|
Mer-Égée
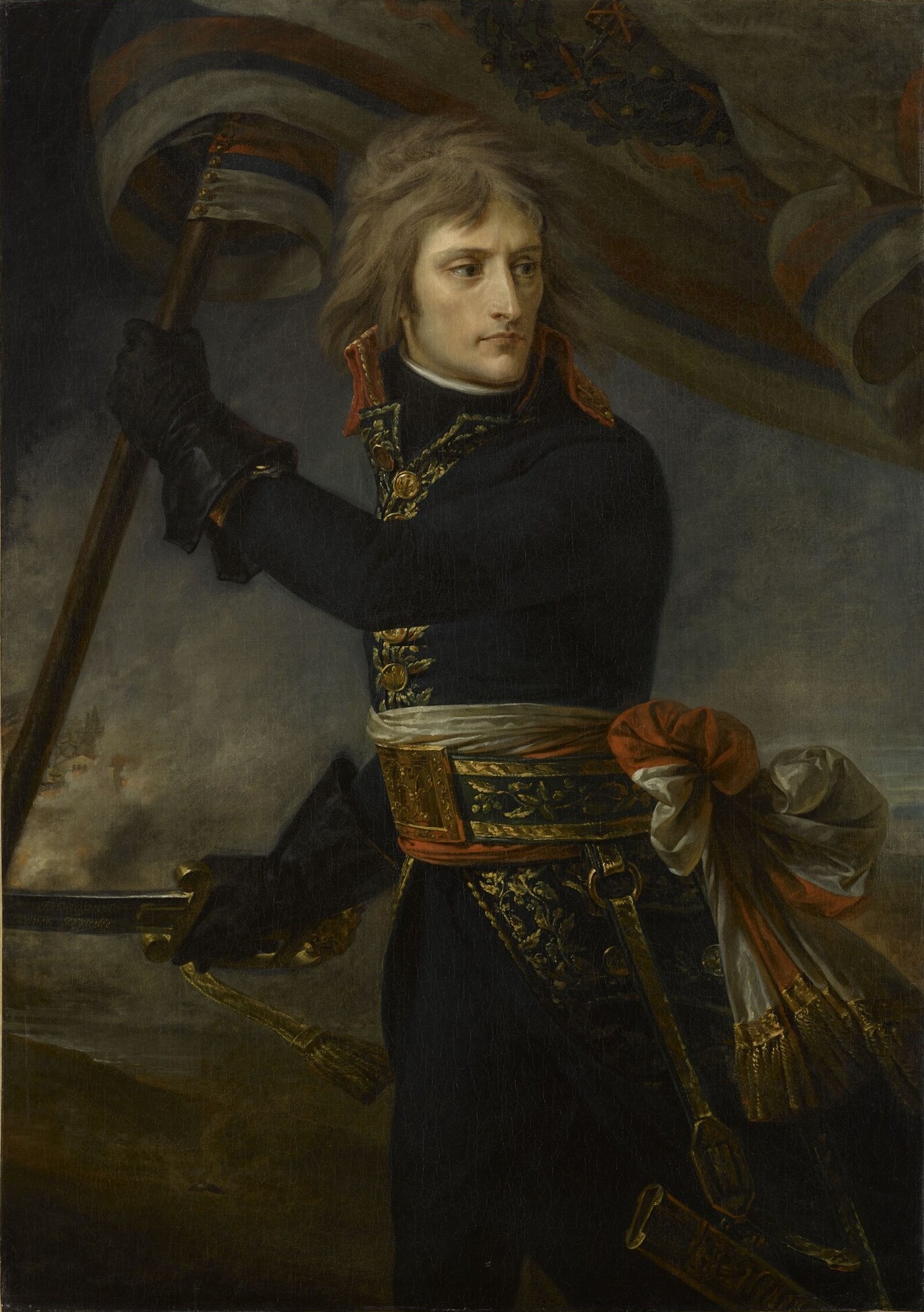
Mer-Égée (; French for "Aegean Sea") was one of three short-lived French departments of Greece. It came into existence after Napoleon's conquest in 1797 of the Republic of Venice, when Venetian Greek possessions such as the Ionian islands fell to the French Directory. History The department included the islands of Zante (Zakynthos), Kythira and the Strofades, as well as Dragamesto (modern Astakos) on the Greek mainland. Despite its name, the department was mostly not in the Aegean, but the Ionian Sea, apart from Kythira and its dependencies. Its prefecture was at the town of Zante (Zakynthos). The territories were lost to Russia in 1798 except Dragamesto that was captured by Ali Pasha, ruler of the Pashalik of Yanina, and the department was officially disbanded in 1802. During the renewed French control of the area in 1807–1809, the department was not re-established, the constitutional form of the Septinsular Republic being kept. Administration Commissioner The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
French Rule In The Ionian Islands (1797–1799)
The First period of French rule in the Ionian Islands (, ; ) lasted from June 1797 to March 1799. Following Fall of the Republic of Venice, the fall of the Republic of Venice in May 1797, the Ionian Islands, a Venetian possession, were occupied by French First Republic, Revolutionary France. The French instituted a new, democratic regime and, following the Treaty of Campo Formio, annexed the islands to France, forming the three departments of France, departments of (Corfu), (Ithaca) and (Aegean Sea). Originally widely welcomed, French rule began to grow oppressive to the islanders, and aroused the enmity of the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman and Russian Empires. In 1798, a joint Russo-Ottoman campaign was launched against the islands, culminating in the Siege of Corfu (1798–99), four-month siege of Corfu. Its fall in March 1799 signalled the end of French rule, and the islands were reorganized as the Russo-Ottoman protectorate of the Septinsular Republic. The islands were French ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ithaque
Ithaque (; French for " Ithaca") was one of three short-lived French departments of Greece. History It came into existence after Napoleon's conquest in 1797 of the Republic of Venice, when Venetian Greek possessions such as the Ionian islands fell to the French Directory. It included the islands of Ithaca, Cephalonia and Lefkada, as well as the cities of Preveza, Arta and Vonitsa on the adjacent mainland. Its prefecture was at Argostoli on Cephalonia. The islands were lost to Russia in 1798 and the department was officially disbanded in 1802. Also Preveza, Arta and Vonitsa were captured in 1798 by Ali Pasha, ruler of the Pashalik of Yanina. During the renewed French control of the area in 1807–1809, the department was not re-established, the constitutional form of the Septinsular Republic being kept. Administration Commissioner The Commissioner of the Directory was the highest state representative in the department. See also * Department of Mer-Égée * Departm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Corcyre
Corcyre (; archaic French for "Corfu"; ) was one of three short-lived French departments of Greece. History It came into existence after Napoleon's conquest in 1797 of the Republic of Venice, when Venetian Greek possessions such as the Ionian islands fell to the French Directory. It consisted of the islands of Kerkyra (Corfu) and Paxoi, as well as the cities of Butrint and Parga on the adjacent mainland. Its prefecture was in the City of Corfu. The island was lost to Russia after the Siege of Corfu (1798–1799) and the department was officially disbanded in 1802. Also, Butrint was captured in 1798 by Ali Pasha, ruler of the Pashalik of Yanina. During the renewed French control in 1807–1814, the department was not re-established, the constitutional form of the former Septinsular Republic being kept. Administration Commissioners The Commissioner of the Directory was the highest state representative in the department. See also * Department of Mer-Égée * De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kythira
Kythira ( ; ), also transliterated as Cythera, Kythera and Kithira, is an island in Greece lying opposite the south-eastern tip of the Peloponnese peninsula. It is traditionally listed as one of the seven main Ionian Islands, although it is distant from the main group. Administratively, it belongs to the Islands regional unit, which is part of the Attica region, despite its distance from the Saronic Islands, around which the rest of Attica is centered. As a municipality, it includes the island of Antikythera to the south. The island is strategically located between the Greek mainland and Crete, and from ancient times until the mid-19th century was a crossroads of merchants, sailors, and conquerors. As such, it has had a long and varied history and has been influenced by many civilizations and cultures. This is reflected in its architecture (a blend of traditional, Aegean and Venetian elements), as well as the traditions and customs, influenced by centuries of coexistence of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Departments Of France
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivity, territorial collectivities"), between the Regions of France, administrative regions and the Communes of France, communes. There are a total of 101 departments, consisting of ninety-six departments in metropolitan France, and five Overseas department and region, overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 333 Arrondissements of France, arrondissements and 2,054 Cantons of France, cantons (as of 2023). These last two levels of government have no political autonomy, instead serving as the administrative basis for the local organisation of police, fire departments, and, in certain cases, elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council (France), departmental council ( , ). From 1800 to April 2015, these were called gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
History Of Zakynthos
Zakynthos (, Zante in Italian) is a Greece, Greek island in the Ionian Sea. It is the third largest of the Ionian Islands. Today, Zakynthos is a separate regional units of Greece, regional unit of the Ionian Islands (region), Ionian Islands region, and its only Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality. It covers an area of and its coastline is roughly in length. The name, like all similar names ending in -nthos, is pre-Mycenaean or Pelasgian in origin. In Greek mythology the island was said to be named after Zakynthos (mythology), Zakynthos, the son of a legendary Arcadia (region), Arcadian chief Dardanus (son of Zeus), Dardanus. The history of Zakynthos is long and complex, even by Greek standards. After the fall of the Byzantine Empire, it has been held by the Kingdom of Naples, the Ottoman Turks, the Republic of Venice, the French, Russians, British, Italians and Germans. Ancient history Zakynthos has been inhabited from at least the Paelolithic and later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ionian Islands
The Ionian Islands (Modern Greek: , ; Ancient Greek, Katharevousa: , ) are a archipelago, group of islands in the Ionian Sea, west of mainland Greece. They are traditionally called the Heptanese ("Seven Islands"; , ''Heptanēsa'' or , ''Heptanēsos''; ), but the group includes many smaller islands in addition to the seven principal ones. As a distinct historic region, they date to the Venetian rule in the Ionian Islands, centuries-long Venetian rule, which preserved them from the Muslim conquests of the Ottoman Empire, and created a distinct cultural identity with many Italian influences. The Ionian Islands became part of the modern Greek state in 1864. Administratively today, they belong to the Ionian Islands Region except for Kythera, which belongs to the Attica Region. Geography The seven primary islands are, from north to south: *Corfu, Kerkyra (Κέρκυρα) usually known as Corfu in English and ''Corfù'' in Italian *Paxi (Παξοί) also known as Paxos in English *L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family. Like all other Romance languages, it descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. French evolved from Northern Old Gallo-Romance, a descendant of the Latin spoken in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien language, Francien) largely supplanted. It was also substratum (linguistics), influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul and by the Germanic languages, Germanic Frankish language of the post-Roman Franks, Frankish invaders. As a result of French and Belgian colonialism from the 16th century onward, it was introduced to new territories in the Americas, Africa, and Asia, and numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole, were established. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Septinsular Republic
The Septinsular Republic (; ), also known as the Republic of the Seven United Islands, was an oligarchic republic that existed from 1800 to 1807 under nominal Russian and Ottoman sovereignty in the Ionian Islands (Corfu, Paxoi, Lefkada, Cephalonia, Ithaca, Zakynthos or Zante, and Kythira). The Republic was established after a joint Russo-Ottoman fleet captured the islands and ended a two-year rule by the French Republic. Although the islanders had hoped for complete independence, the new state was granted only autonomy, becoming tributary to the Ottoman Porte, and de facto under Russian domination. Nevertheless, it was the first time that Greeks had been granted self-government since the fall of the last remnants of the Byzantine Empire to the Ottomans in the mid-15th century. In 1807, the republic was ceded to Napoleon's French Empire, but the islands kept their institutions of government. The British gradually took control of the islands from 1809 on, and following the Trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
French Rule In The Ionian Islands (1807–1814)
The Second period of French rule in the Ionian Islands () began in August 1807, when the Septinsular Republic, a Russian protectorate comprising the seven Ionian Islands, was occupied by the First French Empire in accordance with the Treaty of Tilsit. The French annexed the Republic but maintained most of its institutions for local governance. In 1809–10, the British occupied the southernmost islands, leaving only Corfu, Paxoi, and the mainland exclave of Parga in French hands. The British also imposed a naval blockade on the French-ruled islands, which began to suffer from famine. Finally, the British occupied Paxoi in late 1813 and Parga in March 1814. Following the Abdication of Napoleon, the French governor-general in Corfu, François-Xavier Donzelot, capitulated and the French garrison was evacuated. In 1815, the islands became a British protectorate, the United States of the Ionian Islands. Establishment In the Treaty of Tilsit, concluded in July 1807, Russia cede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pashalik Of Yanina
The Pashalik of Yanina, sometimes referred to as the Pashalik of Ioannina or Pashalik of Janina, was an autonomous pashalik within the Ottoman Empire between 1787 and 1822 covering large areas of Albania, Greece, and North Macedonia. Under the Ottoman Albanian ruler Ali Pasha, the pashalik acquired a high degree of autonomy and even managed to stay '' de facto'' independent, though this was never officially recognized by the Ottoman Empire. Conceiving his territory in increasingly independent terms, Ali Pasha's correspondence and foreign Western correspondence frequently refer to the territories under Ali's control as Albania. The capital of the Pashalik was Ioannina, which along with Tepelena were Ali's headquarters. At its peak, Ali Pasha and his sons ruled over southern and central Albania, the majority of mainland Greece, including Epirus, Thessaly, West Macedonia, western Central Macedonia, Continental Greece (excluding Attica), and the Peloponnese, and parts of so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
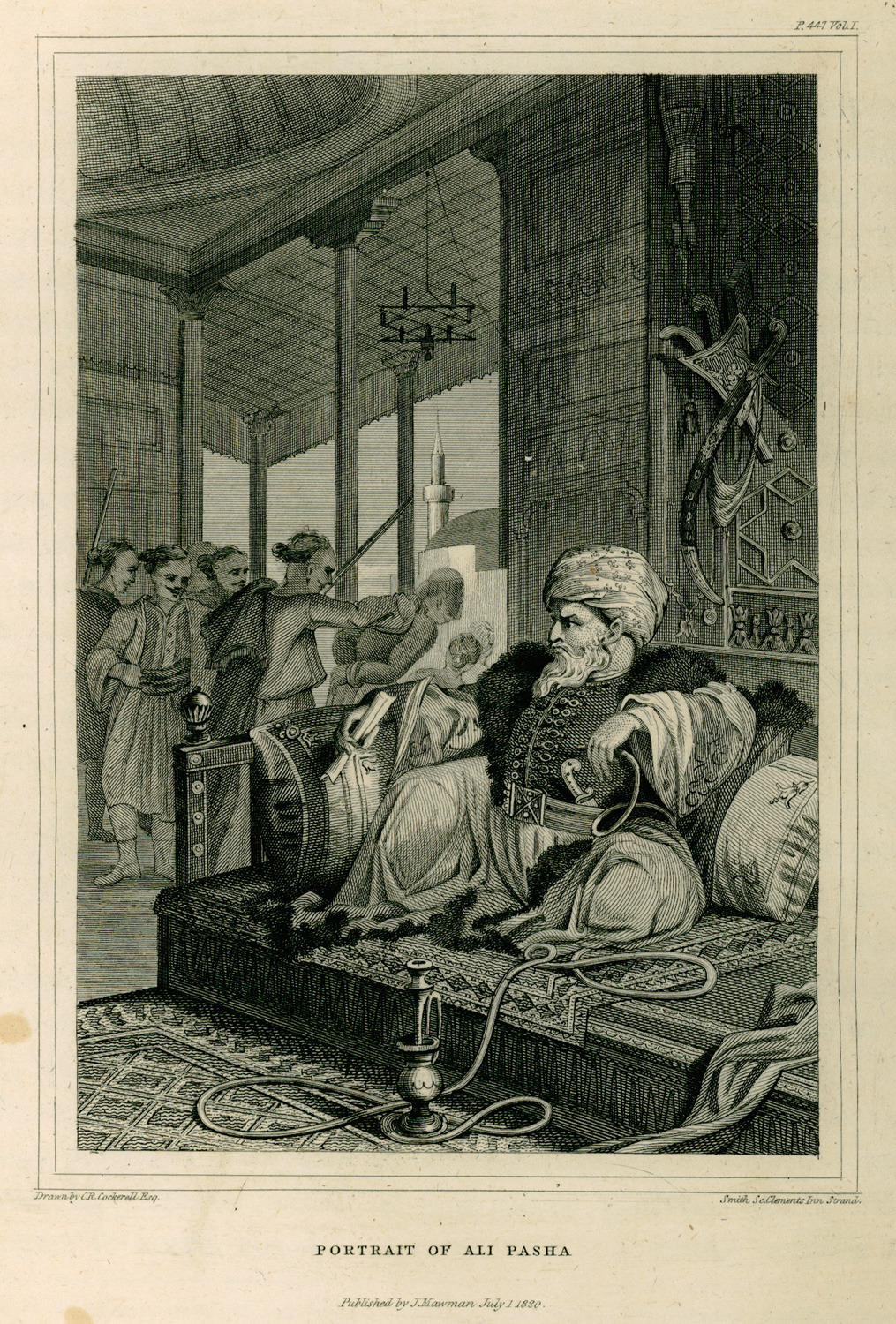
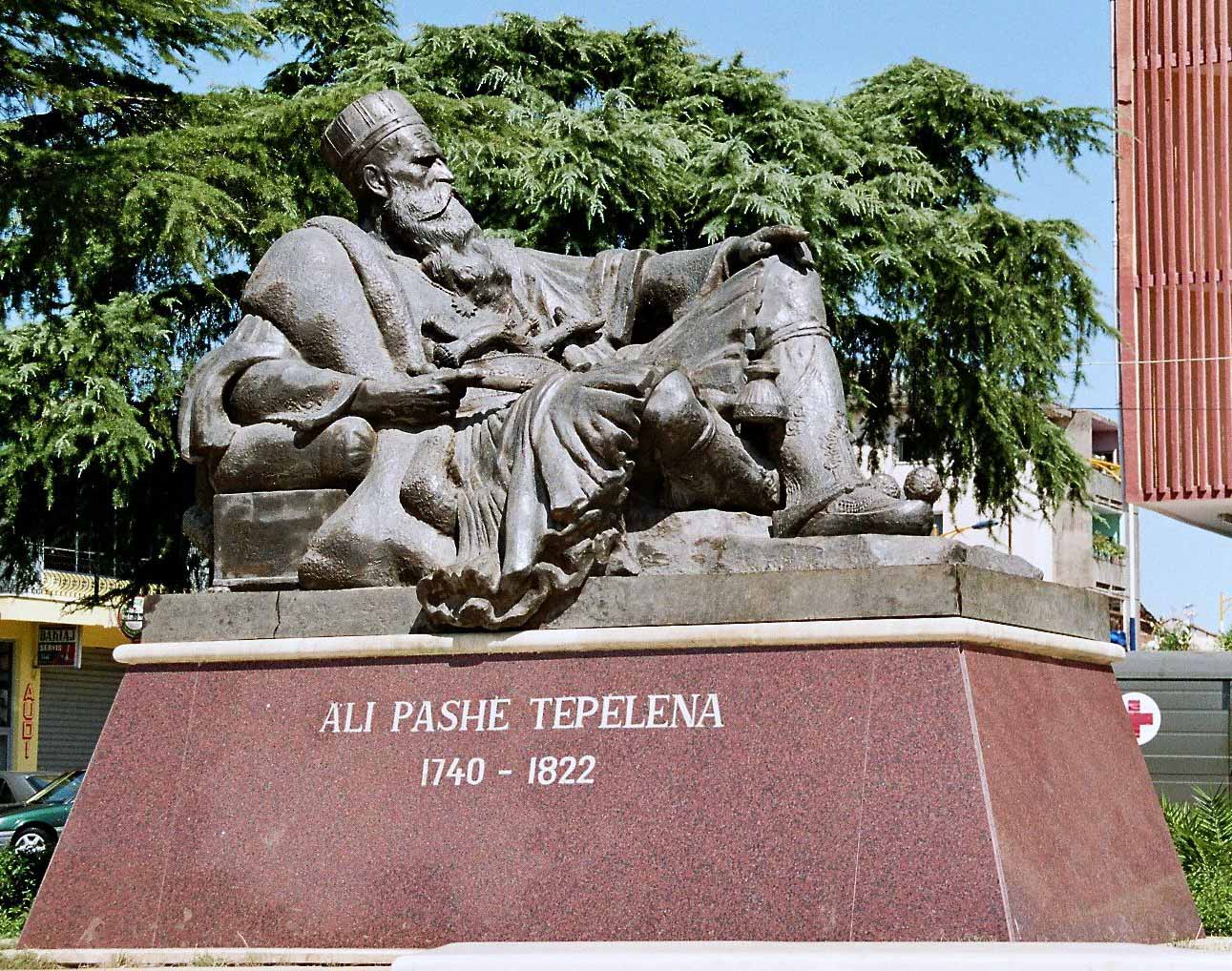
Ali Pasha Of Ioannina
Ali Pasha (1740 – 24 January 1822), commonly known as Ali Pasha of Yanina or Ali Pasha of Tepelena, was an Albanian ruler who served as Ottoman pasha of the Pashalik of Yanina, a large part of western Rumelia. Under his rule, it acquired a high degree of autonomy and even managed to stay '' de facto'' independent. The capital of the Pashalik was Ioannina, which, along with Tepelena, was Ali's headquarters. Conceiving his territory in increasingly independent terms, Ali Pasha's correspondence and foreign Western correspondence frequently refer to the territories under Ali's control as "Albania." This, by Ali's definition, included central and southern Albania, and parts of mainland Greece; in particular, most of the district of Epirus and the western parts of Thessaly and Macedonia. He managed to stretch his control over the sanjaks of Yanina, Delvina, Vlora and Berat, Elbasan, Ohrid and Monastir, Görice, and Tirhala. Ali was granted the Sanjak of Tirhala in 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |