|
Muzo People
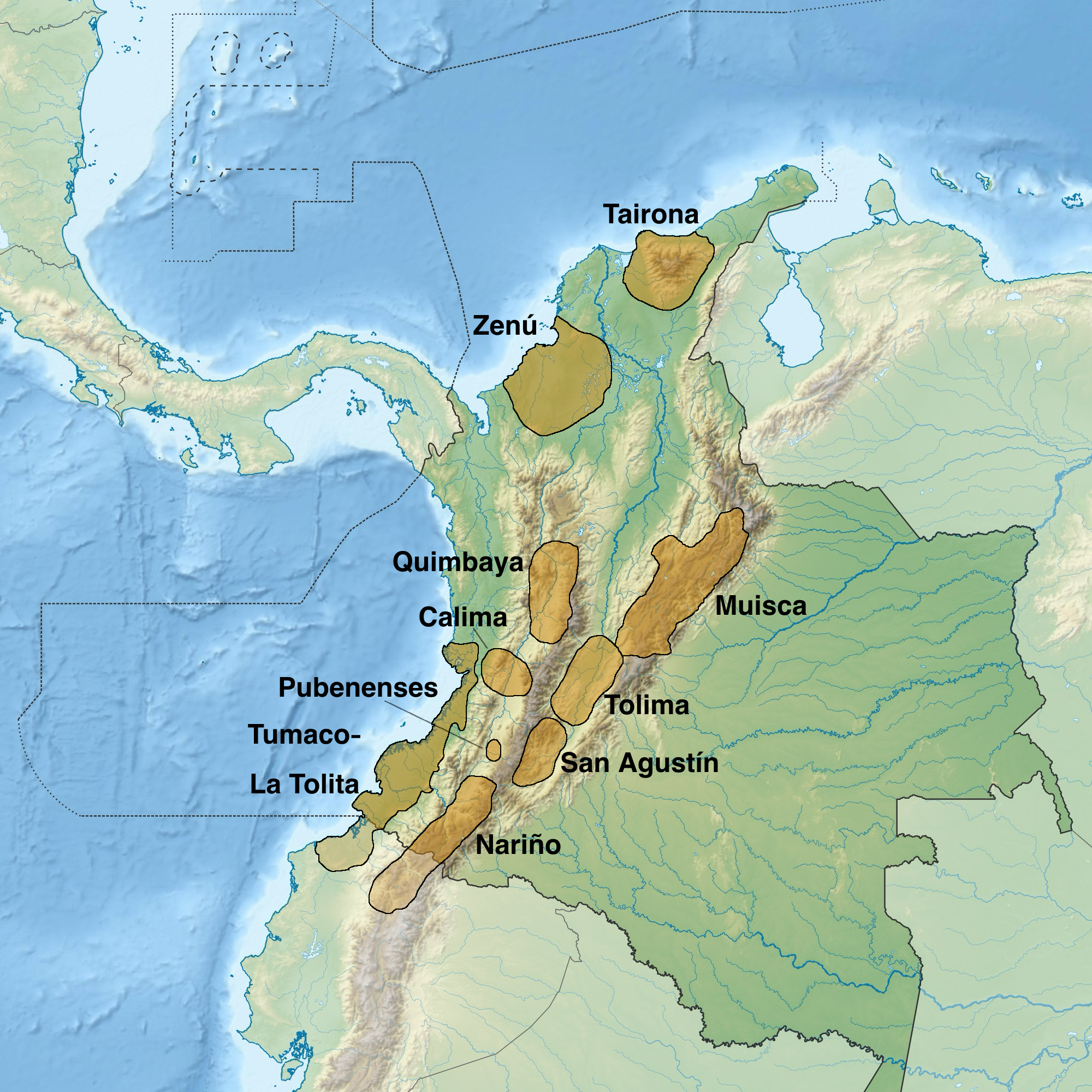
The Muzo people are a Cariban languages, Cariban-speaking Indigenous group who inhabited the western slopes of the eastern Colombian Andes. They were a highly war-like tribe who frequently clashed with their neighbouring Indigenous groups, especially the Muisca. The Muzo inhabited the right banks of the Magdalena River in the lower elevations of western Boyacá Department, Boyacá and Cundinamarca Department, Cundinamarca and were known as the Emerald People, thanks to their exploitation of the gemstone in Muzo. During the time of Spanish conquest of the Muisca, conquest, they resisted heavily against the Spanish invaders taking twenty years to submit the Muzo. Knowledge about the Muzo people has been provided by List of Muisca and pre-Muisca scholars, chroniclers Gonzalo Jiménez de Quesada, Pedro Simón, Juan de Castellanos, Lucas Fernández de Piedrahita and others. Muzo territory The Muzo were inhabiting the lower-elevation northwestern areas of the Cundinamarca departmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Muzo
Muzo () is a town and municipality in the Western Boyacá Province, part of the department of Boyacá, Colombia. It is widely known as the world capital of emeralds for the mines containing the world's highest quality gems of this type. Muzo is situated at a distance of from the departmental capital Tunja and from the capital of the Western Boyacá Province, Chiquinquirá. The urban centre is at an altitude of above sea level. Muzo borders Otanche and San Pablo de Borbur in the north, Maripí and Coper in the east, Quípama in the west and the department of Cundinamarca in the south. Etymology The town of Muzo was called Villa de la Santísima Trinidad de los Muzos, or simply Trinidad, when the Spanish conquistadors first founded the settlement in western Boyacá. Muzo is the autonym of the Muzo, the indigenous people who inhabited the region before the Spanish conquest. Climate The median temperature of Muzo is and the annual precipitation . History B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pedro Simón
''Fray'' Pedro Simón ( San Lorenzo de la Parrilla, Spain, 1574 - Ubaté, New Kingdom of Granada, ca. 1628) was a Spanish Franciscan friar, professor and chronicler of the indigenous peoples of modern-day Colombia and Venezuela, at the time forming the New Kingdom of Granada. Pedro Simón is one of the most important Muisca scholars whose writings were the basis for later scholars such as Lucas Fernández de Piedrahita, Alexander von Humboldt, and twenty first-century scholar Javier Ocampo López. Biography Pedro Simón studied in Cartagena, Spain and went to Cartagena de Indias in 1603.Biography Pedro Simón - Biografías y Vidas Simón accompanied Juan de Borja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Departments Of Colombia
Colombia is a unitary state, unitary republic made up of thirty-two administrative divisions referred to as departments (Spanish language, Spanish: ''departamentos'', sing. ) and one Capital District (''Capital districts and territories, Distrito Capital''). Departments are administrative division, country subdivisions and are granted a certain degree of autonomy. Each department has a governor (''gobernador'') and an Assembly (''Asamblea Departamental''), elected by popular vote for a four-year period. The governor cannot be re-elected in consecutive periods. Departments are formed by a grouping of municipalities of Colombia, municipalities (''municipios'', sing. ''municipio''). Municipal government is headed by mayor (''alcalde'') and administered by a municipal council (''concejo municipal''), both of which are elected by popular vote for four-year periods. Internal subdivisions within departments The current borders and number of the departments of Colombia was finally se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ermitaño River
Chavacano or Chabacano () is a group of Spanish-based creole language varieties spoken in the Philippines. The variety spoken in Zamboanga City, located in the southern Philippine island group of Mindanao, has the highest concentration of speakers. Other currently existing varieties are found in Cavite City and Ternate, located in the Cavite province on the island of Luzon. Chavacano is the only Spanish-based creole in Asia. The 2020 Census of Population and Housing counted 106,000 households generally speaking Chavacano. The one responsible for this Spanish creole was Don Sebastian Hurtado de Corcuera, then governor of Panama, who was also responsible for settling Zamboanga City by employing Peruvian soldiers and colonists. There was an Asian-American route, which led to traders and adventurers carrying silver from Peru through Panama to reach Acapulco, Mexico before sailing to Manila, Philippines using the famed Manila galleons. The different varieties of Chavacano differ in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Suárez River
The Suárez River, originally Saravita, is a river in the Cordillera Oriental (Colombia), Eastern Ranges of the Colombian Andes. The river originates in Lake Fúquene on the border of Cundinamarca Department, Cundinamarca and Boyacá Department, Boyacá and its mouth is the confluence with the Chicamocha River, forming the Sogamoso River in Santander Department, Santander. It is part of the Magdalena River, Magdalena Basin flowing towards the Caribbean Sea. The long river is one of the longest on the Altiplano Cundiboyacense and forms the natural borders of Cundinamarca and Boyacá and Boyacá and Santander in its upstream and downstream part respectively. The river formed the trajectory for the Spanish conquest of the Muisca, when the conquistadors went uphill into the Andes from the tropical lowlands of Barrancabermeja in the north. The difference in altitude along the river course, from at the source to at its mouth, in its large basin causes climatic variations, especially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sogamoso River
{{Colombia-river-stub ...
Sogamoso River () is a river of northern Colombia. It flows into the Magdalena River and on to the Caribbean Sea. The Sogamoso Dam on the river near Bucaramanga was completed in 2014. Course The Sogamoso River is a river in northern Colombia, which is formed by the confluence of the Suárez River and the Chicamocha River after crossing the Chicamocha Canyon, and flows into the Magdalena River between Puerto Wilches and Barrancabermeja, and this in turn empties into the Caribbean Sea. See also * List of rivers of Colombia References Further reading * Rivers of Colombia Magdalena River Rivers A river is a natural stream of fresh water that flows on land or inside caves towards another body of water at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, lake, or another river. A river may run dry before reaching the end of its course if it ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Santander Department
Santander () is a department of Colombia. Santander inherited the name of one of the nine original states of the United States of Colombia. It is located in the central northern part of the country, borders the Magdalena River to the east, Boyacá to the south and southeast, the Norte de Santander Department to the northeast, the Cesar Department to the north, the Bolivar and Antioquia Departments to the west. Its capital is the city of Bucaramanga. History Pre-Columbian era Prior to the arrival of the Spaniards, the territory now known as Santander was inhabited by Amerindian ethnic groups: Muisca, Chitareros, Laches, Yariguí, Opón, Carare and Guanes. Their political and social structure was based on ''cacicazgos'', a federation of tribes led by a ''cacique'', with different social classes. Their main activity was planting maize, beans, yuca, arracacha, cotton, agave, tobacco, tomato, pineapple and guava, among others. Their agricultural skills were suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Carare River
Carare River is a river of northern Colombia. It flows into the Caribbean Sea. See also *List of rivers of Colombia Atlantic Ocean Amazon River Basin * Amazon River ** Guainía River or Negro River *** Vaupés River or Uaupés River **** Papuri River **** Querary River *** Isana River or Içana River **** Cuiari River *** Aquio River ** Caquetá Ri ... References *Rand McNally, The New International Atlas, 1993. Rivers of Colombia Magdalena River {{Colombia-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saboyá
Saboyá is a town and municipality in the Western Boyacá Province, part of the Colombian department of Boyacá. Etymology Saboyá is an Italian name brought by European colonizers. - conceptosdelahistoria.com History Before the on the central highlands of the Colombian , Saboyá was ruled by a '''' with the same name. The first |
Colima People
Colima, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Colima, is among the 31 states that make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It shares its name with its capital and main city, Colima. Colima is a small state of western Mexico on the central Pacific coast, and includes the four oceanic Revillagigedo Islands. Mainland Colima shares borders with the states of Jalisco and Michoacán. In addition to the capital city of Colima, the main cities are Manzanillo, Villa de Alvarez and Tecomán. Colima is the fourth smallest state in Mexico and has the smallest population, but has one of Mexico's highest standards of living and the lowest unemployment. It is also the state with the highest murder rate per capita and one of the highest crime rates, due to its ports being a contested area for cartels. Geography The state covers a territory of 5,455 km2 and is the fourth smallest federal entity after Tlaxcala, Morelos and the Federal District of Mexico City, containing only 0. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Altiplano Cundiboyacense
The Altiplano Cundiboyacense () is a high plateau located in the Eastern Cordillera of the Colombian Andes covering parts of the departments of Cundinamarca and Boyacá. (Do not confuse with The Altiplano or the Altiplano Nariñense, both further south.) The altiplano corresponds to the ancient territory of the Muisca. The Altiplano Cundiboyacense comprises three distinctive flat regions; the Bogotá savanna, the valleys of Ubaté and Chiquinquirá, and the valleys of Duitama and Sogamoso. The average altitude of the altiplano is about above sea level but ranges from roughly to . Etymology ''Altiplano'' in Spanish means "high plain" or "high plateau", the second part is a combination of the departments Cundinamarca and Boyacá. Geography The limits of the Altiplano are not strictly defined. The high plateau is enclosed by the higher mountains of the Eastern Ranges, with the Sumapaz mountains in the south and Chingaza to the east. The Tenza Valley is locate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |