|
Military Soyuz
file:Soyuz 7K-OK(A) drawing.png, Soyuz 7K-OK spacecraft with an active docking unit The Soviet Union planned several military Soyuz spacecraft models. These versions were named Soyuz P, Soyuz PPK, Soyuz R, Soyuz 7K-VI, and Soyuz OIS (Orbital Research Station). However, none of the spacecraft ever flew in space. Soyuz P, R and PPK Soyuz P The Soyuz P (''Perekhvatchik'', Interceptor) space interceptor and Soyuz R (''Razvedki'', intelligence) command-reconnaissance spacecraft was proposed in December 1962 by Sergei Korolev. In the initial draft project, the Soyuz P would use the Soyuz-B, Soyuz 9K rocket stage and Soyuz-V, Soyuz 11K tanker spacecraft to conduct a series of dockings and re-fueling operations. The complete complex would then conduct intercepts of enemy satellites in orbits up to 6,000 km in altitude. Soyuz P was cancelled in 1963. Soyuz R The Soyuz-R system (1963-1966) consisted of two separately launched spacecraft, including the small orbital station 11F7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos 670
Kosmos 670 ( meaning ''Cosmos 670'') was an unmanned space mission, unmanned Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz Military_Soyuz#Soyuz_7K-S, 7K-S test. It used a new and unique inclination of 50.6 degree. The experience from these flights were used in the development of the successor program Soyuz spacecraft the Soyuz 7K-ST. Mission parameters *Spacecraft: 7K-S *Mass: 6700 kg *Crew: None *Launched: August 6, 1974 *Landed: August 8, 1974 23:59 UTC. *Perigee: 221 km *Apogee: 294 km *Inclination: 50.6 deg *Duration: 2.99 days See also *Kosmos 772 *Kosmos 869 References Kosmos satellites, Kosmos 0670 1974 in the Soviet Union Spacecraft launched in 1974 Soyuz uncrewed test flights {{USSR-spacecraft-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
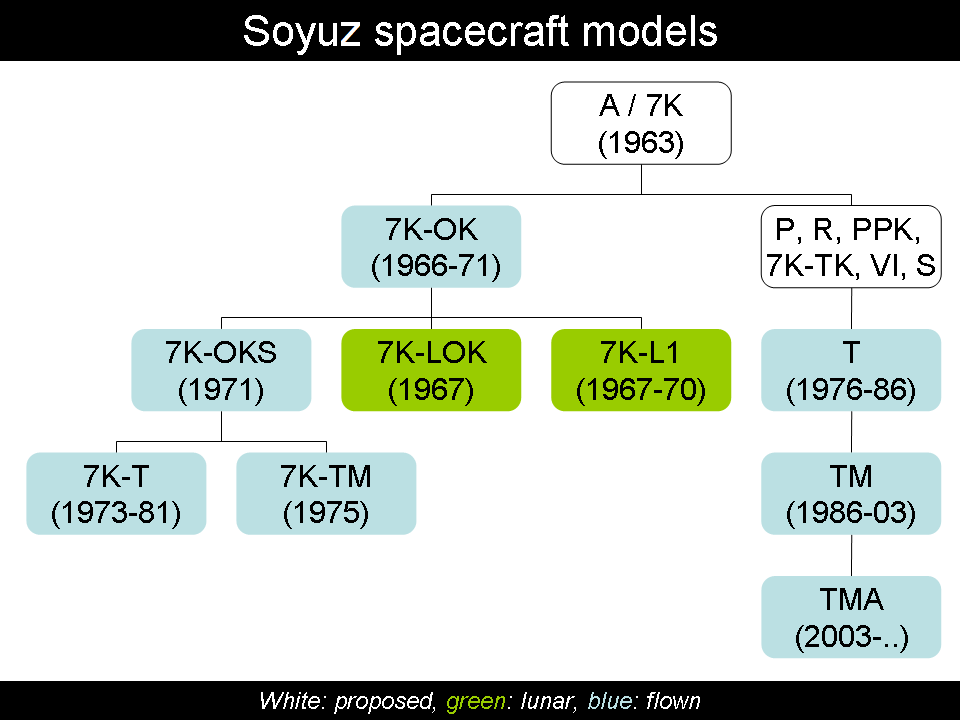
Chart Of Soyuz Spacecraft Models
A chart (sometimes known as a graph) is a graphical representation for data visualization, in which "the data is represented by symbols, such as bars in a bar chart, lines in a line chart, or slices in a pie chart". A chart can represent tabular numeric data, functions or some kinds of quality structure and provides different info. The term "chart" as a graphical representation of data has multiple meanings: * A data chart is a type of diagram or graph, that organizes and represents a set of numerical or qualitative data. * Maps that are adorned with extra information (map surround) for a specific purpose are often known as charts, such as a nautical chart or aeronautical chart, typically spread over several map sheets. * Other domain-specific constructs are sometimes called charts, such as the chord chart in music notation or a record chart for album popularity. Charts are often used to ease understanding of large quantities of data and the relationships between parts of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Almaz
The Almaz () program was a highly secret Soviet Union, Soviet military space station program, begun in the early 1960s. Three crewed military reconnaissance stations were launched between 1973 and 1976: Salyut 2, Salyut 3 and Salyut 5. To cover the military nature of the program, the three launched Almaz stations were designated as civilian Salyut programme, Salyut space stations. Salyut 2 failed shortly after achieving orbit, but Salyut 3 and Salyut 5 both conducted successful crewed testing. Following Salyut 5, the Ministry of Defense (Soviet Union), Soviet Ministry of Defense judged in 1978 that the time and resources consumed by station maintenance outweighed the benefits relative to automatic reconnaissance satellites. Still, it had some achievements along with the Salyut program, the heritage of the twin program continues, with the International Space Station module Zarya (ISS module), Zarya being one example. The space stations' cores were known internally as OPS (, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kosmos 772
Kosmos 772 ( meaning ''Cosmos 772'') was an uncrewed military Soyuz 7K-S test. It was an unsuccessful mission as only one transmitter worked. Only the 166 MHz frequency transmitter operated, all of the other normal Soyuz wavelengths transmitters failed. The experience from these flights were used in the development of the successor program Soyuz spacecraft the Soyuz 7K-ST. Mission parameters *Spacecraft: Soyuz 7K-S *Mass: 6750 kg *Crew: None *Launched: September 29, 1975 *Landed: October 3, 1975 4:10 UTC *Perigee: 154 km *Apogee An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values. Apsides perta ...: 245 km *Inclination: 51.8 deg *Duration: 3.99 days Maneuver Summary *193 km X 270 km orbit to 195 km X 300 km orbit. Delta V: 8 m/s. *196 km X 300 km orbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo–Soyuz
Apollo–Soyuz was the first crewed international Space exploration, space mission, carried out jointly by the United States and the Soviet Union in July 1975. Millions of people around the world watched on television as an American Apollo command and service module, Apollo spacecraft Docking and berthing of spacecraft, docked with a Soviet Soyuz (spacecraft), Soyuz capsule. The project, and its "handshake" in space, was a symbol of détente between the two superpowers amid the Cold War. The Americans officially called the mission the Apollo–Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) while the Soviets called it Experimental flight "Soyuz"–"Apollo" () and Soyuz 19. The unnumbered American spacecraft was left over from canceled Apollo missions and was the last Apollo module to fly. The mission consisted of three American astronauts (Thomas P. Stafford, Vance D. Brand, and Deke Slayton) and two Soviet cosmonauts (Alexei Leonov and Valery Kubasov) who performed both joint and separate scientifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launch Escape System
A launch escape system (LES) or launch abort system (LAS) is a crew-safety system connected to a space capsule. It is used in the event of a critical emergency to quickly separate the capsule from its launch vehicle in case of an emergency requiring the abort of the launch, such as an impending explosion. The LES is typically controlled by a combination of automatic rocket failure detection, and a manual activation for the crew commander's use. The LES may be used while the launch vehicle is on the launch pad, or during its ascent. Such systems are usually of three types: *A solid-fueled rocket, mounted above the capsule on a tower, which delivers a relatively large thrust for a brief period of time to send the capsule a safe distance away from the launch vehicle, at which point the capsule's parachute recovery system can be used for a safe landing on ground or water. The escape tower and rocket are jettisoned from the space vehicle in a normal flight at the point where it is eit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Panel
A solar panel is a device that converts sunlight into electricity by using photovoltaic (PV) cells. PV cells are made of materials that produce excited electrons when exposed to light. These electrons flow through a circuit and produce direct current (DC) electricity, which can be used to power various devices or be stored in battery (electricity), batteries. Solar panels are also known as solar cell panels, solar electric panels, or PV modules. Solar panels are usually arranged in groups called arrays or systems. A photovoltaic system consists of one or more solar panels, an solar inverter, inverter that converts DC electricity to alternating current (AC) electricity, and sometimes other components such as charge controller, controllers, Measuring instrument, meters, and solar tracker, trackers. Most panels are in solar farms or Rooftop solar power, rooftop solar panels which grid-connected photovoltaic system, supply the electricity grid. Some advantages of solar panels are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gennadiy Kolesnikov
Gennady ( rus, Геннадий, p=ɡʲɪˈnadʲɪj), also transcribed Gennadi or Gennadiy, is a Russian male name. It is derived from the Greek given name Γεννάδιος (Gennadios), latinized Gennadius. People *Gennady Dobrokhotov, Soviet boxer *Gennady Gladkov, Soviet and Russian composer *Gennady Golovkin, Kazakh boxer *Gennady Gudkov, Russian politician and businessman * Gennadi Karponosov, Soviet and Russian Olympic and world champion ice dancer and coach *Gennady Korotkevich, Belarusian sport programmer * Gennady Logofet, Soviet and Russian footballer and football coach *Gennady Semenovich Makanin, Russian mathematician *Gennady Mikhasevich, prolific Soviet serial killer and rapist *Gennady of Novgorod, Russian archbishop *Gennady Padalka, Russian cosmonaut *Gennady Rozhdestvensky, Soviet and Russian conductor *Gennadi Syomin, Russian footballer and football coach *Genndy Tartakovsky, Russian-American cartoonist *Gennady Yanayev, the only vice president of the Soviet Uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boris Nikolaevich Belousov
Boris may refer to: People * Boris (given name), a male given name * *List of people with given name Boris * Boris (surname) Arts and media * Boris (band), a Japanese experimental rock trio * ''Boris'' (EP), by Yezda Urfa, 1975 * "Boris" (song), by the Melvins, 1991 * ''Boris'' (TV series), a 2007–2010, 2022–present Italian comedy series * '' Boris: The Film'', a 2011 Italian film based on the TV series * '' Boris: The Rise of Boris Johnson'', a 2006 biography by Andrew Gimson Other uses * Boris (crater), a lunar crater * Hurricane Boris (other), several cyclones in the Eastern Pacific * Boris, a tribe of the Adi people See also * Borris (other) * Boris stones Boris Stones (, ; ), also called Dvina Stones (), are seven medieval Artifact (archaeology), artifacts erected along the bank of the Western Dvina between Polotsk and Drissa, Belarus. They probably predate Christianity in the area, but were insc ..., seven medieval artifacts in Belarus {{disa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Gulyaev
Vladimir Leonidovich Gulyaev (; 30 October 1924, Yekaterinburg, RSFSR — 3 October 1997, Moscow) was a Soviet actor of theater and cinema. Biography He was born October 30, 1924, in Sverdlovsk (now Yekaterinburg, Russia). His father was as candidate of historical sciences and the deputy head of the political department of the Molotov Military Aviation. During World War II, he went to work as a mechanic in an aviation workshop, and in 1942, became a cadet of Molotovskaya military aviation school of pilots. Having graduated with honors and received in November 1943 and received the rank of Junior Lieutenant of the Air Force. He fought in Belarus and the Baltic States. He ended his service as a Red Army lieutenant in East Prussia. He participated in the Moscow Victory Parade of 1945 on Red Square. He graduated from Gerasimov Institute of Cinematography in 1951. As a student, he married his classmate Rimma Shorokhov. By the mid-1950s, the couple broke up. Form 1951-1988, he was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |