|
Minoan Eruption
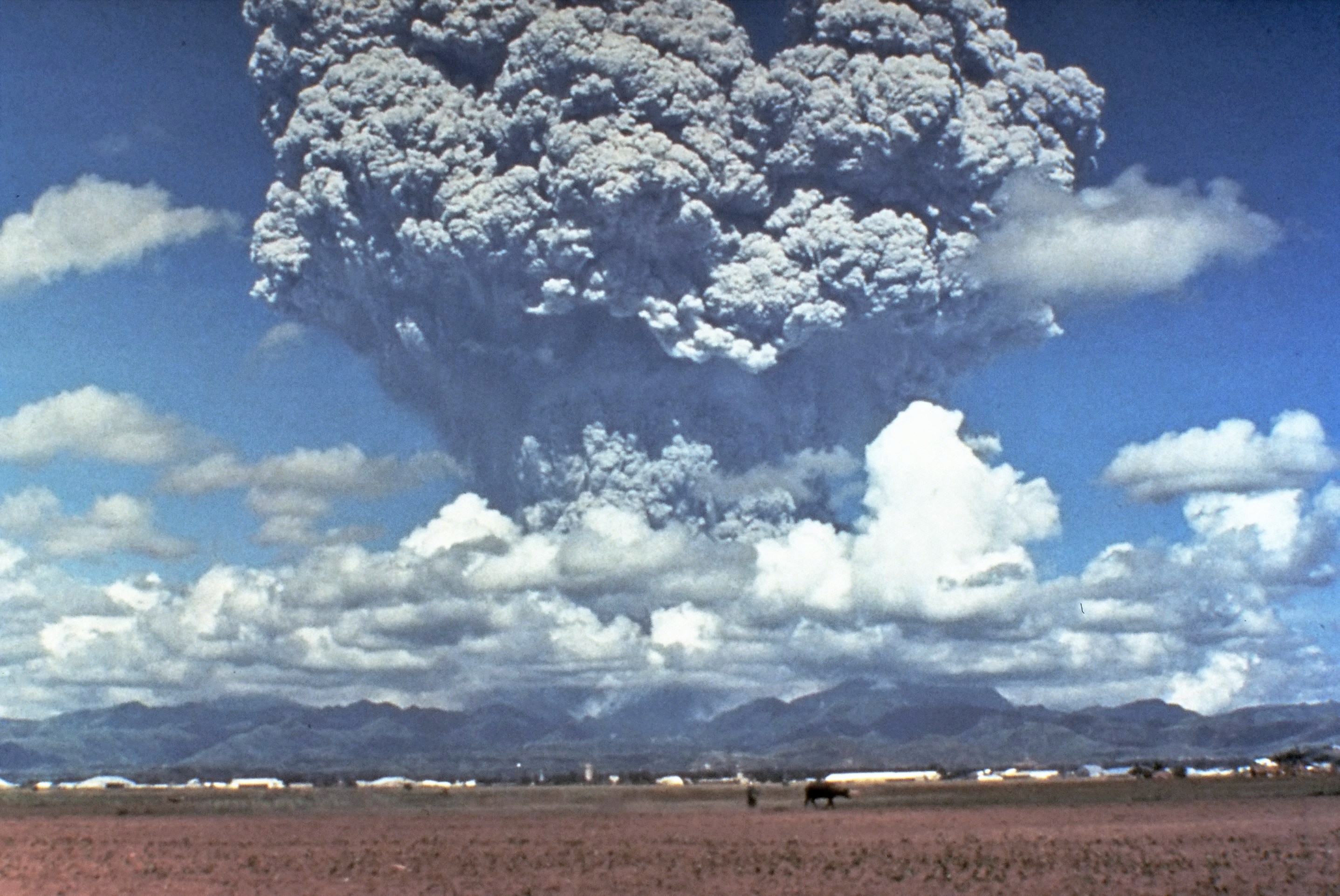
The Minoan eruption was a catastrophic volcanic eruption that devastated the Aegean island of Thera (also called Santorini) circa 1600 BCE. It destroyed the Minoan settlement at Akrotiri, as well as communities and agricultural areas on nearby islands and the coast of Crete with subsequent earthquakes and paleotsunamis. With a Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of 7, it resulted in the ejection of approximately of dense-rock equivalent (DRE), the eruption was one of the largest volcanic events in human history. Since tephra from the Minoan eruption serves as a marker horizon in nearly all archaeological sites in the Eastern Mediterranean, its precise date is of high importance and has been fiercely debated among archaeologists and volcanologists for decades, without coming to a definite conclusion. Although there are no clear ancient records of the eruption, its plume and volcanic lightning may have been described in the Egyptian Tempest Stele. The Chinese ''Bamboo Annal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcanic eruption. An eruption that ejects large volumes of magma over a short period of time can cause significant detriment to the structural integrity of such a chamber, greatly diminishing its capacity to support its own roof and any substrate or rock resting above. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a Volcanic crater, crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur over the course of a century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times within a given window of 100 years. Only eight caldera-forming collapses are known to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Large Holocene Volcanic Eruptions
This is a list of volcanoes that have had large explosive eruptions during the Holocene (since about 11,650 years Before Present), with a volcanic explosivity index (VEI) of 5 or higher, or a plume height of at least 30 km. To date, there have been no eruptions with a confirmed VEI of 8 in the Holocene; and only a few VEI-7 eruptions are thought to have occurred during this time: the most recent was the 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora. This is not a complete list. Common Era (CE) Before Common Era (BCE) Exact year unknown See also *Year Without a Summer *Volcanic winter of 536 *List of largest volcanic eruptions *List of Quaternary volcanic eruptions *Timeline of volcanism on Earth Notes {{notelist References Holocene The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1815 Eruption Of Mount Tambora
In April 1815, Mount Tambora, a volcano on the island of Sumbawa in present-day Indonesia (then part of the Dutch East Indies), erupted in what is now considered the most powerful volcanic eruption in recorded human history. This eruption, with a volcanic explosivity index (VEI) of 7, ejected of dense-rock equivalent (DRE) material into the atmosphere, and was the most recent confirmed VEI-7 eruption. Although the Mount Tambora eruption reached a violent climax on 10 April 1815, increased steaming and small phreatic eruptions occurred during the next six months to three years. The ash from the eruption column dispersed around the world and lowered global temperatures in an event sometimes known as the Year Without a Summer in 1816. This brief period of significant climate change triggered extreme weather and harvest failures in many areas around the world. Several climate forcings coincided and interacted in a systematic manner that has not been observed after any other la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year Without A Summer
The year 1816 is known as the Year Without a Summer because of severe climate abnormalities that caused average global temperatures to decrease by . Summer temperatures in Europe were the coldest of any on record between 1766 and 2000, resulting in crop failures and major food shortages across the Northern Hemisphere. Evidence suggests that the anomaly was predominantly a volcanic winter event caused by the massive 1815 eruption of Mount Tambora in April in modern-day Indonesia (commonly referred to as the Dutch East Indies at the time). This eruption was the largest in at least 1,300 years (after the hypothesized eruption causing the volcanic winter of 536); its effect on the climate may have been exacerbated by the 1814 eruption of Mayon in the Philippines. The significant amount of volcanic ash and gases released into the atmosphere blocked sunlight, leading to global cooling. Countries such as the United Kingdom and France experienced significant hardship, with food riot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Winter
A volcanic winter is a reduction in global temperatures caused by droplets of sulfuric acid obscuring the Sun and raising Earth's albedo (increasing the reflection of solar radiation) after a large, sulfur-rich, particularly explosive volcanic eruption. Climate effects are primarily dependent upon the amount of injection of SO2 and H2S into the stratosphere where they react with OH and H2O to form H2SO4 on a timescale of a week, and the resulting H2SO4 aerosols produce the dominant radiative effect. Volcanic stratospheric aerosols cool the surface by reflecting solar radiation and warm the stratosphere by absorbing terrestrial radiation for several years. Moreover, the cooling trend can be further extended by atmosphere–ice–ocean feedback mechanisms. These feedbacks can continue to maintain the cool climate long after the volcanic aerosols have dissipated. Physical process An explosive volcanic eruption releases magma materials in the form of volcanic ash and gases into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shang Dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou dynasty. The classic account of the Shang comes from texts such as the '' Book of Documents'', '' Bamboo Annals'' and '' Shiji''. Modern scholarship dates the dynasty between the 16th and 11th centuries BC, with more agreement surrounding the end date than beginning date. The Shang dynasty is the earliest dynasty within traditional Chinese history that is firmly supported by archaeological evidence. The archaeological site of Yinxu, near modern-day Anyang, corresponds to the final Shang capital of Yin. Excavations at Yinxu have revealed eleven major royal tombs, the foundations of former palace buildings, and the remains of both animals and humans that were sacrificed in official state rituals. Tens of thousands of bronze, jade, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bamboo Annals
The ''Bamboo Annals'' ( zh, t=竹書紀年, p=Zhúshū Jìnián), also known as the ''Ji Tomb Annals'' ( zh, t=汲冢紀年, p=Jí Zhǒng Jìnián), is a chronicle of ancient China. It begins in the earliest legendary time (the age of the Yellow Emperor) and extends to 299 BC, with the later centuries focusing on the history of the State of Wei in the Warring States period. It thus covers a similar period to Sima Qian's '' Records of the Grand Historian'' (91 BC). The original may have been lost during the Song dynasty, and the text is known today in two versions, a "current text" (or "modern text") of disputed authenticity and an incomplete "ancient text". Textual history The original text was buried with King Xiang of Wei (died 296 BC) and re-discovered nearly six centuries later in 281 AD ( Western Jin dynasty) in the Jizhong discovery. For this reason, the chronicle survived the burning of the books by Emperor Qin Shi Huang. Other texts recovered from the same tomb in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tempest Stele
The Tempest Stele (alt. Storm Stele) was erected by pharaoh Ahmose I early in the 18th Dynasty of Egypt, . The stele describes a great storm striking Egypt during this time, destroying tombs, temples and pyramids in the Theban region and the work of restoration ordered by the king.Shaw, Ian. The Oxford History of Ancient Egypt. p. 209−210 Oxford University Press. 2000. Text Broken pieces of this stele were found in the 3rd pylon of the temple of Karnak at Thebes between 1947 and 1951 by French archaeologists. It was restored and published by Claude Vandersleyen in 1967 and 1968. The part of the stele that describes the storm is the most damaged part of the stele, with many lacunae in the meteorological description. The other parts of the stele are much better preserved. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic Lightning
Volcanic lightning is an electrical discharge caused by a volcanic eruption rather than from an ordinary thunderstorm. Volcanic lightning arises from colliding, fragmenting particles of volcanic ash (and sometimes ice), which generate static electricity within the volcanic plume, leading to the name dirty thunderstorm. Moist convection currents and ice formation also drive the eruption plume dynamics and can trigger volcanic lightning. Unlike ordinary thunderstorms, volcanic lightning can also occur when there are no ice crystals in the ash cloud. The earliest recorded observations of volcanic lightning are from Pliny the Younger, describing the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, "There was a most intense darkness rendered more appalling by the fitful gleam of torches at intervals obscured by the transient blaze of lightning." The first studies of volcanic lightning were also conducted at Mount Vesuvius by Luigi Palmieri who observed the eruptions of 1858, 1861, 1868, and 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
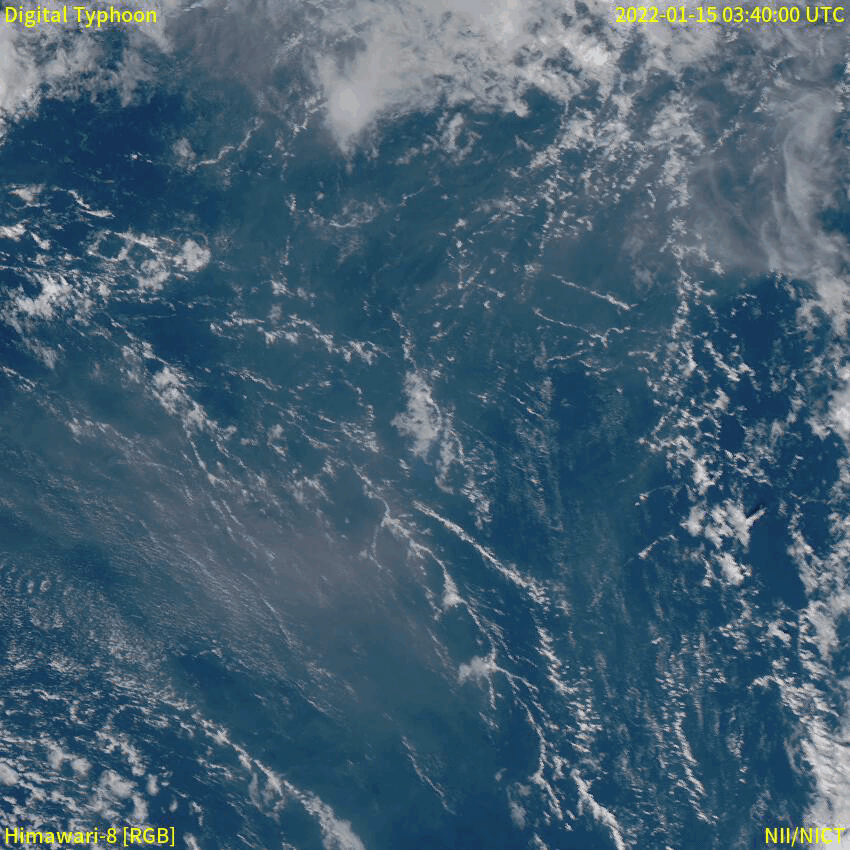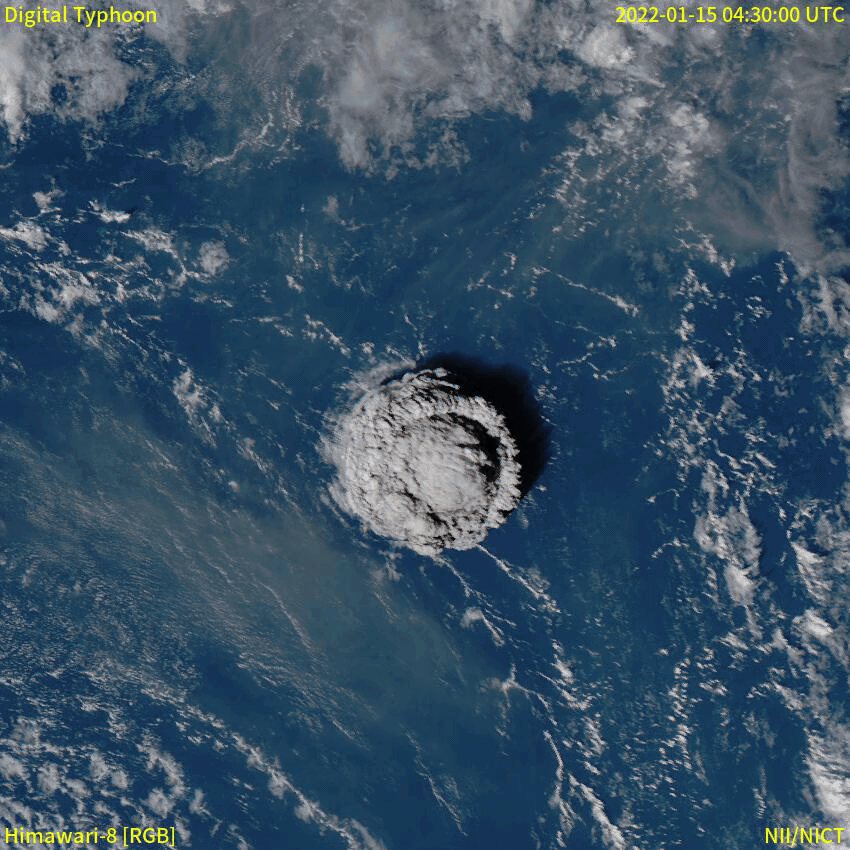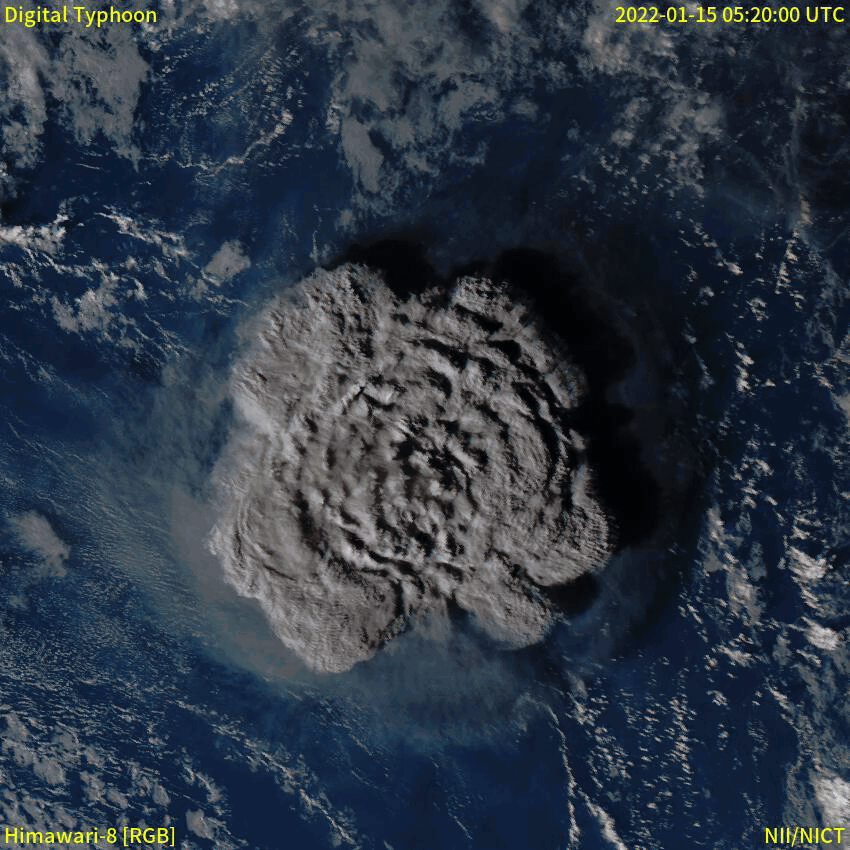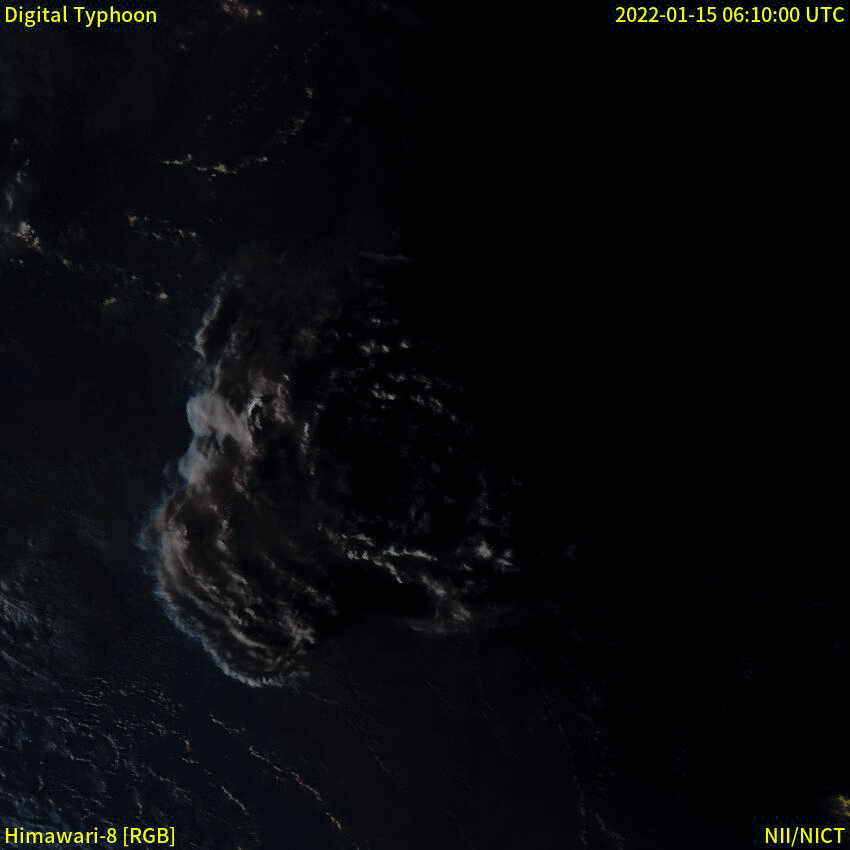
Eruption Column
An eruption column or eruption plume is a cloud of super-heated Volcanic ash, ash and tephra suspended in volcanic gas, gases emitted during an explosive eruption, explosive volcanic eruption. The volcanic materials form a vertical column or Plume (fluid dynamics), plume that may rise many kilometers into the air above the vent of the volcano. In the most explosive eruptions, the eruption column may rise over , penetrating the stratosphere. Injection of Particulate, aerosols into the stratosphere by volcanoes is a major cause of short-term Volcanic winter, climate change. A common occurrence in explosive eruptions is ''column collapse'' when the eruption column is or becomes too dense to be lifted high into the sky by air convection, and instead falls down the slopes of the volcano to form pyroclastic flows or pyroclastic surge, surges (although the latter is less dense). On some occasions, if the material is not dense enough to fall, it may create pyrocumulonimbus clouds. Forma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeometry (journal)
''Archaeometry'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering archaeological science, particularly absolute dating methods, artefact studies, quantitative archaeology, remote sensing, conservation science, and environmental archaeology. It is published bimonthly by Wiley-Blackwell, on behalf of the Research Laboratory for Archaeology and the History of Art at the University of Oxford, in association with the '' Gesellschaft für Naturwissenschaftliche Archäologie Archäometrie'' and the Society for Archaeological Sciences. Its current editors are A. Mark Pollard, Ina Reiche, Brandi MacDonald, Gilberto Artioli, and Catherine Batt. The journal was founded as the ''Bulletin of the Research Laboratory for Archaeology and the History of Art'' in 1958. It has been published by Wiley-Blackwell since 2001. Research papers published in ''Archaeometry'' are typically "technical expositions of physical and chemical methods applicable to dating and materials identification in arch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanologist
A volcanologist, or volcano scientist, is a geologist who focuses on understanding the formation and eruptive activity of volcanoes. Volcanologists frequently visit volcanoes, sometimes active ones, to observe and monitor volcanic eruptions, collect eruptive products including tephra (such as Volcanic ash, ash or pumice), Rock (geology), rock and lava samples. One major focus of inquiry in recent times is the prediction of eruptions to alleviate the impact on surrounding populations and monitor natural hazards associated with volcanic activity. Geologists who research volcanic materials that make up the solid Earth are referred to as igneous petrologists. Etymology The word ''volcanologist'' (or ''vulcanologist'') is derived from the English volcanology (volcano + wikt:-logy, -logy), which was derived from the French wikt:volcanologie#French, volcanologie (or vulcanologie), which was further derived from the French word wikt:volcan#French, volcan (volcano), which was even furt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |