusebius of Caesarea and Jerome described Bethel as a small village that lay 12 Roman miles north of Jerusalem, to the right or east of the road leading to Neapolis.Robinson and Smith, 1856, pp. 449–450. Most schola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jezreel (city)
Tel Jezreel ( he, יִזְרְעֶאל ''Yīzrə‘e’l'', "God will sow") is an archaeological site in the eastern Jezreel Valley in northern Israel. The city of Jezreel served as a main fortress of the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel under king Ahab in the 9th century BCE. Biblical references Prior to the division of the United Kingdom of Israel, the city was the hometown of Ahinoam, second wife of King David, Michal, Saul's daughter, being the first, Ahinoam being his second, and Abigail, widow of Nabal, being his third (). According to the First Books of Kings, Book of Kings, the royal palace of Ahab, King Ahab, "one of the most famous of the royal residences of the kings of Israel", was in Jezreel, adjacent to the vineyard of Naboth (). Ahab's capital remained in Samaria (ancient city), Samaria. According to , following the prophet Elijah's victory over the prophets of Baal, Ba'al at Mount Carmel, Elijah instructs Ahab to return home to Jezreel, where he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joshua
Joshua () or Yehoshua ( ''Yəhōšuaʿ'', Tiberian: ''Yŏhōšuaʿ,'' lit. 'Yahweh is salvation') ''Yēšūaʿ''; syr, ܝܫܘܥ ܒܪ ܢܘܢ ''Yəšūʿ bar Nōn''; el, Ἰησοῦς, ar , يُوشَعُ ٱبْنُ نُونٍ '' Yūšaʿ ibn Nūn''; la, Iosue functioned as Moses' assistant in the books of Exodus and Numbers, and later succeeded Moses as leader of the Israelite tribes in the Hebrew Bible's Book of Joshua. His name was Hoshea ( ''Hōšēaʿ'', lit. 'Save') the son of Nun, of the tribe of Ephraim, but Moses called him "Yehoshua" (translated as "Joshua" in English),''Bible'' the name by which he is commonly known in English. According to the Bible, he was born in Egypt prior to the Exodus. The Hebrew Bible identifies Joshua as one of the twelve spies of Israel sent by Moses to explore the land of Canaan. In Numbers 13:1, and after the death of Moses, he led the Israelite tribes in the conquest of Canaan, and allocated lands to the tribes. According to bib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samaria
Samaria (; he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn, ar, السامرة, translit=as-Sāmirah) is the historic and biblical name used for the central region of Palestine, bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The first-century historian Josephus set the Mediterranean Sea as its limit to the west, and the Jordan River as its limit to the east. Its territory largely corresponds to the biblical allotments of the tribe of Ephraim and the western half of Manasseh. It includes most of the region of the ancient Kingdom of Israel, which was north of the Kingdom of Judah. The border between Samaria and Judea is set at the latitude of Ramallah. The name "Samaria" is derived from the ancient city of Samaria, capital of the northern Kingdom of Israel. The name Samaria likely began being used for the entire kingdom not long after the town of Samaria had become Israel's capital, but it is first documented after its conquest by Sargon II of Assyria, who turned the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Israel (united Monarchy)
The United Monarchy () in the Hebrew Bible refers to History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israel and Judah under the reigns of Saul, David, and Solomon. It is traditionally dated to have lasted between and . According to the biblical account, on the succession of Solomon's son Rehoboam, the United Monarchy would have split into two separate kingdoms: the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel in the north, containing the cities of Shechem and Samaria (ancient city), Samaria; and the Kingdom of Judah in the south, containing the city of Jerusalem and the Temple in Jerusalem, Jewish Temple. However, whether or not the United Monarchy actually existed is a matter of ongoing academic debate. In the 1990s, Israeli archaeologist Israel Finkelstein contested that existing archaeological evidence for the United Monarchy in the 10th century BCE should actually be dated to the 9th century BCE. This model placed the biblical kingdom in Iron Age, Iron Age I, suggesting that it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timnath-heres
Timnath-heres or Timnath-serah ( he, תמנת חרס), later Thamna, was the town given by the Israelites to Joshua according to the Hebrew Bible. He requested it and the people gave it to him "at the order of the Lord". He built up the town and lived in it (). According to the Septuagint version of the Book of Joshua, Joshua placed there "the stone knives, with which he had circumcised the children of Israel". On his death, he was buried there (). Jewish tradition also places the tomb of Caleb there. In 2022, excavations by Israeli archaeologists were launched at Khirbet Tibnah in Samaria, a hilltop site commonly identified as biblical Timnath. Kifl Hares One possible location Timnath-heres has been identified with is the Palestinian village of Kifl Hares, located 6 kilometres west of Salfit in the West Bank.Finkelstein et al, 1997, p. 460 Khirbet Tibnah Another candidate is Khirbet Tibnah, located between Deir Nidham and Nabi Salih,Finkelstein ''et al.'', 1997, p. 367 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Gaash
Mount Gaash was the name of a hill in ancient Israel, in the mountainous region of Ephraim, mentioned several times in the Hebrew Bible. It is mentioned as a place of torrent valleys, which may refer to ravines in the vicinity: * Joshua son of Nun was buried in the hill country of Ephraim, which was north of Mount Gaash. *Hurai from the "Ravines of Gaash" participated as one of David's Mighty Warriors in conquering the City of David.2 Samuel Samuel ''Šəmūʾēl'', Tiberian: ''Šămūʾēl''; ar, شموئيل or صموئيل '; el, Σαμουήλ ''Samouḗl''; la, Samūēl is a figure who, in the narratives of the Hebrew Bible, plays a key role in the transition from the bibl ... 23:30 and References Hebrew Bible mountains {{Hebrew-Bible-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biblical Judges
The biblical judges ''šōp̄êṭ''/''shofet'', pl. ''šōp̄əṭîm''/''shoftim'') are described in the Hebrew Bible, and mostly in the Book of Judges, as people who served roles as military leaders in times of crisis, in the period before an Israelite monarchy was established. Role A cyclical pattern is regularly recounted in the Book of Judges to show the need for the various judges: apostasy of the Israelite people, hardship brought on as punishment from God, crying out to the Lord for rescue. The story of the judges seems to describe successive individuals, each from a different tribe of Israel, described as chosen by God to rescue the people from their enemies and establish justice. While ''judge'' is a literalistic translation of the Hebrew term used in the Masoretic text, the position as described is more one of unelected non-hereditary leadership than that of legal pronouncement. However, Cyrus H. Gordon argued that they may have come from among the hereditary lea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deborah
According to the Book of Judges, Deborah ( he, דְּבוֹרָה, ''Dəḇōrā'', " bee") was a prophetess of the God of the Israelites, the fourth Judge of pre-monarchic Israel and the only female judge mentioned in the Bible. Many scholars contend that the phrase, "a woman of Lappidot", as translated from biblical Hebrew in Judges 4:4 denotes her marital status as the wife of Lappidot.Van Wijk-Bos, Johanna WH. ''The End of the Beginning: Joshua and Judges''. Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2019. Alternatively, "lappid" translates as "torch" or "lightning", therefore the phrase, "woman of Lappidot" could be referencing Deborah as a "fiery woman." Deborah told Barak, an Israelite general from Kedesh in Naphtali, that God commanded him to lead an attack against the forces of Jabin king of Canaan and his military commander Sisera (Judges 4:6–7); the entire narrative is recounted in chapter 4. Judges chapter 5 gives the same story in poetic form. This passage, often called ''Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |