|
Mus'ab Ibn 'Umair
Muṣʿab ibn ʿUmayr () also known as Muṣʿab al-Khayr ("the Good") was a ''sahabi'' (companion) of Muhammad. From the Banū ʿAbd al-Dār branch of the Quraysh, he embraced Islam in 614 CE and was the first ambassador of Islam. He died in the Battle of Uhud in 625 CE. Early life Mus‘ab ibn Umair was born to the Banu Abd al-Dar branch of the Quraysh tribe. His exact birth year is not known; it is believed that he was born sometime between 594 and 598 CE since he was very young when he embraced Islam in 614. Mus‘ab was the son of Umayr ibn Hashim and Khunas bint Malik, and his parents were wealthy. Even as a young man, he was permitted to attend meetings of the Quraysh elders. Conversion to Islam The first Muslims used to meet with Muhammad at the house of Al-Arqam known as the Islamic Learning Center. Mus'ab became interested and went to this house to find out more about Islam. As a result of hearing the reciting of the Qur'an and the preaching of Muhammad, he con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above sea level. Its metropolitan population in 2022 was 2.4million, making it the List of cities in Saudi Arabia by population, third-most populated city in Saudi Arabia after Riyadh and Jeddah. Around 44.5% of the population are Saudis, Saudi citizens and around 55.5% are Muslim world, Muslim foreigners from other countries. Pilgrims more than triple the population number every year during the Pilgrimage#Islam, pilgrimage, observed in the twelfth Islamic calendar, Hijri month of . With over 10.8 million international visitors in 2023, Mecca was one of the ten List of cities by international visitors, most visited cities in the world. Mecca is generally considered "the fountainhead and cradle of Islam". Mecca is revered in Islam as the birthp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hijra (Islam)
The Hijrah, () also Hegira (from Medieval Latin), was the journey the prophets and messengers in Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad and his followers took from Mecca to Medina. The year in which the Hijrah took place is also identified as the epoch of the Islamic calendar, Lunar Hijri and Solar Hijri calendar, Solar Hijri calendars; its date equates to 16 July 622 in the Julian calendar. Early in Muhammad's preaching of Islam, his followers only included his close friends and relatives. Most of his tribesmen, the Quraysh, however, were indifferent to his activities, as they did not appear to be particularly interested in devotional meetings, and accordingly, Muhammad did not encounter any serious opposition from them; that was the case until he began to challenge their beliefs, which caused tensions to arise. In May 622, after having convened twice with members of the Medinan tribes of Banu Aws, Aws and Khazraj at al-'Aqabah near Mina, Saudi Arabia, Mina, Muhammad secretly left ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walid Ibn Utba
Al-Walīd ibn ʿUtba ibn Abī Sufyān () (died 684) was an Umayyad ruling family member and statesman during the reigns of the Umayyad caliphs Mu'awiya I () and Yazid I (). He served two stints as the governor of Medina in 677/78–680 and 681–682. He was dismissed during his first term for failing to secure oaths of allegiance from Husayn ibn Ali and other senior Muslim figures who opposed Yazid's accession. After his relocation to Damascus during the Second Fitna, he was imprisoned in 684 for proclaiming his support for continued Umayyad rule and condemning the anti-Umayyad caliph Abd Allah ibn al-Zubayr. He was freed shortly after by his kinsman Khalid ibn Yazid and the pro-Umayyad Banu Kalb tribe. Life Al-Walid belonged to the Umayyad clan and was a son of Utba ibn Abi Sufyan and thus a paternal nephew of Caliph Mu'awiya I (), founder of the Umayyad Caliphate centered in Syria.Howard 1990, p. 2, note 8. He may have led the annual Hajj pilgrimage to Mecca in October 676. Acc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amr Ibn Hishām
Amr ibn Hisham (), better known as Abū Jahl (; ) was the Meccan Quraysh polytheist leader of the Mushrikites known for his opposition to the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was the most prominent flag-bearer of opposition towards Islam. A prominent head of the Makhzum clan, Amr was known as ''Abu al-Hakam'' ('Father of Wisdom') among pre-Islamic Arabs. After Muhammad started preaching monotheism, Amr opposed him and often physically attacked early Muslims. He persecuted many Muslim converts, including Sumayya, and Yasir ibn Amir. His cruel torture methods towards Muslims made Muhammad give him the title ''Abu Jahl'' ('Father of Ignorance') and ''Firawn al-Umma'' ('Pharaoh of the Nation'). Following the migration to Medina, Amr gathered a large army of polytheists to attack Medina and kill Muslims. On 13 March 624, the Battle of Badr took place, in which Amr was a major leader. In the battle, Amr was fatally wounded by Mu'awwidh ibn Amr and Mu'ādh ibn 'Amr and eventually kille ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
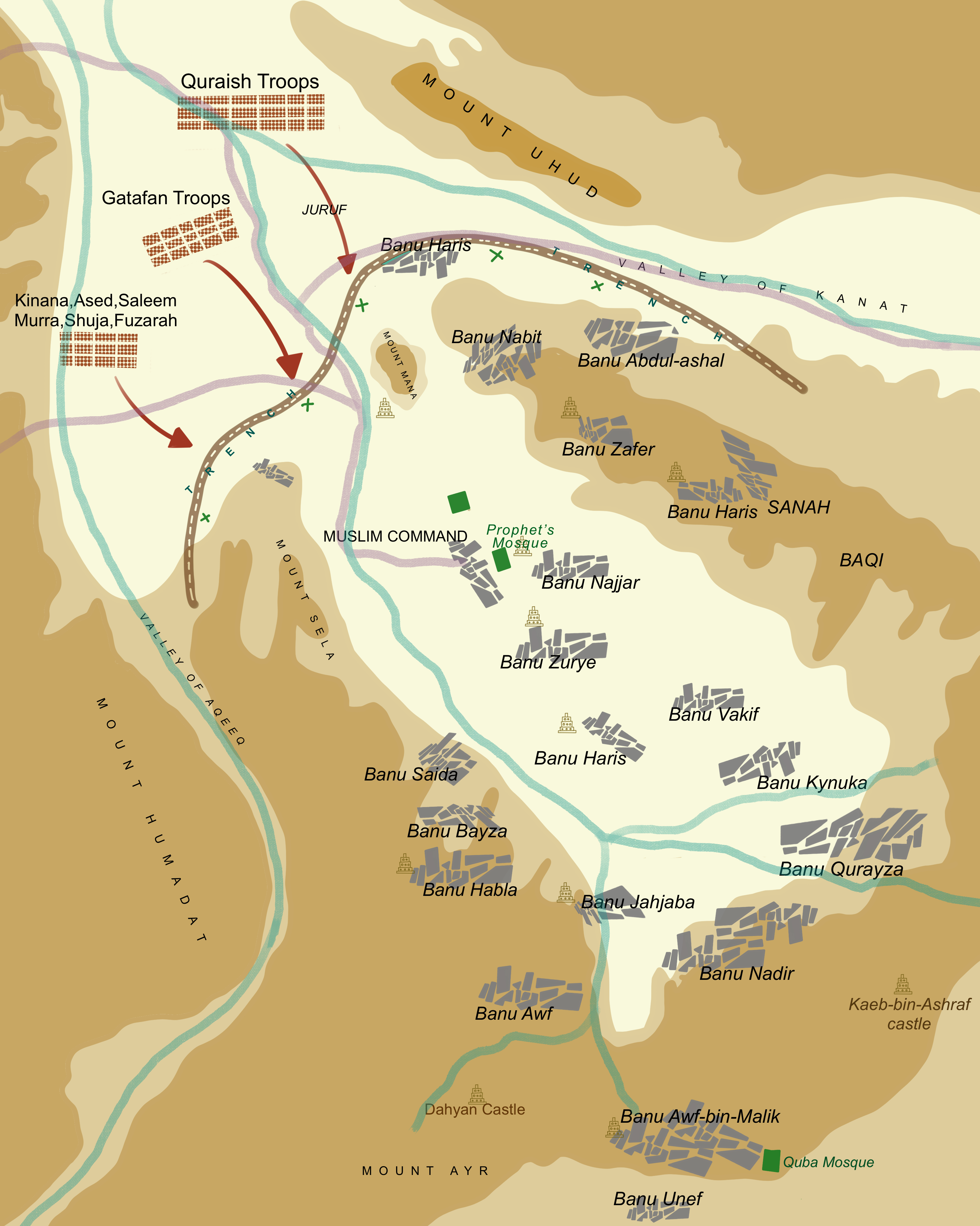
Salman The Persian
Salman Farsi (; ) was a Persian religious scholar and one of the companions of Muhammad. As a practicing Zoroastrian, he dedicated much of his early life to studying to become a magus, after which he began travelling extensively throughout Western Asia to engage in constructive dialogue with non-Zoroastrian groups. His quests eventually prompted his conversion to Christianity and later his conversion to Islam, which occurred after he met and befriended Muhammad in the city of Yathrib. He was a prominent non-Arab companion and one of Muhammad's closest friends; Muhammad had once stated to a gathering of his followers that he regarded Salman as a part of his family. In meetings with the other companions, he was often referred to by the . Prior to the Battle of the Trench in 627, Salman suggested to Muhammad and the other early Muslims that a large trench be dug around Yathrib (citing a technique commonly used by the Sasanian army) in order to help defend against the Quraysh, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ruqayyah Bint Muhammad
Ruqayya bint Muhammad (; –March 624) was the second eldest daughter of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and Khadija. She married the third caliph Uthman and the couple had a son Abd Allah. In 624, Ruqayya died from an illness. Early life Born in Mecca around 601 or 602 CE, Ruqayya was the 3rd child and the second daughter of Muhammad and Khadija, his first wife, who was also a successful merchant. Marital life Marriage with Utbah She was married before August 610 to Utbah ibn Abi Lahab, but the marriage was never consummated.Ibn Ishaq/Guillaume p. 314. Ruqayya became a Muslim when her mother did. When Muhammad began to preach openly in 613, the Quraysh reminded Muhammad that they had "relieved him of his care for his daughters" and decided to return them so that he would have to support them at his own expense. They told Utbah that they would give him "the daughter of Aban ibn Sa'id ibn Al-As or the daughter of Sa'id ibn Al-As" if he divorced Ruqayya. After Muhammad warne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uthman
Uthman ibn Affan (17 June 656) was the third caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruling from 644 until his assassination in 656. Uthman, a second cousin, son-in-law, and notable companion of the Islamic Prophet Muhammad, played a major role in early Islamic history. During his reign as caliph, he was known for ordering the official compilation of the standardized version of the Quran, known as Uthman's Quran, that is still being used today. Before his predecessor, Caliph Umar (), died in office, he appointed a committee of trustees to elect a successor. Uthman, who was then aged 68–71 years, was elected to succeed him and became the oldest person to hold such a high position. During his premiership, the Caliphate expanded further into Persia in 650 and reached as far as the provinces of Khorasan in 651. Uthman instituted centralized reforms in order to create a more cohesive administrative structure and fostered rapid economic growth. However, the last years of his re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Dharr Al-Ghifari
Abu Dharr Al-Ghifari Al-Kinani (, '), also spelled Abu Tharr or Abu Zar, born Jundab ibn Junādah (), was the fourth or fifth person converting to Islam, and a member of the Muhajirun. He belonged to the Banu Ghifar, the Kinanah tribe. His date of birth is unknown. He died in 652 CE, at Al-Rabadha, in the desert east of Medina. Abu Dharr is remembered for his strict piety and also his opposition to Muawiyah during the caliphate of Uthman ibn Affan. He is venerated by Shia Muslims as one of The Four Companions, early Muslims who were followers (Shia) of Ali ibn Abi Talib. He was regarded by many, including Ali Shariati, Muhammad Sharqawi and Sami Ayad Hanna, as a principal antecedent of Islamic socialism, or the first Islamic socialist. He protested against the accumulation of wealth by the ruling class during 'Uthmān's caliphate and urged the equitable redistribution of wealth. Early life Little is known of his life before his conversion to Islam. Abu Dharr is said to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammar Ibn Yasir
Ammar ibn Yasir (; July 657 C.E.) was a ''Sahabi'' (Companion) of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and a commander in the early Muslim conquests. His parents, Sumayya and Yasir ibn Amir, were the first martyrs of the Ummah. Ammar converted to Islam by the invitation of Abu Bakr and was amongst the . After the migration to Medina, he participated in building the Prophet's Mosque and fought in most of the early Muslim expeditions. He fought in the Ridda wars under Caliph Abu Bakr () and in the Muslim conquest of Iran under Caliph Umar (). Ammar served as governor of Kufa under Umar. Following Uthman's assassination, Ammar became a devout partisan of Caliph Ali () and died while fighting on Ali's side in the Battle of Siffin. Before Islam Ammar belonged to the Malik clan of the Madhhij tribe in Yemen. Hijaz (current-day Saudi Arabia). He was born in or around the Year of the Elephant, which was the same year as Muhammad's birth, in Mecca, and was one of the intermediaries i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zubair Ibn Al-Awam
Al-Zubayr ibn al-Awwam ibn Khuwaylid al-Asadi (; ) was an Arab Muslim commander in the service of the Islamic prophet Muhammad and the caliphs Abu Bakr () and Umar () who played a leading role in the Ridda wars against rebel tribes in Arabia in 632–633 and later participated in early Muslim conquests of Sasanid Persia in 633–634, Byzantine Syria in 634–638, and the Exarchate of Africa in 639–643. An early convert to Islam, Zubayr was a commander in the Battle of Badr in 624, in which the latter was instrumental in defeating the opponent forces of the Quraysh. He participated in almost all of the early Muslim battles and expeditions under Muhammad. In the Battle of the Trench, due to his military service, Muhammad bestowed the title ''Hawari Rasul Allah'' ('Disciple of Messenger of God') upon him. After Muhammad's demise, Zubayr was appointed as a commander, in the Ridda Wars, by caliph Abu Bakr. He was involved in the defense of Medina and Battle of Yamama. During Umar's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamza Ibn Abd Al-Muttalib
Ḥamza ibn ʿAbd al-Muṭṭalib ibn Hāshim ibn ʿAbd Manāf al-Qurashī (; )Muhammad ibn Saad. ''Kitab al-Tabaqat al-Kabir'' vol. 3. Translated by Bewley, A. (2013). ''The Companions of Badr''. London: Ta-Ha Publishers. was a foster brother, paternal uncle, maternal second-cousin, and companion of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He was martyred in the Battle of Uhud on 23 March 625 (7 Shawwal 3 hijri). His '' kunyas'' were "Abū ʿUmāra" () and "Abū Yaʿlā" (). He had the by-names '' Asad Allāh'' (, "Lion of God") and '' " Asad of His Messenger''" , and Muhammad gave him the posthumous title ''Sayyid al- Shuhadāʾ'' (, "Master of Martyrs"). Early life Ibn Sa'd basing his claim on al-Waqidi states that Hamza was reportedly four years older than Muhammad. He could also be two years older as said in other hadith. This is disputed by Ibn Sayyid, who said: " Zubayr narrated that Hamza was four years older than the Prophet. Ibn Hajar wrote of Ibn Sayyid's hadiths: "Hamza w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansar (Islam)
The Ansar (), also spelled Ansaar or Ansari, were the local inhabitants of Medina (mostly Muslims) who supported the Islamic prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad, and his followers (the ''Muhajirun''), when they fled from Mecca to Medina during the ''hijrah''. The Ansar belonged to the Arabian tribes of Banu Khazraj and Banu Aws. Background The Medinese, which consisted of Banu Aws and Banu Khazraj, along with their Jewish tribes of Arabia, Arabian Jewish allies (Banu Nadir, Banu Qurayza, and Banu Qaynuqa), were involved in degenerating years of warfare such as battle of Sumair, battle of Banu Jahjaha of Aus-Banu Mazin of Khazraj, battle of Sararah day, battle of Banu Wa'il ibn Zayd, battle of Zhufr-Malik, battle of Fari', battle of Hathib, battle of Rabi' day, first battle of Fijar in Yathrib (not Harb al-fijar, Fijar war between Qays with Kinana in Mecca), battle of Ma'is, battle of Mudharras, and second battle of Fijar in Yathrib. The Medinese also even contacted against fore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |