|
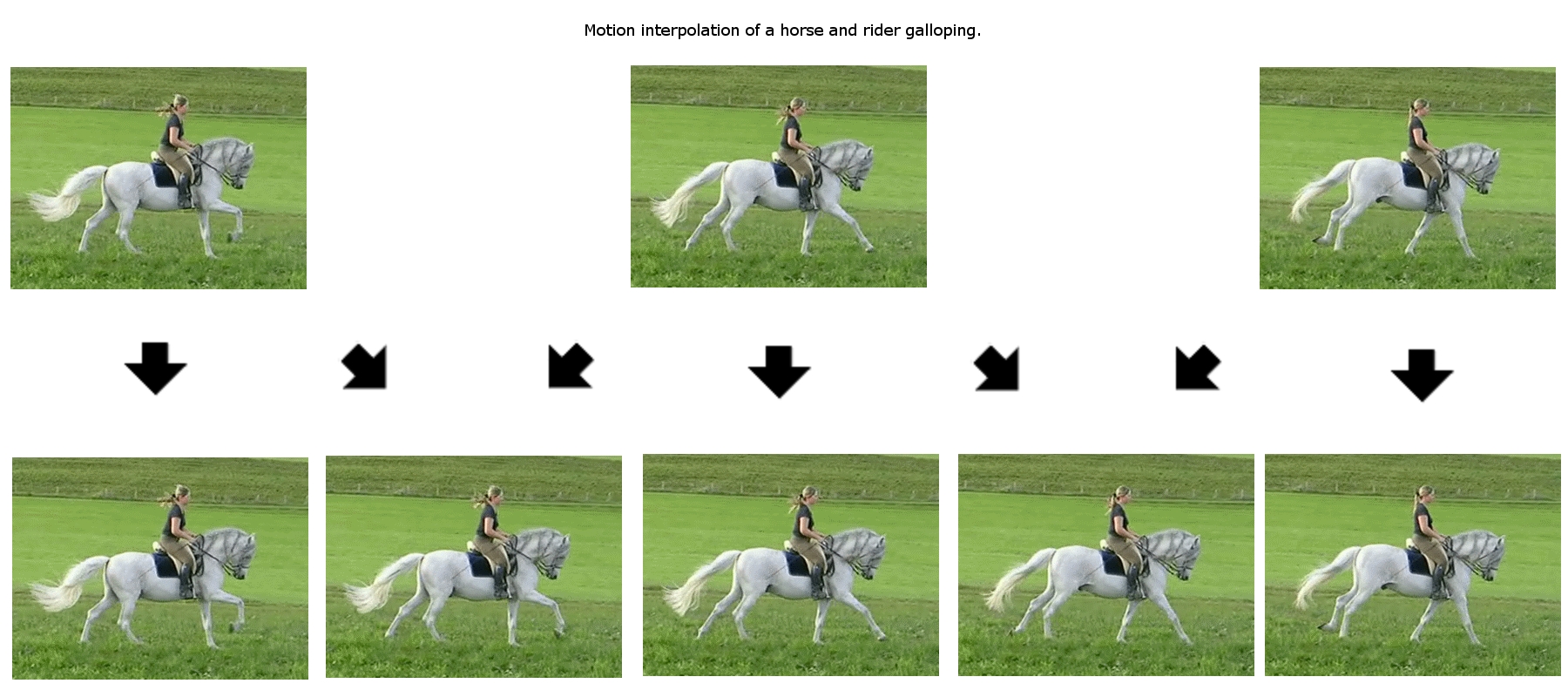
Motion Vector
In computer vision and image processing, motion estimation is the process of determining ''motion vectors'' that describe the transformation from one 2D image to another; usually from adjacent frames in a video sequence. It is an ill-posed problem as the motion happens in three dimensions (3D) but the images are a projection of the 3D scene onto a 2D plane. The motion vectors may relate to the whole image (''global motion estimation'') or specific parts, such as rectangular blocks, arbitrary shaped patches or even per pixel. The motion vectors may be represented by a translational model or many other models that can approximate the motion of a real video camera, such as rotation and translation in all three dimensions and zoom. Related terms More often than not, the term motion estimation and the term ''optical flow'' are used interchangeably. It is also related in concept to ''image registration'' and ''stereo correspondence''. In fact all of these terms refer to the process of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affine Motion Estimation
Affine may describe any of various topics concerned with connections or affinities. It may refer to: * Affine, a relative by marriage in law and anthropology * Affine cipher, a special case of the more general substitution cipher * Affine combination, a certain kind of constrained linear combination * Affine connection, a connection on the tangent bundle of a differentiable manifold * Affine Coordinate System, a coordinate system that can be viewed as a Cartesian coordinate system where the axes have been placed so that they are not necessarily orthogonal to each other. See tensor. * Affine differential geometry, a geometry that studies differential invariants under the action of the special affine group * Affine gap penalty, the most widely used scoring function used for sequence alignment, especially in bioinformatics * Affine geometry, a geometry characterized by parallel lines * Affine group, the group of all invertible affine transformations from any affine space over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vision Processing Unit
A vision processing unit (VPU) is (as of 2023) an emerging class of microprocessor; it is a specific type of AI accelerator, designed to accelerate machine vision tasks. Overview Vision processing units are distinct from graphics processing units (which are specialised for video encoding and decoding) in their suitability for running machine vision algorithms such as CNN (convolutional neural networks), SIFT (scale-invariant feature transform) and similar. They may include direct interfaces to take data from cameras (bypassing any off chip buffers), and have a greater emphasis on on-chip dataflow between many parallel execution units with scratchpad memory, like a manycore DSP. But, like video processing units, they may have a focus on low precision fixed point arithmetic for image processing. Contrast with GPUs They are distinct from GPUs, which contain specialised hardware for rasterization and texture mapping (for 3D graphics), and whose memory architecture is o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics Processing Unit
A graphics processing unit (GPU) is a specialized electronic circuit designed for digital image processing and to accelerate computer graphics, being present either as a discrete video card or embedded on motherboards, mobile phones, personal computers, workstations, and game consoles. GPUs were later found to be useful for non-graphic calculations involving embarrassingly parallel problems due to their parallel structure. The ability of GPUs to rapidly perform vast numbers of calculations has led to their adoption in diverse fields including artificial intelligence (AI) where they excel at handling data-intensive and computationally demanding tasks. Other non-graphical uses include the training of neural networks and cryptocurrency mining. History 1970s Arcade system boards have used specialized graphics circuits since the 1970s. In early video game hardware, RAM for frame buffers was expensive, so video chips composited data together as the display was being scann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moving Object Detection
Moving object detection is a technique used in computer vision and image processing. Multiple consecutive frames from a video are compared by various methods to determine if any moving object is detected. Moving objects detection has been used for wide range of applications like video surveillance, activity recognition, road condition monitoring, airport safety, monitoring of protection along marine border, etc. Definition Moving object detection is to recognize the physical movement of an object in a given place or region. J. S. Kulchandani and K. J. Dangarwala, "Moving object detection: Review of recent research trends," 2015 International Conference on Pervasive Computing (ICPC), Pune, 2015, pp. 1-5. doi: 10.1109/PERVASIVE.2015.7087138. By acting [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Cremers
Daniel Cremers (born 1971) is a German computer scientist, Professor of Informatics and Mathematics and Chair of Computer Vision & Artificial Intelligence at the Technische Universität München. His research foci are computer vision, mathematical image, partial differential equations, convex and combinatorial optimization, machine learning and statistical inference. Career Cremers received a bachelor's degree in mathematics (1994) and Physics (1994), and later a master's degree in Theoretical Physics (1997) from the University of Heidelberg. He obtained a PhD in Computer Science from the University of Mannheim in 2002. He was a postdoctoral researcher at UCLA. He was associate professor at the University of Bonn from 2005 until 2009. He received a Starting Grant (2009), a Consolidator Grant (2015) and an Advanced Grant (2020) by the European Research Council The European Research Council (ERC) is a public body for funding of scientific and technological research conducted w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simultaneous Localization And Mapping
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is the computational problem of constructing or updating a map of an unknown environment while simultaneously keeping track of an Intelligent agent, agent's location within it. While this initially appears to be a chicken or the egg problem, there are several algorithms known to solve it in, at least approximately, tractable time for certain environments. Popular approximate solution methods include the particle filter, extended Kalman filter, covariance intersection, and GraphSLAM. SLAM algorithms are based on concepts in computational geometry and computer vision, and are used in robot navigation, robotic mapping and odometry for virtual reality or augmented reality. SLAM algorithms are tailored to the available resources and are not aimed at perfection but at operational compliance. Published approaches are employed in self-driving cars, unmanned aerial vehicles, autonomous underwater vehicles, Rover (space exploration), planetary r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
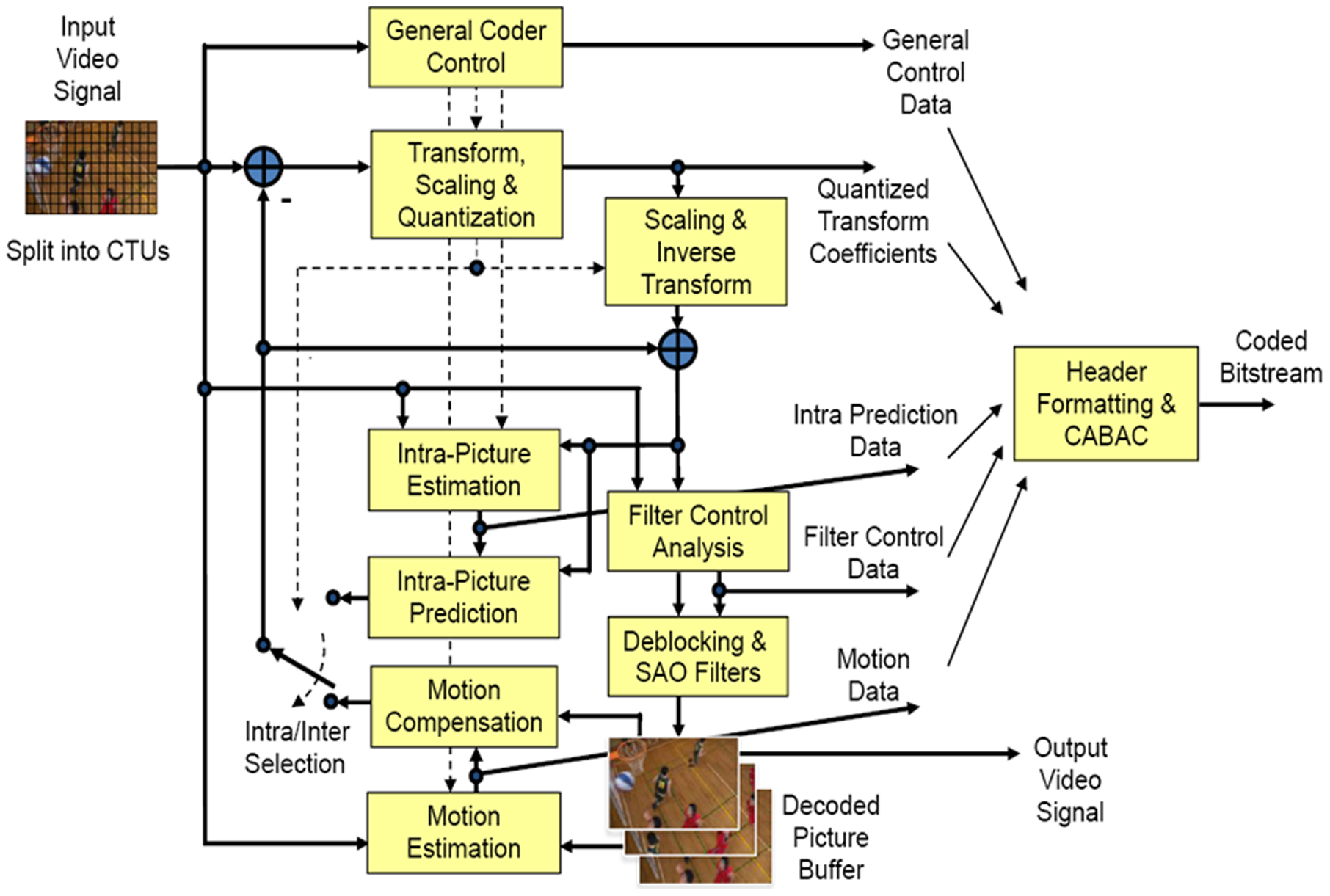
HEVC
High Efficiency Video Coding (HEVC), also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2, is a video compression standard designed as part of the MPEG-H project as a successor to the widely used Advanced Video Coding (AVC, H.264, or MPEG-4 Part 10). In comparison to AVC, HEVC offers from 25% to 50% better data compression at the same level of video quality, or substantially improved video quality at the same bit rate. It supports resolutions up to 8192×4320, including 8K UHD, and unlike the primarily 8-bit AVC, HEVC's higher fidelity Main 10 profile has been incorporated into nearly all supporting hardware. While AVC uses the integer discrete cosine transform (DCT) with 4×4 and 8×8 block sizes, HEVC uses both integer DCT and discrete sine transform (DST) with varied block sizes between 4×4 and 32×32. The High Efficiency Image Format (HEIF) is based on HEVC. Concept In most ways, HEVC is an extension of the concepts in H.264/MPEG-4 AVC. Both work by comparing different parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPEG
The Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) is an alliance of working groups established jointly by International Organization for Standardization, ISO and International Electrotechnical Commission, IEC that sets standards for media coding, including compression coding of audio compression (data), audio, video compression, video, graphics, and Compression of Genomic Sequencing Data, genomic data; and transmission and Container format (digital), file formats for various applications.John Watkinson, ''The MPEG Handbook'', p. 1 Together with Joint Photographic Experts Group, JPEG, MPEG is organized under ISO/IEC JTC 1/ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 29, SC 29 – ''Coding of audio, picture, multimedia and hypermedia information'' (ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1, Subcommittee 29). MPEG formats are used in various multimedia systems. The most well known older MPEG media formats typically use MPEG-1, MPEG-2, and MPEG-4 AVC media coding and MPEG-2 systems MPEG transport stream, transport streams an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression reduces bits by identifying and eliminating Redundancy (information theory), statistical redundancy. No information is lost in lossless compression. Lossy compression reduces bits by removing unnecessary or less important information. Typically, a device that performs data compression is referred to as an encoder, and one that performs the reversal of the process (decompression) as a decoder. The process of reducing the size of a data file is often referred to as data compression. In the context of data transmission, it is called source coding: encoding is done at the source of the data before it is stored or transmitted. Source coding should not be confused with channel coding, for error detection and correction or line coding, the means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taylor & Francis
Taylor & Francis Group is an international company originating in the United Kingdom that publishes books and academic journals. Its parts include Taylor & Francis, CRC Press, Routledge, F1000 (publisher), F1000 Research and Dovepress. It is a division of Informa, a United Kingdom-based publisher and conference company. Overview Founding The company was founded in 1852 when William Francis (chemist), William Francis joined Richard Taylor (editor), Richard Taylor in his publishing business. Taylor had founded his company in 1798. Their subjects covered agriculture, chemistry, education, engineering, geography, law, mathematics, medicine, and social sciences. Publications included the ''Philosophical Magazine''. Francis's son, Richard Taunton Francis (1883–1930), was sole partner in the firm from 1917 to 1930. Acquisitions and mergers In 1965, Taylor & Francis launched Wykeham Publications and began book publishing. T&F acquired Hemisphere Publishing in 1988, and the compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Coding Standards
A video coding format (or sometimes video compression format) is a content representation format of digital video content, such as in a data file or bitstream. It typically uses a standardized video compression algorithm, most commonly based on discrete cosine transform (DCT) coding and motion compensation. A computer software or hardware component that compresses or decompresses a specific video coding format is a video codec. Some video coding formats are documented by a detailed technical specification document known as a video coding specification. Some such specifications are written and approved by standardization organizations as technical standards, and are thus known as a video coding standard. There are ''de facto'' standards and formal standards. Video content encoded using a particular video coding format is normally bundled with an audio stream (encoded using an audio coding format) inside a multimedia container format such as AVI, MP4, FLV, RealMedia, or M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |