|
Mitotic Index
In cell biology, the mitotic index is defined as the ratio between the number of a population's Cell (biology), cells undergoing mitosis to its total number of cells. Purpose The mitotic index is a measure of cellular cell proliferation, proliferation. It is defined as the percentage of cells undergoing mitosis in a given population of cells. Mitosis is the division of somatic cells into two daughter cells. Durations of the cell cycle and mitosis vary in different cell types. An elevated mitotic index indicates more cells are dividing. In cancer cells, the mitotic index may be elevated compared to normal growth of tissues or cellular repair of the site of an injury. The mitotic index is therefore an important prognostic factor predicting both overall survival and response to chemotherapy in most types of cancer. It may lose much of its predictive value for elderly populations. For example, a low mitotic index loses any prognostic value for women over 70 years old with breast can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Biology
Cell biology (also cellular biology or cytology) is a branch of biology that studies the structure, function, and behavior of cells. All living organisms are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of life that is responsible for the living and functioning of organisms. Cell biology is the study of the structural and functional units of cells. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and has many subtopics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, biochemistry, and cell composition. The study of cells is performed using several microscopy techniques, cell culture, and cell fractionation. These have allowed for and are currently being used for discoveries and research pertaining to how cells function, ultimately giving insight into understanding larger organisms. Knowing the components of cells and how cells work is fundamental to all biological sciences while also being essential for research in biomedical fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitosis
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new Cell nucleus, nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Mitosis is preceded by the S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is followed by telophase and cytokinesis, which divide the cytoplasm, organelles, and cell membrane of one cell into two new cell (biology), cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic phase (M phase) of a cell cycle—the cell division, division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation requires both cell growth and cell division to occur at the same time, such that the average size of cells remains constant in the population. Cell division can occur without cell growth, producing many progressively smaller cells (as in cleavage of the zygote), while cell growth can occur without cell division to produce a single larger cell (as in growth of neurons). Thus, cell proliferation is not synonymous with either cell growth or cell division, despite these terms sometimes being used interchangeably. Stem cells undergo cell proliferation to produce proliferating "transit amplifying" daughter cells that later differentiate to construct tissues during normal development and tissue growth, during tissue regeneration after da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Somatic Cell
In cellular biology, a somatic cell (), or vegetal cell, is any biological cell forming the body of a multicellular organism other than a gamete, germ cell, gametocyte or undifferentiated stem cell. Somatic cells compose the body of an organism and divide through mitosis. In contrast, gametes derive from meiosis within the germ cells of the germline and they fuse during sexual reproduction. Stem cells also can divide through mitosis, but are different from somatic in that they differentiate into diverse specialized cell types. In mammals, somatic cells make up all the internal organs, skin, bones, blood and connective tissue, while mammalian germ cells give rise to spermatozoa and ova which fuse during fertilization to produce a cell called a zygote, which divides and differentiates into the cells of an embryo. There are approximately 220 types of somatic cell in the human body. Theoretically, these cells are not germ cells (the source of gametes); they transmit their mut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm, chromosomes and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division. In eukaryotic cells (having a cell nucleus) including animal, plant, fungal, and protist cells, the cell cycle is divided into two main stages: interphase, and the M phase that includes mitosis and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, and replicates its DNA and some of its organelles. During the M phase, the replicated Chromosome, chromosomes, organelles, and cytoplasm separate into two new daughter cells. To ensure the proper replication of cellular components and division, there are control mechanisms kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prognostic
Prognosis (Greek: πρόγνωσις "fore-knowing, foreseeing"; : prognoses) is a medical term for predicting the likelihood or expected development of a disease, including whether the signs and symptoms will improve or worsen (and how quickly) or remain stable over time; expectations of quality of life, such as the ability to carry out daily activities; the potential for complications and associated health issues; and the likelihood of survival (including life expectancy). A prognosis is made on the basis of the normal course of the diagnosed disease, the individual's physical and mental condition, the available treatments, and additional factors. A complete prognosis includes the expected duration, function, and description of the course of the disease, such as progressive decline, intermittent crisis, or sudden, unpredictable crisis. When applied to large statistical populations, prognostic estimates can be very accurate: for example the statement "45% of patients with severe s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Cancer
Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or a red or scaly patch of skin. In those with Metastatic breast cancer, distant spread of the disease, there may be bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, shortness of breath, or yellow skin. Risk factors for developing breast cancer include obesity, a Sedentary lifestyle, lack of physical exercise, alcohol consumption, hormone replacement therapy during menopause, ionizing radiation, an early age at Menarche, first menstruation, having children late in life (or not at all), older age, having a prior history of breast cancer, and a family history of breast cancer. About five to ten percent of cases are the result of an inherited genetic predisposition, including BRCA mutation, ''BRCA'' mutations among others. Breast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prophase
Prophase () is the first stage of cell division in both mitosis and meiosis. Beginning after interphase, DNA has already been replicated when the cell enters prophase. The main occurrences in prophase are the condensation of the chromatin reticulum and the disappearance of the nucleolus. Staining and microscopy Microscopy can be used to visualize condensed chromosomes as they move through meiosis and mitosis. Various DNA stains are used to treat cells such that condensing chromosomes can be visualized as the move through prophase. The giemsa G-banding technique is commonly used to identify mammalian chromosomes, but utilizing the technology on plant cells was originally difficult due to the high degree of chromosome compaction in plant cells. G-banding was fully realized for plant chromosomes in 1990. During both meiotic and mitotic prophase, giemsa staining can be applied to cells to elicit G-banding in chromosomes. Silver staining, a more modern technology, in conj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
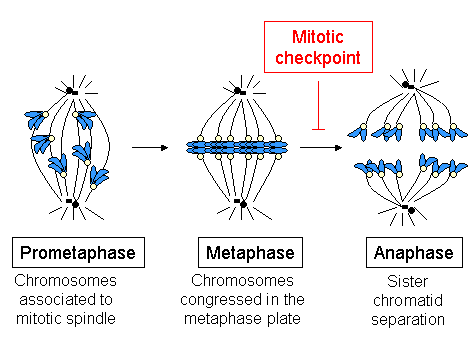
Metaphase
Metaphase ( and ) is a stage of mitosis in the eukaryotic cell cycle in which chromosomes are at their second-most condensed and coiled stage (they are at their most condensed in anaphase). These chromosomes, carrying genetic information, align in the equator of the cell between the spindle poles at the metaphase plate, before being separated into each of the two daughter nuclei. This alignment marks the beginning of metaphase. Metaphase accounts for approximately 4% of the cell cycle's duration. In metaphase, microtubules from both duplicated centrosomes on opposite poles of the cell have completed attachment to kinetochores on condensed chromosomes. The centromeres of the chromosomes convene themselves on the metaphase plate, an imaginary line that is equidistant from the two spindle poles. This even alignment is due to the counterbalance of the pulling powers generated by the opposing kinetochore microtubules, analogous to a tug-of-war between two people of equal strength, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaphase
Anaphase () is the stage of mitosis after the process of metaphase, when replicated chromosomes are split and the newly-copied chromosomes (daughter chromatids) are moved to opposite poles of the cell. Chromosomes also reach their overall maximum condensation in late anaphase, to help chromosome segregation and the re-formation of the nucleus. Anaphase starts when the anaphase promoting complex marks an Chaperone (protein), inhibitory chaperone called securin for destruction by Ubiquitin, ubiquitylating it. Securin is a protein which inhibits a protease known as separase. The destruction of securin unleashes separase which then breaks down cohesin, a protein responsible for holding sister chromatids together. At this point, three subclasses of microtubule unique to mitosis are involved in creating the forces necessary to separate the chromatids: kinetochore microtubules, interpolar microtubules, and Aster_(cell_biology)#Astral_microtubules, astral microtubules. The centromere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telophase
Telophase () is the final stage in both meiosis and mitosis in a eukaryotic cell. During telophase, the effects of prophase and prometaphase (the nucleolus and nuclear membrane disintegrating) are reversed. As chromosomes reach the cell poles, a nuclear envelope is re-assembled around each set of chromatids, the nucleoli reappear, and chromosomes begin to decondense back into the expanded chromatin that is present during interphase. The mitotic spindle is disassembled and remaining spindle microtubules are depolymerized. Telophase accounts for approximately 2% of the cell cycle's duration. Cytokinesis typically begins before late telophase and, when complete, segregates the two daughter nuclei between a pair of separate daughter cells. Telophase is primarily driven by the dephosphorylation of mitotic cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) substrates. Dephosphorylation of Cdk substrates The phosphorylation of the protein targets of M-Cdks (Mitotic Cyclin-dependent Kinases) drives sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |