|
Microcystin
Microcystins—or cyanoginosins—are a class of cyanotoxins, which are toxins produced by cyanobacteria, sometimes known as blue-green algae. Over 250 different microcystins have been discovered so far, of which microcystin-LR is the most common. Chemically they are cyclic heptapeptides produced through nonribosomal peptide synthases. Cyanobacteria can produce microcystins in large quantities during algal blooms which then pose a major threat to drinking and irrigation water supplies, and the environment at large. Characteristics Microcystins—or cyanoginosins—are a class of toxins produced by certain freshwater cyanobacteria; primarily ''Microcystis aeruginosa'' but also other '' Microcystis'', as well as members of the ''Planktothrix'', ''Anabaena'', ''Oscillatoria'' and ''Nostoc'' genera. Microcystin-LR (i.e. ''X'' = leucine, ''Z'' = arginine) is the most toxic form of over 80 known toxic variants, and is also the most studied by chemists, pharmacologists, biologists, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcystin-LR
Microcystin-LR (MC-LR) is a toxin produced by cyanobacteria. It is the most toxic of the microcystins. Structure Microcystins are cyclic heptapeptides. The seven amino acids that are involved in the structure of a microcystin include the unique amino acids ADDA and D-β-methyl-isoaspartate (D-β-Me-isoAsp). Furthermore, microcystins contain two variable residues, which make the differentiation between variants of microcystins. These two variable functionalities are always standard proteinogenic amino acids - In microcystin-LR these are leucine and arginine. More than 250 microcystins have been identified to date,''Structural Diversity, Characterization and Toxicology of Microcystins'', doi: 10.3390/toxins11120714 representing differences in the two variable residues and some modifications in the other amino acids. These modifications include demethylation of Masp and Mdha and methylesterification of D-Glu. Different microcystins have different toxicity profiles, with microcys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodularin
Nodularins are potent toxins produced by the cyanobacterium ''Nodularia spumigena'', among others. This aquatic, photosynthetic cyanobacterium forms visible colonies that present as algal blooms in brackish water bodies throughout the world. The late summer blooms of ''Nodularia spumigena'' are among the largest cyanobacterial mass occurrences in the world. Cyanobacteria are composed of many toxic substances, most notably of microcystins and nodularins: the two are not easily differentiated. A significant homology of structure and function exists between the two, and microcystins have been studied in greater detail. Because of this, facts from microcystins are often extended to nodularins. Nodularin-R is the predominant toxin variant, though 10 variants of nodularin have been discovered to date. Nodularins are cyclic nonribosomal pentapeptides and contain several unusual non-proteinogenic amino acids such as N-methyl-didehydroaminobutyric acid and the β-amino acid ADDA. These ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanotoxin
Cyanotoxins are toxins produced by cyanobacteria (also known as blue-green algae). Cyanobacteria are found almost everywhere, but particularly in lakes and in the ocean where, under high concentration of phosphorus conditions, they reproduce exponentially to form blooms. Blooming cyanobacteria can produce cyanotoxins in such concentrations that they can poison and even kill animals and humans. Cyanotoxins can also accumulate in other animals such as fish and shellfish, and cause poisonings such as shellfish poisoning. Some of the most powerful natural poisons known are cyanotoxins. They include potent neurotoxins, hepatotoxins, cytotoxins, and endotoxins. The ''cyano'' in the term cyanobacteria refers to its colour, not to its relation to cyanides, though cyanobacteria can catabolize hydrogen cyanide during nitrogen fixation. Exposure to cyanobacteria can result in gastro-intestinal and hayfever symptoms or pruritic skin rashes. Exposure to the cyanobacteria neurotoxin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcystis Aeruginosa
''Microcystis aeruginosa'' is a species of freshwater cyanobacteria that can form harmful algal blooms of economic and ecological importance. They are the most common toxic cyanobacterial bloom in eutrophic fresh water. Cyanobacteria produce neurotoxins and peptide hepatotoxins, such as microcystin and cyanopeptolin. ''Microcystis aeruginosa'' produces numerous congeners of microcystin, with microcystin-LR being the most common. Microcystis blooms have been reported in at least 108 countries, with the production of microcystin noted in at least 79. Characteristics As the etymological derivation implies, ''Microcystis'' is characterized by small cells (of only a few micrometers diameter), which lack individual sheaths. Cells usually are organized into colonies (large colonies of which may be viewed with the naked eye) that begin in a spherical shape, but lose their coherence to become perforated or irregularly shaped over time in culture. Recent evidence suggests one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanobacteria
Cyanobacteria ( ) are a group of autotrophic gram-negative bacteria that can obtain biological energy via oxygenic photosynthesis. The name "cyanobacteria" () refers to their bluish green (cyan) color, which forms the basis of cyanobacteria's informal common name, blue-green algae. Cyanobacteria are probably the most numerous taxon to have ever existed on Earth and the first organisms known to have produced oxygen, having appeared in the middle Archean eon and apparently originated in a freshwater or terrestrial environment. Their photopigments can absorb the red- and blue-spectrum frequencies of sunlight (thus reflecting a greenish color) to split water molecules into hydrogen ions and oxygen. The hydrogen ions are used to react with carbon dioxide to produce complex organic compounds such as carbohydrates (a process known as carbon fixation), and the oxygen is released as a byproduct. By continuously producing and releasing oxygen over billions of years, cyanobacte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcystis
''Microcystis'' is a genus of freshwater cyanobacteria that includes the harmful algal bloom-forming '' Microcystis aeruginosa''. Over the last few decades, cyanobacterial blooms caused by eutrophication have become a major environmental problem in aquatic ecosystems worldwide, and the most representative and harmful cyanobacteria is ''Microcystis''.'''' ''Microcystis'' blooms have increased due to global climate change, spanning six continents and causing increased health risks to wildlife and humans. This article will address the conditions for the growth of ''Microcystis,'' physical characteristics, ecology, geographic distribution'','' and health risks of ''Microcystis.'' Conditions for ''Microcystis'' During the summer in temperate systems, ''Microcystis'' can rise to form blooms on the water surface. These blooms, linked to anthropogenic nutrient loading, occur generally when water temperatures exceed 15 °C. But, as the global climate changes, the intensity and oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planktothrix
''Planktothrix'' is a diverse genus of filamentous cyanobacteria observed to amass in algal blooms in water ecosystems across the globe. Like all Oscillatoriales, ''Planktothrix'' species have no heterocyst, heterocysts and no akinetes. ''Planktothrix'' are unique because they have Trichome#Algal trichomes, trichomes and contain gas vacuoles unlike typical planktonic organisms. Previously, some species of the taxon were grouped within the genus ''Oscillatoria'', but recent work has defined ''Planktothrix'' as its own genus. A tremendous body of work on ''Planktothrix'' ecology and physiology has been done by A.E. Walsby, Anthony E. Walsby, and the 55.6 kb microcystin synthetase gene which gives these organisms the ability to synthesize toxins has been sequenced. ''P. agardhii'' is an example of a Holotype, type species of the genus. ''P. agardhii'' and ''P. rubescens'' are commonly observed in lakes of the Northern Hemisphere where they are known producers of potent hepatotoxins ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonribosomal Peptide
Nonribosomal peptides (NRP) are a class of peptide secondary metabolites, usually produced by microorganisms like bacterium, bacteria and fungi. Nonribosomal peptides are also found in higher organisms, such as nudibranchs, but are thought to be made by bacteria commensalism, inside these organisms. While there exist a wide range of peptides that are not synthesized by ribosomes, the term ''nonribosomal peptide'' typically refers to a very specific set of these as discussed in this article. Nonribosomal peptides are synthesized by nonribosomal peptide synthetases, which, unlike the ribosomes, are independent of messenger RNA. Each nonribosomal peptide synthetase can synthesize only one type of peptide. Nonribosomal peptides often have cyclic compound, cyclic and/or branched structures, can contain non-proteinogenic amino acids including D-amino acids, carry modifications like ''Nitrogen, N''-methyl and ''N''-formyl groups, or are Glycosylation, glycosylated, Acylation, acylated, Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pansteatitis
Pansteatitis, or yellow fat disease, is a physiological condition in which the body fat becomes inflamed. Presentations The condition has been found in cats, fish, herons, terrapins and Nile crocodiles, piscivores such as otters, cormorants, Pel's fishing-owls and fish eagles. The disorder is also regularly found in captive-bred animals fed on high fish diets, such as mink, pigs and poultry. It shows as a rubber-like hardening of fat reserves which then become unavailable for normal metabolism, resulting in extreme pain, loss of mobility and death. Causes It is thought to be brought about by any or a combination of a number of factors which include: * Vitamin E deficiency *Microcystin and nodularin poisoning, via inhibition of protein phosphatases *Heavy metals and other fat-accumulated pollutants such as DDT, Polychlorinated biphenyls, PCBs, PCDDs and brominated flame retardants *Ingestion of affected animals *Pathogens as yet unidentified Incidents In 2008 about 170 crocodile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
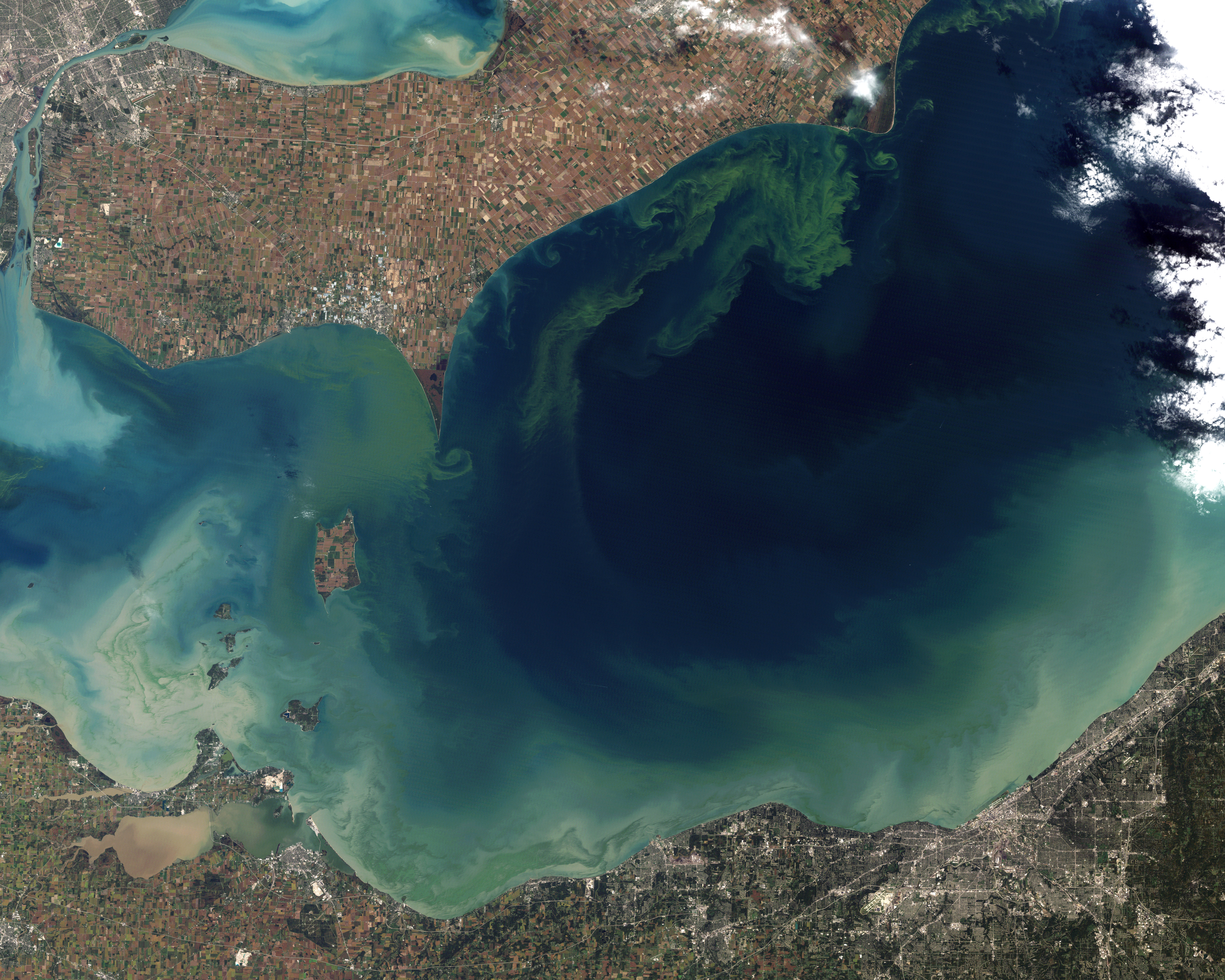
Hartebeespoort Dam
Hartbeespoort Dam (also known as ''Harties'') is an arch type dam situated in the North West (South African province), North West Province of South Africa. It lies in a valley to the south of the Magaliesberg mountain range and north of the Witwatersberg mountain range, about 35 kilometres north west of Johannesburg and 20 kilometres west of Pretoria. The name of the dam means "dam at the gorge of the hartebeest" (a species of antelope) in Afrikaans language, Afrikaans. This "poort" in the Magaliesberg was a popular spot for hunters, where they cornered and shot the hartebeest. The dam was originally designed for irrigation, which is currently its primary use, as well as for domestic and industrial use. The dam is considered to be in a Trophic state index, hypereutrophic state since the early 1970s. Mismanagement of waste water treatment from urban zones within the Hartbeespoort Dam catchment area is largely to blame, having distorted the food web with over 280 tons of phosphate an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
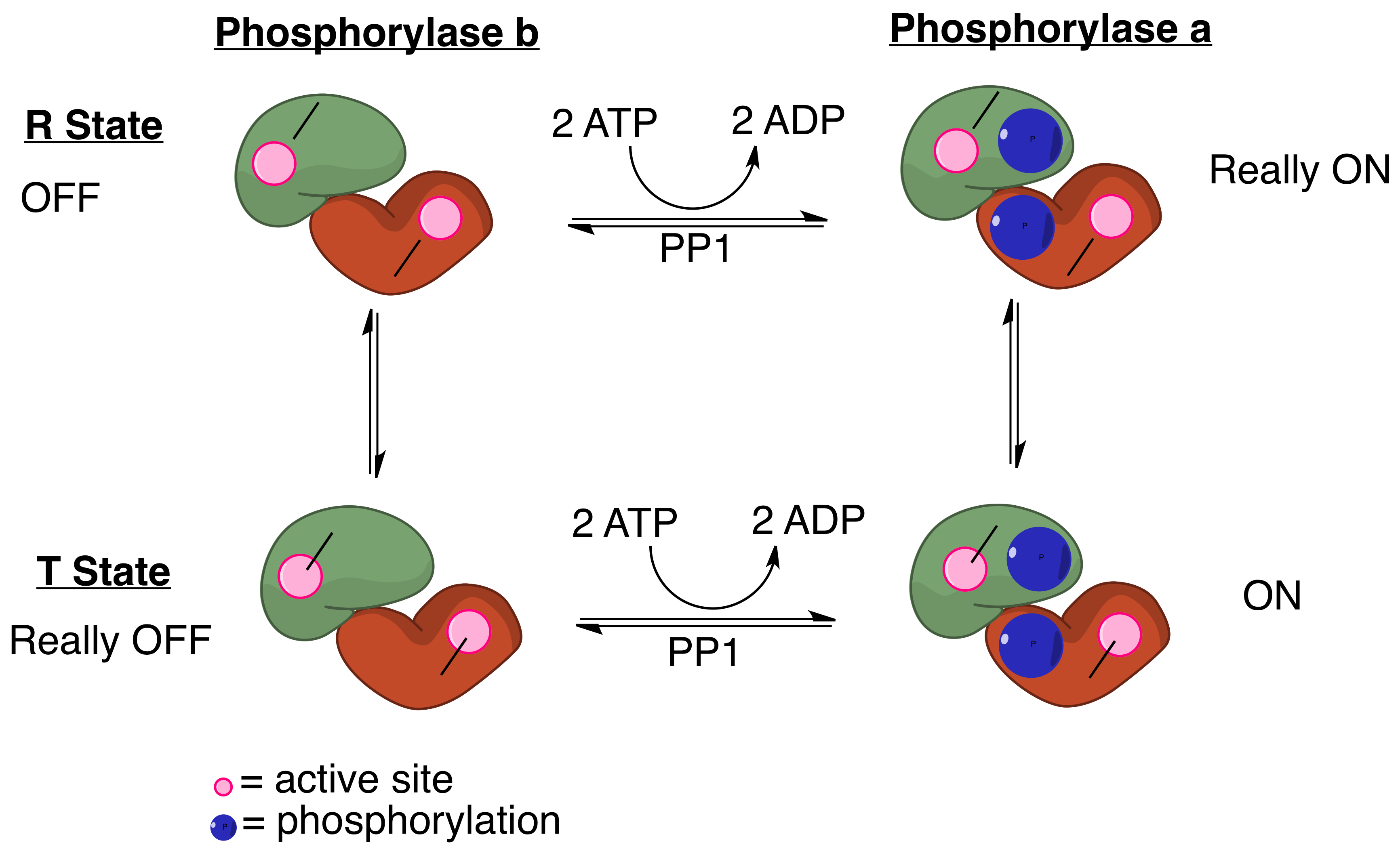
Protein Phosphatase 1
Protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) belongs to a certain class of phosphatases known as protein serine/threonine phosphatases. This type of phosphatase includes metal-dependent protein phosphatases (PPMs) and aspartate-based phosphatases. PP1 has been found to be important in the control of glycogen metabolism, muscle contraction, cell progression, neuronal activities, splicing of RNA, mitosis, cell division, apoptosis, protein synthesis, and regulation of membrane receptors and channels. Structure Each PP1 enzyme contains both a catalytic subunit and at least one regulatory subunit. The catalytic subunit consists of a 30-kD single-domain protein that can form complexes with other regulatory subunits. The catalytic subunit is highly conserved among all eukaryotes, thus suggesting a common catalytic mechanism. The catalytic subunit can form complexes with various regulatory subunits. These regulatory subunits play an important role in substrate specificity as well as Cellular compartmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |