|
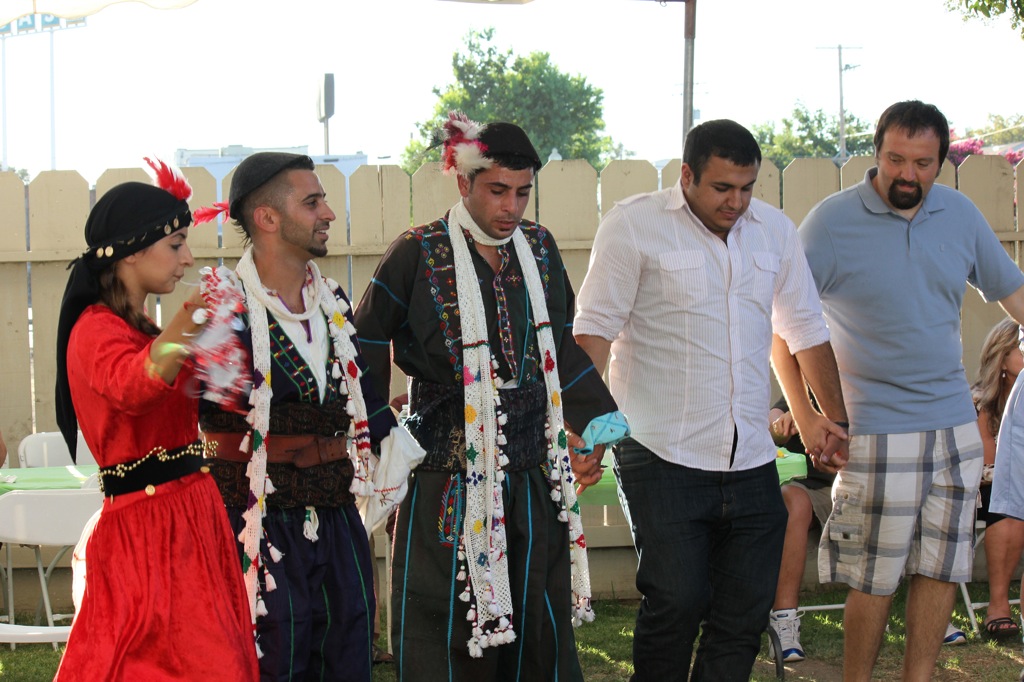
Mizo People
The Mizo people, historically called the Lushais, are a Tibeto-Burman ethnic group primarily from Mizoram in northeastern India. They speak Mizo, one of the state's official languages and its lingua franca. Beyond Mizoram, sizable Mizo communities live in neighboring northeast Indian states like Manipur, Assam, Meghalaya, and Tripura, with minority populations also found in Myanmar and the United States. Mizoram is the most literate state in India, and the first to reach 100%. The Chin people of Myanmar and the Kuki people of India and Bangladesh are the kindred tribes of Mizos and many of the Mizo migrants in Myanmar have accepted the Chin identity. The Chin, Kuki, Mizo, and southern Naga peoples are collectively known as Zo people ( Mizo: ''Zohnahthlak''; lit. "descendants of Zo") which all speak the Mizo language Definition and subgroups The term "Mizo" is a collective name for the people inhabiting the State of Mizoram who have close affinity in dialect, origin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheraw (dance)
Cheraw dance is a traditional bamboo dance performed by the Mizo people of Mizoram, India, consisting of mostly six to eight people holding pairs of bamboo staves on another horizontally placed bamboo on the ground. The male performers then clap the bamboos rhythmically while groups of female dancers dance in intricate steps between the beating bamboo. Modern Later practice of Cheraw is accompanied by accordion, mandolin and guitar played in non traditional clothes. Dress code The common costumes worn by the performers during the Cheraw dance include: Women *Vakiria - is a female headress made of bamboo and decorated with feathers, beetles wings and other colorful objects, from the 1960s it evolved into the present form. *Kawrchei - White red green black blouse. *Puanchei - White red green black sarong. Men *Khumbeu - Asian conical hat, Bamboo hat *Mizo Shawl All these traditional costumes of Cheraw Dance come in vibrant colors that further brighten up the surrounding environ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chin People
The Chin peoples (, ) are collection of ethnic groups native to the Chin State, Myanmar that speak the Kuki-Chin-Mizo languages, which are closely related but mutually unintelligible. The Chin identity, as a pan-ethnic identity, is a modern construction, shaped by British rule, Christian missionary influence, and post-independence ethnic politics that has built upon older tribal and regional identities. Ethnonyms Chin (ချင်း, MLCTS: khyang:) is a pseudo-exonym, a Burmese language adaptation of the Asho Chin word ''khlong'' or ''khlaung'', which means "man" or "person." Burmese speakers approximated the Asho Chin word, and began to apply the exonym to all nearby groups residing in the Arakan Mountains and Chin Hills. The Burmese term first appeared in stone inscriptions dating to the reign of King Kyansittha in the 11th century. The term "Chin" is not universally accepted by all groups living in Chin State nor by all Kuki-Chin groups. Groups in the north pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mizo Literature
Mizo literature is the literature written in Mizo ṭawng, the principal language of the Mizo peoples, which has both written and oral traditions. It has undergone a considerable change in the 20th century. The language developed mainly from the Lushai language, with significant influence from Pawi language, Paite language and Hmar language, especially at the literary level. Pre-Christianisation period This period of Mizo (written) literature usually refers to the period between 1860 and 1894. Although the Mizo alphabet proper was created around May 1894, written Mizo literature can be said to start from the publication of ''Progressive Colloquial Exercises in the Lushai Dialect'' by Thangliana (which is the Mizo name of Thomas Herbert Lewin) in 1874. In this book he wrote down two Mizo folktales ''Chemtatrawta'' and ''Lalruanga leh Kungawrhi'' with their English translations, and included some Mizo words with their English meaning.Khiangte, Laltluangliana, ''Thuhlaril'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Literacy In India
Literacy in India is a key for social-economic progress. The 2011 census, indicated a 2001–2011 literacy growth of 9.2%, which is slower than the growth seen during the previous decade. At the then-current rate of progress in 1990, one study projected that universal literacy might be reached by 2060. The census of India pegged the average literacy rate as 73% in 2011 while National Statistical Commission surveyed literacy to be 80.6% in 2017–18. Meanwhile, the National Sample Survey Office (India), National Sample Survey Office in its 2023–2024 annual PLFS report stated the total literacy rate of India to be 80.9%. Literacy rate in urban areas was 90%, higher than rural areas with 77%. There is a wide gender disparity in the literacy rate in India and effective literacy rates (age 7 and above) was 88% for men and 81% for women. The lower female literacy rate has a dramatically negative impact on Family planning in India, family planning and population stabilisation efforts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingua Franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, link language or language of wider communication (LWC), is a Natural language, language systematically used to make communication possible between groups of people who do not share a First language, native language or dialect, particularly when it is a third language that is distinct from both of the speakers' native languages. Linguae francae have developed around the world throughout human history, sometimes for commercial reasons (so-called "trade languages" facilitated trade), but also for cultural, religious, diplomatic and administrative convenience, and as a means of exchanging information between scientists and other scholars of different nationalities. The term is taken from the medieval Mediterranean Lingua Franca, a Romance languages, Romance-based pidgin language used especially by traders in the Mediterranean Basin from the 11th to the 19th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since 2023; and, since its independence in 1947, the world's most populous democracy. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the southwest, and the Bay of Bengal on the southeast, it shares land borders with Pakistan to the west; China, Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. In the Indian Ocean, India is near Sri Lanka and the Maldives; its Andaman and Nicobar Islands share a maritime border with Thailand, Myanmar, and Indonesia. Modern humans arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa no later than 55,000 years ago., "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by modern humans originating in Africa. ... Coalescence dates for most non-European populations averag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast India
Northeast India, officially the North Eastern Region (NER), is the easternmost region of India representing both a geographic and political Administrative divisions of India, administrative division of the country. It comprises eight States and union territories of India, states—Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Tripura (commonly known as the "Seven Sisters"), and the "brother" state of Sikkim. The region shares an international border of 5,182 kilometres (3,220 mi) (about 99 per cent of its total geographical boundary) with several neighbouring countries – it borders China to the north, Myanmar to the east, Bangladesh to the south-west, Nepal to the west, and Bhutan to the north-west. It comprises an area of , almost 8 per cent of that of India. The Siliguri Corridor connects the region to the Mainland India, rest of mainland India. The states of North Eastern Region are officially recognised under the North Eastern Council (NEC), co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnic Group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, religion, history or social treatment. Ethnicities may also have a narrow or broad spectrum of genetic ancestry, with some groups having mixed genetic ancestry. ''Ethnicity'' is sometimes used interchangeably with ''nation'', particularly in cases of ethnic nationalism. It is also used interchangeably with '' race'' although not all ethnicities identify as racial groups. By way of assimilation, acculturation, amalgamation, language shift, intermarriage, adoption and religious conversion, individuals or groups may over time shift from one ethnic group to another. Ethnic groups may be divided into subgroups or tribes, which over time may become separate ethnic groups themselves due to endogamy or physical isolation from the parent gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibeto-Burman Languages
The Tibeto-Burman languages are the non- Sinitic members of the Sino-Tibetan language family, over 400 of which are spoken throughout the Southeast Asian Massif ("Zomia") as well as parts of East Asia and South Asia. Around 60 million people speak Tibeto-Burman languages. The name derives from the most widely spoken of these languages, Burmese and the Tibetic languages, which also have extensive literary traditions, dating from the 12th and 7th centuries respectively. Most of the other languages are spoken by much smaller communities, and many of them have not been described in detail. Though the division of Sino-Tibetan into Sinitic and Tibeto-Burman branches (e.g. Benedict, Matisoff) is widely used, some historical linguists criticize this classification, as the non-Sinitic Sino-Tibetan languages lack any shared innovations in phonology or morphology to show that they comprise a clade of the phylogenetic tree. History During the 18th century, several scholars noticed paral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jingpo People
The Jingpo people (; ; ''siŋphou''), also spelt Jinghpaw or Jingphaw, are a Tibeto-Burman ethnic group who inhabit northern Burma, northeastern India, and southwestern China. The Jingpo are the largest subgroup of the Kachin peoples. The Jingpo speak the Jingpo language, which is used as a lingua franca among the Kachin peoples and is distantly related to other Kachin languages. Ethnonyms Jingpo () is the Chinese exonym for the ethnic group. The endonym is Jinghpaw, which is also transcribed Jingphaw. In India, the Jingpo are known as the Singpho. Kachin is often used interchangeably with Jingpo, especially in Burmese, although the former more precisely refers to the collection of ethnic groups including the Jingpo. The Jingpo were previously known by various exonyms in Chinese: ''Echang'', ''Zhexie'', and ''Yeren'' (野人, )—the latter used in China from the Yuan dynasty until the formation of the People's Republic of China in 1949. The Burmese government officiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
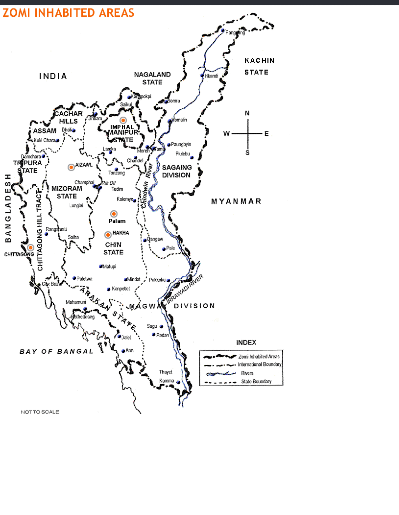
Zo People
The Zo people is a term to denote the ethnolinguistically related speakers of the Kuki-Chin languages who primarily inhabit northeastern India, western Myanmar, and southeastern Bangladesh. The dispersal across international borders resulted from a British colonial policy that drew borders on political, rather than ethnic, grounds. Ethnonyms Beginning in the 1990s, the generic name Chin have been rejected by some for "Zomi", a name used by a group speaking Northern Kuki languages. The speakers of the Northern Kuki languages are sometimes lumped together as the Zomi's. Some Zomi nationalists have stated that the use of the label Chin would mean subtle domination by Burmese groups. In 2023, during the Manipur violence the Kuki tribes of Manipur were referred to Kuki-Zo, Before it was specifically only Kuki in context of Manipur, Assam, Nagaland, and Tripura. Origin The Zo people trace their ancestry to the Tibeto-Burman family, migrating from the Mekong River basi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |