|
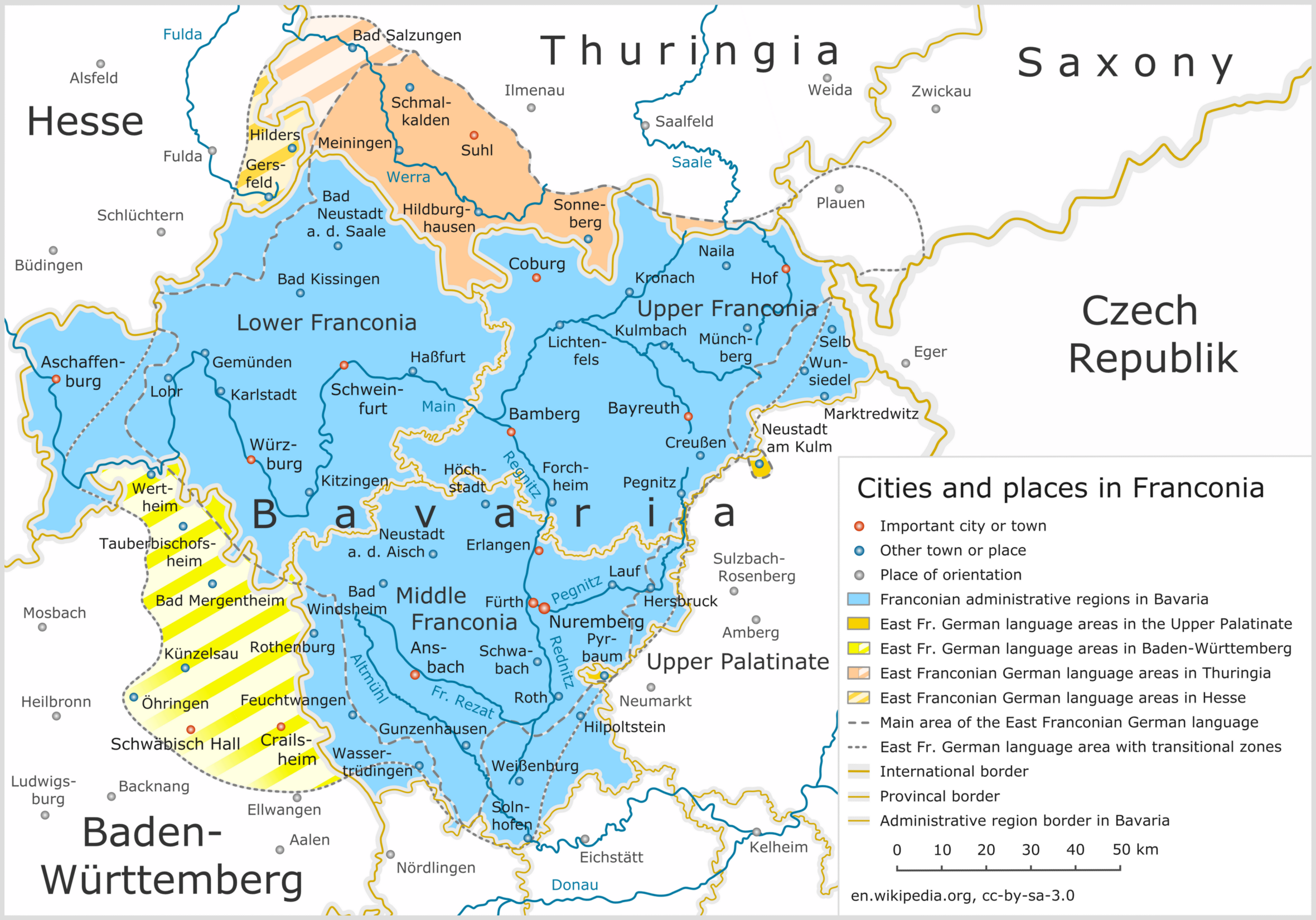
Mergentheim
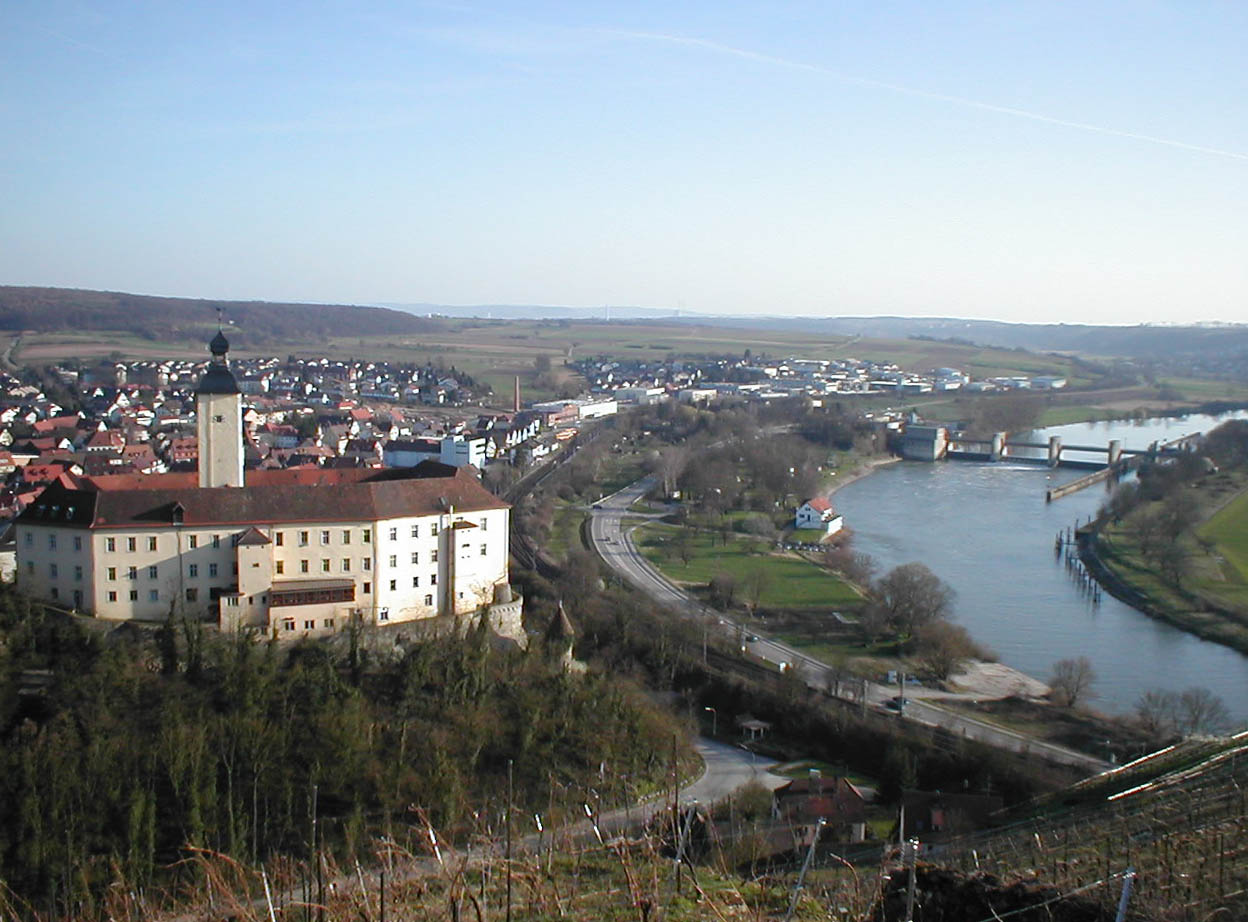
Bad Mergentheim (; Mergentheim until 1926; East Franconian: ''Märchedol'') is a town in the Main-Tauber-Kreis district in the German state of Baden-Württemberg. It has a population of around 23,000. An officially recognized spa town since 1926, Bad Mergentheim is also known as the headquarters of the Teutonic Order from 1526 until 1809. Geography Subdivisions Since administrative reform in the 1970s the following villages have been part of the municipality: Althausen ''(pop. 600)'', Apfelbach ''(350)'', Dainbach ''(370)'', Edelfingen ''(1,400''; birthplace of the American biochemist Julius Adler), Hachtel ''(360)'', Herbsthausen ''(200)'', Löffelstelzen ''(1,000)'', Markelsheim ''(2,000)'', Neunkirchen ''(1,000)'', Rengershausen ''(480)'', Rot ''(260)'', Stuppach ''(680)'', Wachbach ''(1,300)'' History Mergentheim is mentioned in chronicles as early as 1058, as the residence of the family of the counts of Hohenlohe. The brothers Andreas, Heinrich and Friedrich von Hohenlohe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutonic Order
The Teutonic Order is a religious order (Catholic), Catholic religious institution founded as a military order (religious society), military society in Acre, Israel, Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to the Holy Land and to establish hospitals. Its members have commonly been known as the Teutonic Knights, having historically served as a crusades, crusading military order for supporting Catholic rule in the Holy Land and the Northern Crusades during the Middle Ages, as well as supplying military protection for Catholics in Eastern Europe. Purely religious since 1810, the Teutonic Order still confers limited honorary knighthoods. The Bailiwick of Utrecht of the Teutonic Order, a Protestant order of chivalry, chivalric order, is descended from the same medieval military order and also continues to award knighthoods and perform charitable work. Name The name of the Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohenlohe
The House of Hohenlohe () is a German princely dynasty. It formerly ruled an immediate territory within the Holy Roman Empire, which was divided between several branches. In 1806, the area of Hohenlohe was 1,760 km² and its estimated population was 108,000. The motto of the house is (Latin for 'From flames I rise'). The Lords of Hohenlohe were elevated to the rank of Imperial Counts in 1450, and from 1744, the territory and its rulers were princely. In 1825, the German Confederation recognized the right of all members of the house to be styled as Serene Highness (German: ), with the title of for the heads of its branches, and the title of prince/princess for the other members. From 1861, the Hohenlohe- Öhringen branch was also of ducal status as dukes of Ujest. Due to the continuous lineage of the dynasty until the present time, it is considered to be one of the longest-lived noble families in Germany and Europe. The large state coat of arms of Baden-Württemberg to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter Von Cronberg
Walter von Cronberg (before 14804 April 1543) was the 38th Grand Master of the Teutonic Order, from 1527 to 1543. Biography Von Cronberg hailed from a rather poor family of knights from Kronberg Castle near Frankfurt. He joined the Teutonic Order in 1497 and held the post of a tax collector in the Komturei of Mergentheim from 1499. He became the Komtur of Frankfurt in 1504. During the times of his predecessor, Albert of Brandenburg-Ansbach, von Cronberg was the legate to King Sigismund I (the Old) of Poland. In 1517, he founded the Brotherhood of St. Sebastian and, in 1526, he was chosen ''Deutschmeister'' (the Master of the German branch of the Order). In 1525, when Albert had converted to Lutheranism and was excommunicated, von Cronberg declared himself the next Grand Master. His claim was based on a statute of Werner von Orseln from the 14th century, which stated that in the case of the absence of the Grand Master, the Master of one of the other branches of the Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main-Tauber-Kreis
Main-Tauber-Kreis is a ''Landkreis'' (district) in the northeast of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Neighboring districts are (from northwest clockwise) Miltenberg, Main-Spessart, Würzburg, Neustadt (Aisch)-Bad Windsheim and Ansbach (all in Bavaria), and the districts of Schwäbisch Hall, Hohenlohe and Neckar-Odenwald. History Traces of human population in the area were found to go back as early as 5500 B.C. Throughout the 18th and 19th century, during the so''-''called ''Kleinstaaterei'', southern parts of today's district were part of the free imperial city of Rothenburg ob der Tauber, the Principality of Ansbach, while the city of Weikersheim played a major role in the history of the Hohenlohe dynasty and temporarily was one of its seats. Later, the biggest part of the district was part of the Bishopric of Würzburg until 1803. Bad Mergentheim belonged to the Teutonic order and Tauberbischofsheim, the districts capitcal, was part of Kurmainz from 1237 to 1803. Coat o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Adler (biochemist)
Julius Adler (April 30, 1930 – April 2, 2024) was an American biochemist. He had been an Emeritus Professor of biochemistry and genetics at the University of Wisconsin–Madison since 1997. Early life Adler was born in Edelfingen, Germany in 1930. He came to the United States in 1938 at the age of 8 and became a naturalized citizen in 1943. His family settled in Grand Forks, North Dakota where their relatives were among the first Europeans to arrive in 1880. Since he was child, Adler had been fascinated by how organisms sense and respond to the environment. Education Adler attended Harvard University and received his A.B. in Biochemical Sciences in 1952. He then studied with Henry A. Lardy at the University of Wisconsin–Madison and earned an M.S. in Biochemistry in 1954 and a Ph.D. in Biochemistry in 1957. After graduating, Adler did postdoctoral fellowships with Arthur Kornberg in the Department of Microbiology at Washington University School of Medicine (1957–59) a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Franconian German
East Franconian ( ), usually referred to as Franconian (' ) in German, is a dialect spoken in Franconia, the northern part of the federal state of Bavaria and other areas in Germany around Nuremberg, Bamberg, Coburg, Würzburg, Hof, Bayreuth, Meiningen, Bad Mergentheim, and Crailsheim. The major subgroups are ' (spoken in Lower Franconia and southern Thuringia), ' (spoken in Upper and Middle Franconia) and ' (spoken in some parts of Middle Franconia and Hohenlohe). Until the wholesale expulsion of Germans from Bohemia, the dialect was also spoken around Saaz (today: Žatec). In the transitional area between Rhine Franconian in the northwest and the Austro-Bavarian dialects in the southeast, East Franconian has elements of Central German and Upper German. The same goes only for South Franconian German in adjacent Baden-Württemberg Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spa Town
A spa town is a resort town based on a mineral spa (a developed mineral spring). Patrons visit spas to "take the waters" for their purported health benefits. Thomas Guidott set up a medical practice in the English town of Bath, Somerset, Bath in 1668. He became interested in the curative properties of the hot mineral waters there and in 1676 wrote ''A discourse of Bathe, and the hot waters there. Also, Some Enquiries into the Nature of the water''. This brought the purported health-giving properties of the waters to the attention of the aristocracy, who started to partake in them soon after. The term ''spa'' is used for towns or resorts offering hydrotherapy, which can include cold water or mineral water treatments and geothermal baths, and comes from the Belgian town Spa, Belgium, Spa. Spa towns by country Argentina *Termas de Rio Hondo *Presidencia Roque Sáenz Peña Australia There are mineral springs in the Central Highlands of Victoria. Most are in and around Daylesfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horneck Castle, Germany
Horneck Castle is also known as Burg Horneck, Deutschordenschloss Horneck and Schloss Horneck. A castle located in the town of Gundelsheim, district of Heilbronn, Baden-Württemberg, in southwest Germany. Its name is thought to mean "over the Neckar," as it is overlooking the Neckar River. History The castle was built around 1200 and was given to the Teutonic Order by Konrad von Horneck in 1438, thereby making it the seat of the "Deutschmeister" (German Master) until it was destroyed in 1525 by fire during the German Peasants' War. Despite reconstruction shortly after Horneck Castle's destruction, Mergentheim became the new headquarters for the Teutonic Order The Teutonic Order is a religious order (Catholic), Catholic religious institution founded as a military order (religious society), military society in Acre, Israel, Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Sa ... in that region in 1527. , the castle was occupied by an altenheim (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheinbund
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine or Rhine Confederation, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austrian Empire, Austria and Russian Empire, Russia at the Battle of Austerlitz. Its creation brought about the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire shortly afterward. The Confederation of the Rhine lasted for only seven years, from 1806 to 1813, dissolving after Napoleon's defeat in the War of the Sixth Coalition.Hans A. Schmitt. "Germany Without Prussia: A Closer Look at the Confederation of the Rhine". ''German Studies Review'' 6, No. 4 (1983), pp 9–39. The founding members of the confederation were German princes of the Holy Roman Empire. They were later joined by 19 others, altogether ruling a total of over 15 million people. This granted a significant strategic advantage to the French Empire on its eastern frontier by providing a buffer between France and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maria Theresa
Maria Theresa (Maria Theresia Walburga Amalia Christina; 13 May 1717 – 29 November 1780) was the ruler of the Habsburg monarchy from 1740 until her death in 1780, and the only woman to hold the position suo jure, in her own right. She was the sovereign of Archduchy of Austria, Austria, Kingdom of Hungary, Hungary, Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg), Croatia, Crown of Bohemia, Bohemia, Principality of Transylvania (1711–1867), Transylvania, Slavonia, Duchy of Mantua, Mantua, Duchy of Milan, Milan, Moravia, Galicia and Lodomeria, Dalmatia, Austrian Netherlands, Carinthia, Carniola, Gorizia and Gradisca, Austrian Silesia, Tyrol (state), Tyrol, Styria and Duchy of Parma, Parma. By marriage, she was List of Lorrainian royal consorts#House of Vaudemont, 1473–1737, Duchess of Lorraine, List of Tuscan consorts#House of Lorraine, 1737–1765, Grand Duchess of Tuscany, and List of Holy Roman empresses#House of Lorraine, Holy Roman Empress. Through her aunt, Charlotte Christine of Brunswi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electorate Of Cologne
The Electorate of Cologne (), sometimes referred to as Electoral Cologne (), was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that existed from the 10th to the early 19th century. It consisted of the Hochstift—the temporal possessions—of the archbishop of Cologne, and was ruled by him in his capacity as prince-elector. There were only two other ecclesiastical prince-electors in the Empire: the Electorate of Mainz and the Electorate of Trier. The archbishop-elector of Cologne was also arch-chancellor of Italy (one of the three component titular kingdoms of the Holy Roman Empire, the other two being Germany and Burgundy) and, as such, ranked second among all ecclesiastical and secular princes of the Empire, after the archbishop-elector of Mainz, and before that of Trier. The capital of the electorate was Cologne. Conflicts with the citizens of Cologne caused the elector to move to Bonn. The Free Imperial City of Cologne was recognized after 1475, thus removing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Van Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music repertoire and span the Transition from Classical to Romantic music, transition from the Classical period (music), Classical period to the Romantic music, Romantic era. His early period, during which he forged his craft, is typically considered to have lasted until 1802. From 1802 to around 1812, his middle period showed an individual development from the styles of Joseph Haydn and Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and is sometimes characterised as heroic. During this time, Beethoven began to grow increasingly Hearing loss, deaf. In his late period, from 1812 to 1827, he extended his innovations in musical form and expression. Born in Bonn, Beethoven displayed his musical talent at a young age. He was initially taught intensively by his father, Johann van Bee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |