|
Monastery Of San Nicolò Al Lido
San Nicolò al Lido refers to both the San Nicolò Church (Italian language, Italian: ''Chiesa / Parrocchia di San Nicolò - San Nicoletto'') and most importantly to its annexed Monastery of San Nicolò (Italian language, Italian: ''Abbazia di San Nicolò'') located in Venice, northern Italy. The two Catholic Church, Catholic institutions are located in the northern part of the Lido di Venezia and house the relics of Saint Nicholas, patron of sailors (shared with Bari). From this church, the traditional thanksgiving Mass of the ''Sposalizio del Mare'' ("Marriage of the Sea") is celebrated. The complex houses monks of the Franciscan order. History The convent and the church date to the origins of Venice in the early Middle Ages, founded, according to a legend, by the family. The site stood at a strategic point for the nascent Republic of Venice, Venetian power: at the main access to the sea. From here, in 996 and 998, sailed off the first Venetian expeditions against the Naren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lido Di Venezia
The Lido, or Venice Lido (), is an barrier island in the Venetian Lagoon, Northern Italy; it is home to about 20,400 residents. The Venice Film Festival takes place at the Lido in late August/early September. Geography The Lido island is one of the two barrier islands of the Lagoon of Venice; the other is Pellestrina. They form the central part of the coastline of the lagoon on the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula of Cavallino/Punta Sabbioni forms the northern part and the peninsula of Sottomarina forms the southern part. The sea has access to the lagoon through three inlets between the islands and between the islands and the peninsulas. At the northern end of Lido there is the Lido inlet which separates it from Cavallino/Punta Sabbioni and at the southern end there is the Malamocco inlet which separates it from Pellestrina. These two inlets have been dredged to a greater depth to allow big ships through. The Malamocco inlet is the deepest one and is used by container ships an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pietro Orseolo II
Pietro II Orseolo (961−1009) was the Doge of Venice from 991 to 1009, and a member of the House of Orseolo. He began the period of eastern expansion of Venice that lasted for the better part of 500 years. He secured his influence in the Dalmatian Romanized settlements from the Croats and Narentines, freed Venice from a 50-year-old taxation to the latter, and started Venice's expansions by conquering the islands of Lastovo (Lagosta) and Korčula (Curzola) and acquiring Dubrovnik (Ragusa). Reign Relations with Byzantium In 992 Pietro II Orseolo concluded a treaty with the Byzantine emperor Basil II to transport Byzantine troops in exchange for commercial privileges in Constantinople.J. Norwich, ''Byzantium: The Apogee'', 257 Following repeated complaints by the Dalmatian city-states in 997, the Venetian fleet under Orseolo attacked the Neretvian pirates of Neretva (Narentines) on Ascension Day in 998. Pietro then took the title of ''Dux Dalmatianorum'' (Duke of the Dalmatians) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghibelline
The Guelphs and Ghibellines ( , ; ) were factions supporting the Pope (Guelphs) and the Holy Roman Emperor (Ghibellines) in the Italian city-states of Central Italy and Northern Italy during the Middle Ages. During the 12th and 13th centuries, rivalry between these two parties dominated political life across medieval Italy. The struggle for power between the Papacy and the Holy Roman Empire arose with the Investiture Controversy, which began in 1075 and ended with the Concordat of Worms in 1122. History Origins The conflict between Guelphs and Ghibellines arose from the political divisions caused by the Investiture Controversy, about whether secular rulers or the pope had the authority to appoint bishops and abbots. Upon the death of Emperor Henry V, of the Salian dynasty, the dukes elected an opponent of his dynasty, Lothair III, as the new emperor. This displeased the house of Hohenstaufen, who were allied with and related to the old dynasty. Out of fear of the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid Sultanate. However, a sequence of economic and political events culminated in the Crusader army's 1202 siege of Zara and the 1204 sack of Constantinople, rather than the conquest of Egypt as originally planned. This led to the Partitio terrarum imperii Romaniae or the partition of the Byzantine Empire by the Crusaders and their Venetian allies leading to a period known as Frankokratia, or "Rule of the Franks" in Greek. In 1201, the Republic of Venice contracted with the Crusader leaders to build a dedicated fleet to transport their invasion force. However, the leaders greatly overestimated the number of soldiers who would embark from Venice, since many sailed from other ports, and the army that appeared could not pay the contracted price. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
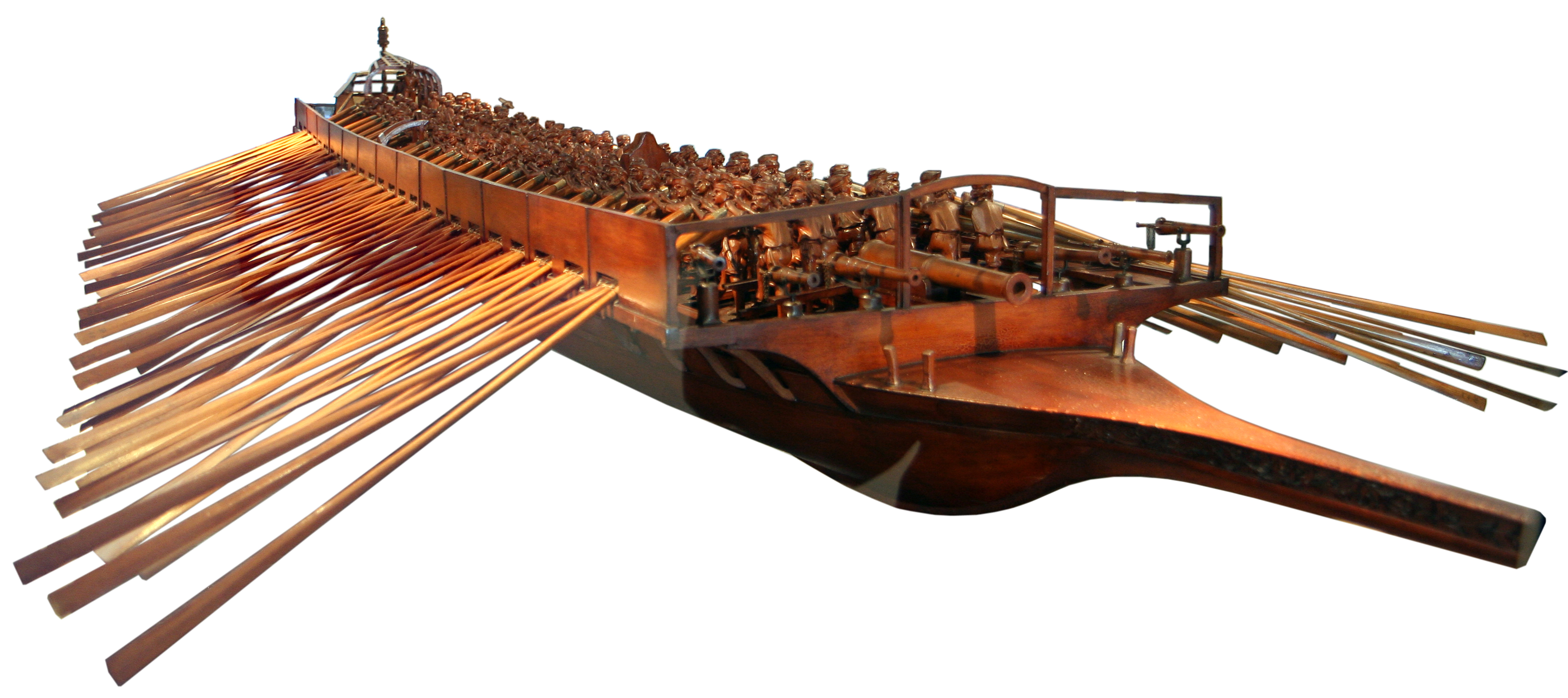
Venetian Fleet
The Venetian navy () was the navy of the Venetian Republic which played an important role in the history of the republic and the Mediterranean world. It was the premier navy in the Mediterranean Sea for many centuries between the medieval and early modern periods, providing Venice with control and influence over trade and politics far in excess of the republic's size and population. It was one of the first navies to mount gunpowder weapons aboard ships, and through an organised system of naval dockyards, armouries and chandlers was able to continually keep ships at sea and rapidly replace losses. The Venetian Arsenal was one of the greatest concentrations of industrial capacity prior to the Industrial Revolution and responsible for the bulk of the republic's naval power. Driven at first by a rivalry with the Byzantine Empire, and later the maritime republics of Pisa and Genoa for primacy over trade with the Levant, the Venetian navy was at times technically innovative and yet oper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Urban II
Pope Urban II (; – 29 July 1099), otherwise known as Odo of Châtillon or Otho de Lagery, was the head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 12 March 1088 to his death. He is best known for convening the Council of Clermont, which ignited the series of Christianity and violence, Christian military expeditions known as the Crusades. Pope Urban was a native of France and a descendant of a noble family from the French commune of Châtillon-sur-Marne. Before his papacy, Urban was the grand prior of Cluny Abbey, Cluny and bishop of Ostia. As pope, he dealt with Antipope Clement III, the infighting of various Christian nations, and the Byzantine–Seljuk wars, Turkish invasions into Anatolia. In 1095, he started preaching for the start of the First Crusade (1096–1099). He promised forgiveness and pardon for all of the past sins of those who would fight to reclaim the Holy Land from Muslims and free the Eastern churches. This pardon would also apply to those fig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lycia
Lycia (; Lycian: 𐊗𐊕𐊐𐊎𐊆𐊖 ''Trm̃mis''; , ; ) was a historical region in Anatolia from 15–14th centuries BC (as Lukka) to 546 BC. It bordered the Mediterranean Sea in what is today the provinces of Antalya and Muğla in Turkey as well some inland parts of Burdur Province. The region was known to history from the Late Bronze Age records of ancient Egypt and the Hittite Empire. Lycia was populated by speakers of Luwic languages. Written records began to be inscribed in stone in the Lycian language after Lycia's involuntary incorporation into the Achaemenid Empire in the Iron Age. At that time (546 BC) the Luwian speakers were displaced as Lycia received an influx of Persian speakers. The many cities in Lycia were wealthy as shown by their elaborate architecture starting at least from the 5th century BC and extending to the Roman period. Lycia fought for the Persians in the Persian Wars, but on the defeat of the Achaemenid Empire by the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myra
Myra (; , ''Mýra'') was a city in Lycia. The city was probably founded by Lycians on the river Myros (; Turkish: ''Demre Çay''), in the fertile alluvial plain between, the Massikytos range (Turkish: ''Alaca Dağ'') and the Aegean Sea. By the 3rd century BC the city was Hellenized. Following the wars of the diadochi the area came under the loose control of the Ptolemies, the Seleucids, and finally the Romans. The region remained under Roman control until it was conquered by the Seljucks and later the Ottomans. During the Ottoman rule the small Turkish town of Kale was established in the area of Myra in the present-day Antalya Province of Turkey. Kale was renamed to Demre in 2005. History Although some scholars equate Myra with the town, of Mira, in Arzawa, there is no proof for the connection. There is no substantiated written reference for Myra before it was listed as a member of the Lycian League (168 BC–AD 43); according to Strabo (14:665), it was one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitale I Michiel
Vital I Michiel (died 1102) was a Doge of Venice; he was the 33rd traditional (31st historic) Doge of the Republic of Venice. A member of one of the so-called “twelve apostolic” families, he was married to Felicia Cornaro, who had influence on his politics. Life When Pope Urban II initiated the First Crusade, Vitale I Michiel did not initially urge Venice’s support, perhaps because he could not see the advantages to Venice of such an expedition. When Doge Vitale I Michiel saw the European commitment to the First Crusade, he then understood the war’s economic importance. In particular, he foresaw that it was vital to Venice’s trade advantage to participate in territorial conquest, lest these advantages inure to the benefit of other marine republics. In July 1099, 207 ships sailed from Venice to support the First Crusade. Doge Vitale I Michiel appointed his son, Vitale Giovanni, and the Bishop of Castello, Enrico Contarini, as the fleet’s commanders. In December 109 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Castello
The Diocese of Castello, originally the Diocese of Olivolo, is a former Roman Catholic diocese that was based on the city of Venice in Italy. It was established in 774, covering the islands that are now occupied by Venice. Throughout its existence there was tension between the diocese, the Patriarchate of Grado to which it was nominally subordinate, and the Doge of Venice. Eventually in 1451 the diocese and the patriarchate were merged to form the Archdiocese of Venice. History Foundation The diocese has its origins in the Patriarchate of Aquileia, founded during the Roman Empire. Hilarius of Panonia is recorded as bishop of Aquileia from about 276–285. As the empire fell into decline, Aquileia was sacked in turn by Visigoths (403), Huns (452) and Lombards (659). During these times of trouble some of the people would take refuge on the offshore islands. By 630 an independent Patriarch of Grado was established on the island of Grado. The islands of Venice had originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Crusade
The First Crusade (1096–1099) was the first of a series of religious wars, or Crusades, initiated, supported and at times directed by the Latin Church in the Middle Ages. The objective was the recovery of the Holy Land from Muslim conquest of the Levant, Islamic rule. While Jerusalem had been under Muslim rule for hundreds of years, by the 11th century the Seljuk Empire, Seljuk takeover of the region threatened local Christian populations, pilgrimages from the West, and the Byzantine Empire itself. The earliest initiative for the First Crusade began in 1095 when List of Byzantine emperors, Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos requested military support from the Council of Piacenza in the empire's conflict with the Seljuk-led Turks. This was followed later in the year by the Council of Clermont, during which Pope Urban II supported the Byzantine request for military assistance and also urged faithful Christians to undertake an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. This call was met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venetian Expedition To The Levant (1099–1100)
In 1099–1100, the Republic of Venice sent a large fleet to assist the First Crusade in the Levant. Under preparation since 1097 or 1096, the fleet sailed after the Siege of Jerusalem (1099), capture of Jerusalem by the Crusaders and after the fleets of Venice's Republic of Genoa, Genoese and Republic of Pisa, Pisan rivals. The details of the expedition are somewhat obscure, as the main source is a single religious text, which reports a naval battle against a Pisan fleet off the harbour of Rhodes, the discovery and translation of relics purporting to belong to Saint Nicholas from Myra to Venice, and the Venetians' participation in the Siege of Haifa (1100), capture of the port city of Haifa in August 1100, before the fleet returned home. Background When Pope Urban II declared the First Crusade in 1095, he also sent envoys to the main Italian maritime republics for naval assistance to the crusading armies. The Republic of Genoa was the first to respond, sending a small squadron east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |