|
Minocycline
Minocycline, sold under the brand name Minocin among others, is a tetracycline antibiotic medication used to treat a number of bacterial infections such as some occurring in certain forms of pneumonia. It is generally (but not always) less preferred than the tetracycline doxycycline. Minocycline is also used for the treatment of acne and rheumatoid arthritis. It is taken by mouth or applied to the skin. Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, dizziness, allergic reactions, and kidney problems. Serious side effects may include anaphylaxis, a lupus-like syndrome, and easy sunburning. Use in the later part of pregnancy may harm the baby and safety during breastfeeding is unclear. It works by decreasing a bacterium's ability to make protein thus stopping its growth. Minocycline was patented in 1961 and came into commercial use in 1971. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 269th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetracycline Antibiotic
Tetracyclines are a group of broad-spectrum antibiotic compounds that have a common basic structure and are either isolated directly from several species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria or produced semi-synthetically from those isolated compounds. Tetracycline molecules comprise a linear fused tetracyclic nucleus (rings designated A, B, C and D) to which a variety of functional groups are attached. Tetracyclines are named after their four ("tetra-") hydrocarbon rings ("-cycl-") derivation ("-ine"). They are defined as a subclass of polyketides, having an octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide skeleton and are known as derivative (chemistry), derivatives of polycyclic naphthacene carboxamide. While all tetracyclines have a common structure, they differ from each other by the presence of chloro, methyl, and hydroxyl groups. These chemical modification, modifications do not change their broad antibacterial activity, but do affect pharmacological properties such as half-life and binding to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doxycycline
Doxycycline is a Broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum antibiotic of the Tetracycline antibiotics, tetracycline class used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat pneumonia, bacterial pneumonia, acne vulgaris, acne, chlamydia infections, Lyme disease, cholera, typhus, and syphilis. It is also used to prevent malaria. Doxycycline may be taken Oral administration, by mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein. Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and an increased risk of sunburn. Use during pregnancy is not recommended. Like other agents of the tetracycline class, it either slows or kills bacteria by inhibiting protein production. It kills malaria by targeting a plastid organelle, the apicoplast. Doxycycline was patented in 1957 and came into commercial use in 1967. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Doxycyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetracycline Antibiotic
Tetracyclines are a group of broad-spectrum antibiotic compounds that have a common basic structure and are either isolated directly from several species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria or produced semi-synthetically from those isolated compounds. Tetracycline molecules comprise a linear fused tetracyclic nucleus (rings designated A, B, C and D) to which a variety of functional groups are attached. Tetracyclines are named after their four ("tetra-") hydrocarbon rings ("-cycl-") derivation ("-ine"). They are defined as a subclass of polyketides, having an octahydrotetracene-2-carboxamide skeleton and are known as derivative (chemistry), derivatives of polycyclic naphthacene carboxamide. While all tetracyclines have a common structure, they differ from each other by the presence of chloro, methyl, and hydroxyl groups. These chemical modification, modifications do not change their broad antibacterial activity, but do affect pharmacological properties such as half-life and binding to pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
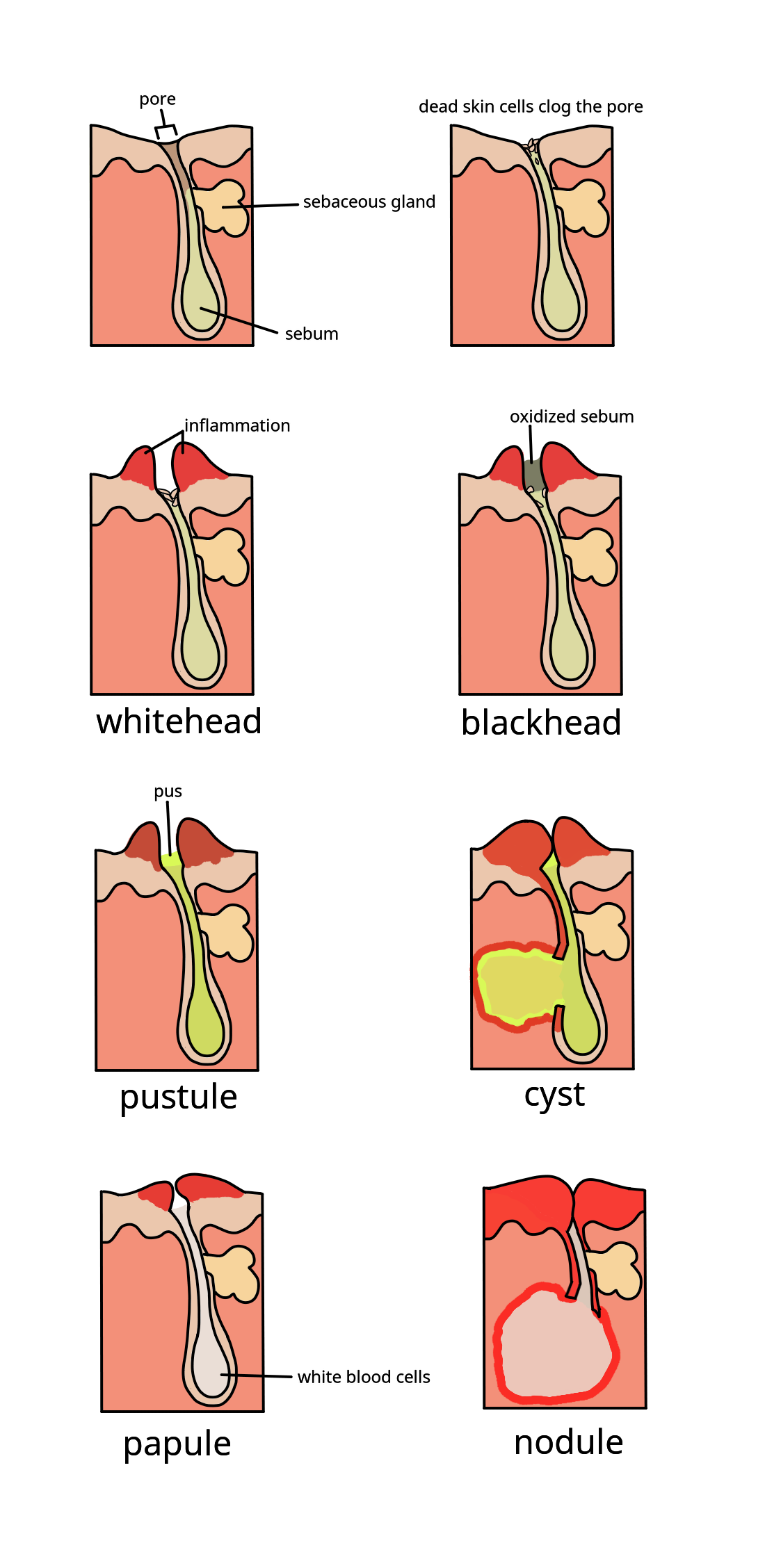
Acne Vulgaris
Acne ( ), also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term Cutaneous condition, skin condition that occurs when Keratinocyte, dead skin cells and Sebum, oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include comedo, blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of sebaceous gland, oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to lack of confidence, anxiety (mood), anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, clinical depression, depression or suicidal ideations, thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither hygiene, cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight are associated with acne. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. It is available in oral and topical formulations. Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and loss of appetite. Other side effects include poor tooth development if used by children less than eight years of age, kidney problems, and sunburning easily. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. It works by inhibiting protein synthesis in bacteria. Tetracycline was patented in 1953 and was approved for prescription use in 1954. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Tetracycline is available as a generic medication. Tetracycline was originally made from bacteria of the genus ''Streptomyces''. Medical uses Spectrum of activity Tetracyclines have a broad spectrum of antibiotic action. Originally, they possessed some lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generic Medication
A generic drug is a pharmaceutical drug that contains the same chemical substance as a drug that was originally protected by chemical patents. Generic drugs are allowed for sale after the patents on the original drugs expire. Because the active chemical substance is the same, the medical profile of generics is equivalent in performance compared to their performance at the time when they were patented drugs. A generic drug has the same active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) as the original, but it may differ in some characteristics such as the manufacturing process, pharmaceutical formulation, formulation, excipients, color, taste, and packaging. Although they may not be associated with a particular company, generic drugs are usually subject to government regulations in the countries in which they are dispensed. They are labeled with the name of the manufacturer and a generic non-proprietary name such as the United States Adopted Name (USAN) or International nonproprietary name, Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indicated
In medicine, an indication is a valid reason to use a certain test, medication, procedure, or surgery. There can be multiple indications to use a procedure or medication. An indication can commonly be confused with the term diagnosis. A diagnosis is the assessment that a particular medical condition is present while an indication is a reason for use. The opposite of an indication is a contraindication, a reason to withhold a certain medical treatment because the risks of treatment clearly outweigh the benefits. In the United States, indications for prescription drugs are approved by the FDA. Indications are included in the Indications and Usage section of the Prescribing Information. The primary role of this section of labeling is to enable health care practitioners to readily identify appropriate therapies for patients by clearly communicating the drug's approved indication(s). The Indications and Usage section states the disease or condition, or manifestation or symptoms thereof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration whereby a substance is taken through the Human mouth, mouth, swallowed, and then processed via the digestive system. This is a common route of administration for many medications. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes of administration, such as Injection (medicine), injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth". The expression is used in medicine to describe a treatment that is taken orally (but not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Administration
Systemic administration is a route of administration of medication, nutrition or other substance into the circulatory system so that the entire body is affected. Administration can take place via enteral administration (absorption of the drug through the gastrointestinal tract) or parenteral administration (generally injection, infusion, or implantation). Contrast with topical A topical medication is a medication that is applied to a particular place on or in the body. Most often topical medication means application to body surfaces such as the skin or mucous membranes to treat ailments via a large range of classes ... administration where the effect is generally local. References Routes of administration {{pharma-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
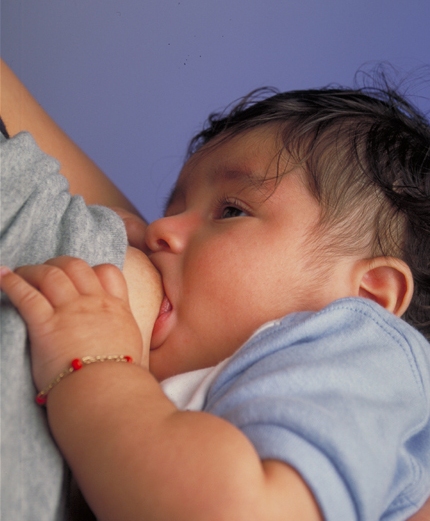
Breastfeeding
Breastfeeding, also known as nursing, is the process where breast milk is fed to a child. Infants may suck the milk directly from the breast, or milk may be extracted with a Breast pump, pump and then fed to the infant. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommend that breastfeeding begin within the first hour of a baby's birth and continue as the baby wants. Health organizations, including the WHO, recommend breastfeeding exclusively for six months. This means that no other foods or drinks, other than vitamin D, are typically given. The WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life, followed by continued breastfeeding with appropriate complementary foods for up to 2 years and beyond. Of the 135 million babies born every year, only 42% are breastfed within the first hour of life, only 38% of mothers practice exclusive breastfeeding during the first six months, and 58% of mothers continue breastfeeding up to the age of two years and beyond. Breastfee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |