|
Mercedes-Benz In Motorsport
Throughout its long history, Mercedes-Benz has been involved in a range of successful motorsport activities, including sportscar racing, touring car racing, Grand Prix racing, and rallying. It is currently active in GT racing, and Formula One. Mercedes is also one of only three constructors to complete the Triple Crown of Motorsport#Teams and manufacturers, Triple Crown of Motorsport (wins at the Indianapolis 500, 24 Hours of Le Mans, and Monaco Grand Prix), a feat that Mercedes achieved as both a ''chassis manufacturer'' and an ''engine manufacturer'' by winning the 1952 24 Hours of Le Mans. Early history The two companies which were merged to form the ''Mercedes-Benz'' brand in 1926 had both already enjoyed success in the new sport of motor racing throughout their separate histories. A single Benz competed in the world's first motor race, the Paris–Rouen (motor race), 1894 Paris–Rouen, where Émile Roger finished 14th in 10 hours 1 minute. In spring 1888, Roger was granted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercedes 35 Hp
The Mercedes () was a radical early car model designed in 1901 by Wilhelm Maybach and Paul Daimler, for Emil Jellinek. Produced in Stuttgart, Germany, by Daimler-Motoren-Gesellschaft (DMG), it began the Mercedes line of cars (since 1926 re-branded Mercedes-Benz). Its name is derived from the power of the engine, , approximately . A significant advancement over the previous generation of automobiles, which were modified stagecoaches, the Mercedes is regarded as the first modern car. It was equipped with a powerful petrol engine, it was both wider and larger with a tailored steel chassis, and its center of mass was near the ground. Originally designed as a racing car, the Mercedes was further developed for normal road use. Historical background In the 19th century, Wilhelm Maybach's career as an industrial designer had been with Gottlieb Daimler in their Cannstatt workshop (near Stuttgart), at which together they had pioneered the petrol engine production and were responsible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autodromo Nazionale Monza
The Monza Circuit ( Italian: ; ) is a race track near the city of Monza, north of Milan, in Italy. Built in 1922, it was the world's third purpose-built motor racing circuit after Brooklands and Indianapolis and the oldest in mainland Europe. The circuit's biggest event is the Italian Grand Prix. With the exception of the 1980 running when the track was closed while undergoing refurbishment, the race has been hosted there since 1949. The circuit is also known as "The Temple of Speed" due to its long straights and high-speed corners. Built in the Royal Villa of Monza park in a woodland setting, the site has three tracks – the Grand Prix track, the Junior track, and a high speed oval track with steep bankings, which was left unused for decades and had been decaying until it was restored in the 2010s. The major features of the main Grand Prix track include the ''Curva Grande'', the ''Curva di Lesmo'', the ''Variante Ascari'' and the ''Curva Alboreto'' (formerly ''Curva Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Grand Prix
The European Grand Prix (also known as the Grand Prix of Europe) was a Formula One event that was introduced during the mid-1980s and was held every year from to , except in . During these years, the European Grand Prix was held in a country that hosted its own national Grand Prix at a different point in the same season, at a different circuit (except in ). The race returned as a one-off in , being held on a street circuit in Baku, Azerbaijan. In earlier years, the European Grand Prix was not a race in its own right, but an honorific title given to one of the national Grands Prix in Europe. The first race to be so named was the 1923 Italian Grand Prix, held at Monza, and the last was the 1977 British Grand Prix at Silverstone. As an honorific title The European Grand Prix was created as an honorific title by the AIACR, the FIA's predecessor in the organisation of motor racing events. The first race to receive the title was the Italian Grand Prix, in 1923; the French Gran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Prix Motor Racing
Grand Prix motor racing, a form of motorsport competition, has its roots in organised automobile racing that began in France as early as 1894. It quickly evolved from simple road races from one town to the next, to endurance tests for car and driver. Innovation and the drive of competition soon saw speeds exceeding , but because early races took place on open roads, accidents occurred frequently, resulting in deaths both of drivers and of spectators. A common abbreviation used for Grand Prix racing is "GP" or "GP racing". Grand Prix motor racing eventually evolved into formula racing, with Formula One considered its direct descendant. Each event of the Formula One World Championships is still called a ''Grand Prix''; Formula One is also referred to as "Grand Prix racing". Some IndyCar championship races are also called "Grands Prix". Origins of organised racing Motor racing was started in France, as a direct result of the enthusiasm with which the French public embrace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benz Tropfenwagen
Benz, an old Germanic clan name dating to the fifth century (related to "bear", "war banner", "gau", or a "land by a waterway") also used in German () as an alternative for names such as Berthold, Bernhard, or Benedict, may refer to: People Surname * Amy Benz (born 1962), American golfer * Bertha Benz (1849–1944), German marketing entrepreneur who was the first to drive an automobile for a long distance, wife of Carl Benz * Carl Benz (1844–1929), German engineer, inventor, and entrepreneur who built the first patented automobile * Derek Benz (born 1971), American author of fantasy fiction for children * Edward J. Benz, Jr., professor of genetics * Gerold Benz (1921–1987), German politician * Gary R. Benz, producer of the GRB Studios * Joe Benz (1886–1957), American Major League Baseball pitcher * Joseph Benz (born 1944), Swiss former bobsledder, Olympic and world champion * Julie Benz (born 1972), American actress * Kafi Benz (born 1941), American author, artist, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph DePalma
Raffaele "Ralph" DePalma (occasionally spelt De Palma, December 19, 1882 – March 31, 1956) was an American racing driver who won the 1915 Indianapolis 500. His entry at the International Motorsports Hall of Fame estimates that he won about 2,000 races. DePalma won the 1908, 1909, 1910, and 1911 American AAA national dirt track championships and is credited with winning 25 American Championship Car Racing, American Championship car races. He won the Canadian national championship in 1929. DePalma estimated that he had earned $1.5 million by 1934 after racing for 27 years. He is inducted in numerous halls of fame. He competed on board track racing, boards and dirt track racing, dirt road courses and ovals. Biography Born in Biccari, Apulia, Kingdom of Italy, Italy, DePalma's family, who was from nearby Troia, Apulia, Troia, emigrated to the United States in 1891. When he arrived in the US he was told that, because his father had become a naturalized US citizen, he was automati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elgin National Road Races
The Elgin Road Races were a series of automobile races that took place on closed public roads in Elgin, Illinois between 1910 and 1920."The Elgin Road Race" . State of Illinois. Retrieved 8/25/07. The races were suspended during and resumed in 1919 and 1920. The Elgin National Trophy became one of the most prestigious American automobile races of the early 20th Century and contributed significantly to the development of the modern automobile. Event history In 1909, the Chicago Motor Club (CMC) organized the first automo ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerodynamically
Aerodynamics () is the study of the motion of air, particularly when affected by a solid object, such as an airplane wing. It involves topics covered in the field of fluid dynamics and its subfield of gas dynamics, and is an important domain of study in aeronautics. The term ''aerodynamics'' is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, the difference being that "gas dynamics" applies to the study of the motion of all gases, and is not limited to air. The formal study of aerodynamics began in the modern sense in the eighteenth century, although observations of fundamental concepts such as aerodynamic drag were recorded much earlier. Most of the early efforts in aerodynamics were directed toward achieving heavier-than-air flight, which was first demonstrated by Otto Lilienthal in 1891. Since then, the use of aerodynamics through mathematical analysis, empirical approximations, wind tunnel experimentation, and computer simulations has formed a rational basis for the development of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
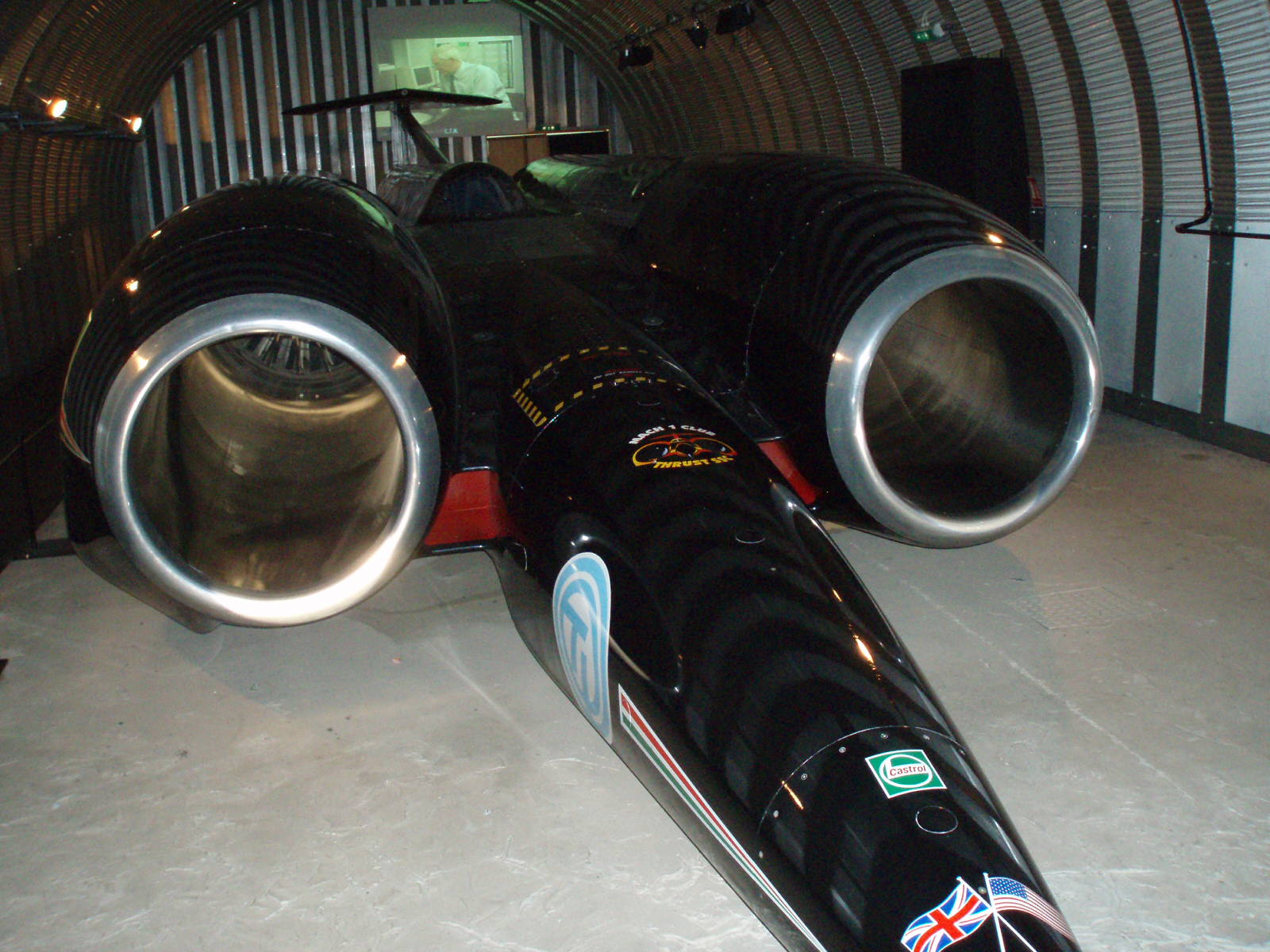
Land Speed Record
The land speed record (LSR) or absolute land speed record is the highest speed achieved by a person using a vehicle on land. By a 1964 agreement between the Fédération Internationale de l'Automobile (FIA) and Fédération Internationale de Motocyclisme (FIM), respective governing bodies for racing in automobiles and motorcycles (two or three wheels), both bodies recognise as the absolute LSR whatever is the highest speed record achieved across any of their various categories. While the three-wheeled Spirit of America (automobile), ''Spirit of America'' set an FIM-validated LSR in 1963, all subsequent LSRs are by vehicles in FIA Category C ("Special Vehicles") in either class JE (jet engine) or class RT (rocket powered). FIA LSRs are officiated and validated by its regional or national affiliate organizations. Speed measurement is standardized over a course measuring either or , Arithmetic mean, averaged over two runs with flying start (commonly called "passes") going in oppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
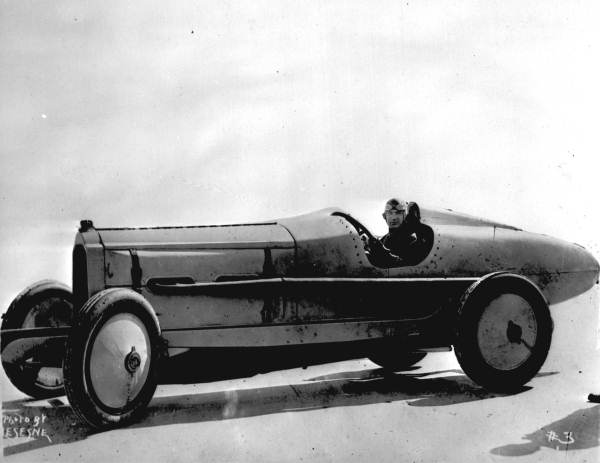
Blitzen Benz
The Blitzen Benz is a race car built by Benz & Cie in Mannheim, Germany, in 1909. In 1910 an enhanced model broke the world land speed record. It was one of six cars based on the Grand Prix car, but it had an enlarged engine, , capacity with , inline-four and improved aerodynamics. History Of the six Blitzen Benzes ever made, only two survive—Mercedes-Benz owns one, while the other belongs to an American collector. At Brooklands on 9 November 1909, land speed racer Victor Hémery of France set a record with an average speed of over a kilometre. At Brooklands on 24 June 1914, land speed racer British driver Lydston Hornsted, in Blitzen Benz No 3, set a record with an average speed of with 2 runs over a 1-mile course, under the new regulations of the '' Association International des Automobile Clubs Reconnus'' (AIACR).Northey, Tom (1974). "Land Speed Record: The Fastest Men on Earth". Tom Northey. ''World of Automobiles''. Vol. 10 (London: Orbis), pp.1163. On 23 April 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |