|
Megan (ship)
MV ''Megan'', formerly known as MV ''GO Searcher'', is one of SpaceX's two Dragon capsule recovery vessels. Owned by SpaceX through Falcon Landing LLC (which also owns SpaceX's fairing recovery vessels and Elon Musk's private jet), this vessel, along with its sister ship, , are converted platform supply vessels now equipped to retrieve Crew and Cargo Dragon capsules after splashdown. When a Dragon capsule is preparing to return to Earth, ''Megan'' or ''Shannon'' are dispatched to wait near the predetermined landing zone. After splashdown, fast boats deployed from the vessel, approach the capsule to perform safety checks, check on the crew, and prepare it to be lifted aboard the recovery vessel, where the astronauts can exit the capsule. NASA requires SpaceX to allow the astronauts to exit within 60 minutes of splashdown. To support its mission, the vessel is equipped with a specialized crane on the stern to pull the capsule up from the water, a medical unit to treat astrona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp., commonly referred to as SpaceX, is an America, American space technology company headquartered at the SpaceX Starbase, Starbase development site in Starbase, Texas. Since its founding in 2002, the company has made numerous advancements in rocket propulsion, reusable launch vehicles, human spaceflight and satellite constellation technology. , SpaceX is the world's dominant space launch provider, its launch cadence eclipsing all others, including private competitors and national programs like the Chinese space program. SpaceX, NASA, and the United States Armed Forces work closely together by means of Government contractor, governmental contracts. SpaceX was founded by Elon Musk in 2002 with a vision of decreasing the costs of space launches, paving the way to SpaceX ambition of colonizing Mars, a sustainable colony on Mars. In 2008, Falcon 1 successfully launched into orbit after three failed launch attempts. The company then pivoted towar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
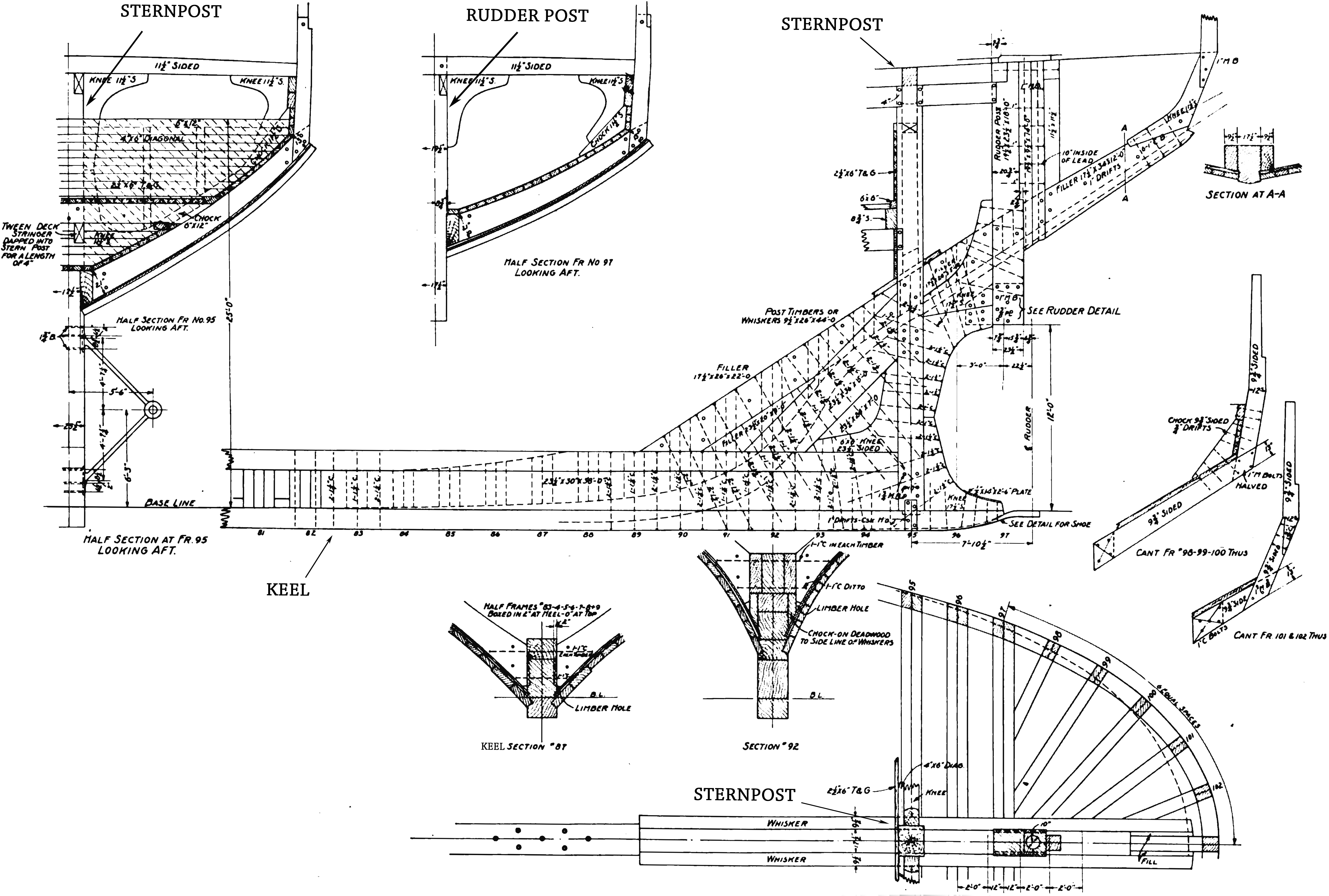
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amos-17
AMOS-17 is an Israeli commercial communications satellite, part of the AMOS series of satellites. History Spacecom, the AMOS satellites operator, announced in December 2016 that it has signed a US$161 million contract with Boeing to build AMOS-17, which is to replace the failed AMOS-5 satellite. Satellite description AMOS-17 is a multi-band high-throughput satellite. It features a Ka-band, Ku-band anc C-band communications payload. It was built on the BSS-702MP satellite bus, transmitting in the Ka-band, Ku-band, and C-bands. It is a replacement for AMOS-5 and provides coverage over the continent of Africa, Europe and Middle East. Launch It was launched on 6 August 2019, at 23:23:00 UTC by a Falcon 9 launch vehicle, from Cape Canaveral, SLC-40, Florida. The mass of the payload was too large to allow the booster to be recovered for reuse, so the customer paid for an "expended" launch. Mission The satellite was reportedly aimed to be located at 17° East ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STP-2
The Space Test Program (STP) is the primary provider of spaceflight for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) space science and technology community. STP is managed by a group within the Advanced Systems and Development Directorate, a directorate of the Space and Missile Systems Center of the United States Space Force. STP provides spaceflight via the International Space Station (ISS), piggybacks, secondary payloads and dedicated launch services. Past activities STP has actually been in existence for 50 years as of 2019, with several thousand launches it has been responsible for. For example, the initial experiments that led to the modern Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite constellation were STP-launched projects. 2001 During August 2001, STP conducted two successful activities using the Space Shuttle and ISS. STS-105 delivered and successfully deployed the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) externally on the ISS. MISSE was a passive m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starlink
Starlink is a satellite internet constellation operated by Starlink Services, LLC, an international telecommunications provider that is a wholly owned subsidiary of American aerospace company SpaceX, providing coverage to around 130 countries and territories. Timestamp 12:00. It also aims to provide global mobile broadband. Starlink has been instrumental to SpaceX's growth. SpaceX began launching Starlink satellites in 2019. , the constellation consists of over 7,600 mass-produced small satellites in low Earth orbit (LEO) that communicate with designated ground transceivers, and Starlink comprises 65% of all active satellites. Nearly 12,000 satellites are planned, with a possible later extension to 34,400. SpaceX announced reaching over 1 million subscribers in December 2022 and 4 million subscribers in September 2024. The SpaceX satellite development facility in Redmond, Washington, houses Starlink research, development, manufacturing, and orbit control facilities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ArabSat-6A
Arabsat-6A is a geostationary communications satellite operated by Arabsat. The satellite was built by Lockheed Martin Space Systems on a modernized A2100 bus. The satellite was successfully launched from Kennedy Space Center LC-39A aboard Falcon Heavy on April 11, 2019. History Arabsat-6A and SaudiGeoSat-1/HellasSat-4 are the two satellites of the Arabsat-6G program, ordered by the Arab League to supply the communications needs of member states. Contracts to build the two satellites were awarded to Lockheed Martin Space Systems in April 2015. Arabsat ultimately awarded the launch contract for Arabsat-6A to SpaceX for a Falcon Heavy flight with no expendable boosters. The Falcon Heavy was chosen over the Falcon 9 due to its far superior thrust; the extra boost would extend the satellite's operational lifespan from 15 years to 18-20 years. Spacecraft Arabsat 6A is based on an updated version of the A2100 bus and is considered among the most advanced communications satellites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
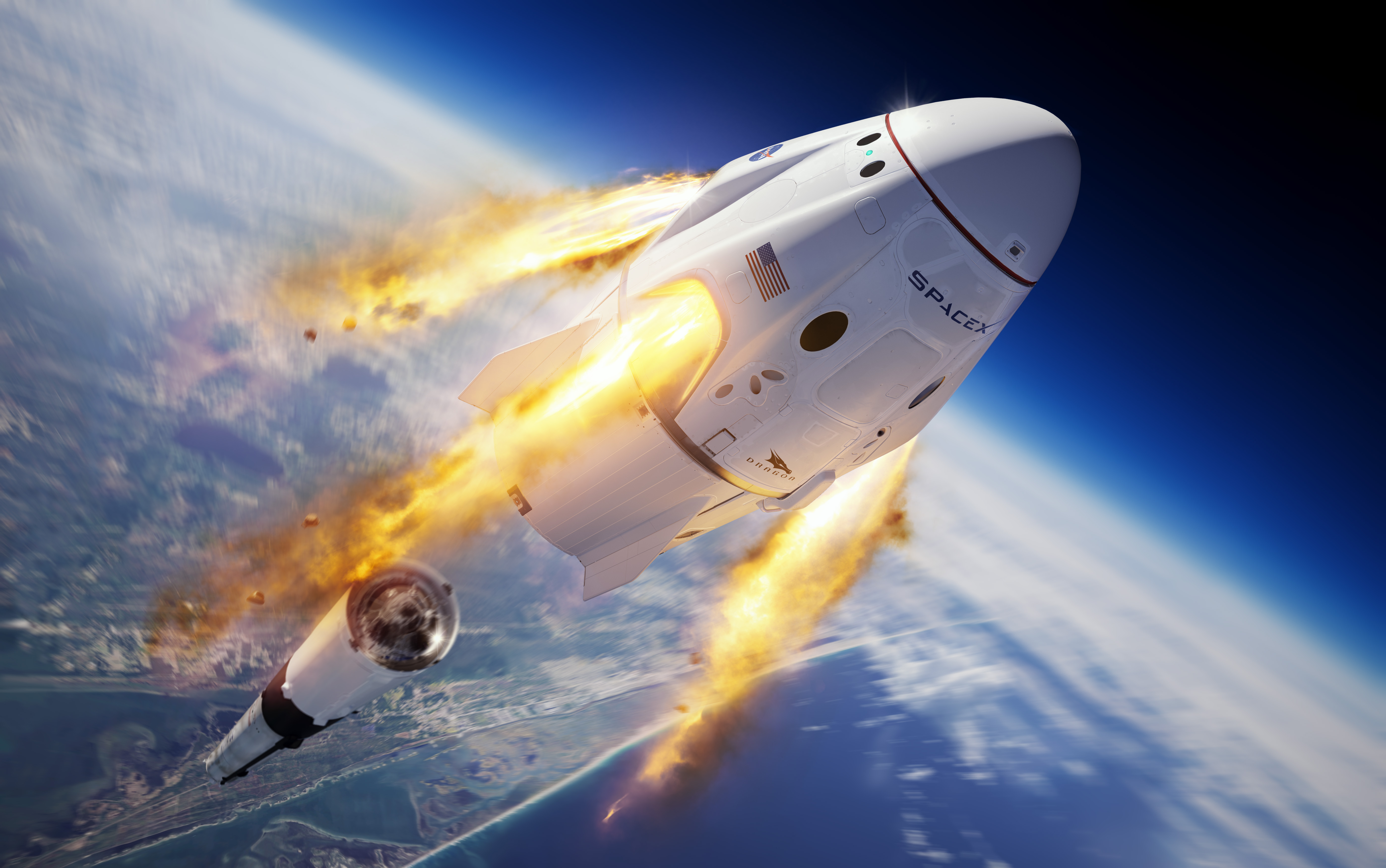
Crew Dragon
Dragon 2 is a class of partially reusable spacecraft developed, manufactured, and operated by the American space company SpaceX for flights to the International Space Station (ISS) and private spaceflight missions. The spacecraft, which consists of a reusable space capsule and an expendable Service module, trunk module, has two variants: the 4-person Crew Dragon and Cargo Dragon, a replacement for the SpaceX Dragon 1, Dragon 1 cargo capsule. The spacecraft launches atop a Falcon 9 Block 5 rocket, and the capsule returns to Earth through splashdown. Crew Dragon's primary role is to transport crews to and from the ISS under NASA's Commercial Crew Program, a task handled by the Space Shuttle until it was Retirement of the Space Shuttle, retired in 2011. It will be joined by Boeing Starliner, Boeing's Starliner in this role when NASA certifies it. Crew Dragon is also used for commercial flights to ISS and other destinations and is expected to be used to transport people to and fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crew Dragon Demo-1
Crew Dragon Demo-1 (officially Crew Demo-1, SpaceX Demo-1, or Demonstration Mission-1) was the first orbital test of the Dragon 2 spacecraft. The mission launched on 2 March 2019 at 07:49:03 UTC, and arrived at the International Space Station on 3 March 2019, a little over 24 hours after the launch. The mission ended with a splashdown on 8 March 2019 at 13:45:08UTC. During a separate test, on 20 April 2019, the capsule used on Crew Demo-1 was unexpectedly destroyed when firing the SuperDraco engines at Landing Zone 1. Mission The spacecraft tested the approach and automated docking procedures with the International Space Station (ISS), consequent undocking from the ISS, full re-entry, splashdown and recovery steps to provide data requisite to subsequently qualify for flights transporting humans to the ISS. Life support systems were monitored throughout the test flight. The capsule was to be re-used in an in-flight abort test, but it was destroyed in an accident during a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inspiration4
Inspiration4 (stylized as Inspirati④n) was a 2021 human spaceflight operated by SpaceX on behalf of Shift4 Payments CEO Jared Isaacman. The mission launched the Crew Dragon Crew Dragon Resilience, ''Resilience'' on 16 September 2021 at 00:02:56 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC from Kennedy Space Center's Kennedy Space Center Launch Complex 39A, Launch Complex 39A atop a Falcon 9 Block 5, Falcon 9 launch vehicle. It placed the Dragon Space capsule, capsule into a low Earth orbit. The mission ended on 18 September 2021 at 23:06:49 UTC, when ''Resilience'' splashed down in the Atlantic Ocean. The trip was the first orbital spaceflight with only private citizens aboard and was part of a charitable effort on behalf of St. Jude Children's Research Hospital in Memphis, Tennessee. Isaacman was named mission commander. The hospital selected two commercial astronauts: cancer survivor Hayley Arceneaux and military veteran Christopher Sembroski. Shift4 selected entrepreneur Sian Proctor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crew Dragon In-Flight Abort Test
The Crew Dragon In-Flight Abort Test (also known as Crew Dragon Launch Escape Demonstration) was a successful test of the SpaceX Dragon 2 abort system, conducted on 19 January 2020. It was the final assessment for the Crew Dragon capsule and Falcon 9 launch system before they would be certified to carry humans into space. Booster B1046.4 and an uncrewed capsule C205 were launched from Launch Complex 39A (LC-39A) on a suborbital trajectory, followed by an in-flight abort of the capsule at max Q and supersonic speed. The test was carried out successfully: the capsule pulled itself away from the booster after launch control commanded the abort, and landed safely. Background For the Commercial Crew Program, NASA requires participating companies to include and test a launch escape system in their crew-carrying vehicles. Prior to this, the last time American crewed spaceflight implemented the capability to escape a rocket during an emergency or anomaly was on the Saturn IB lau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragon 2
Dragon 2 is a class of partially reusable spacecraft developed, manufactured, and operated by the American space company SpaceX for flights to the International Space Station (ISS) and private spaceflight missions. The spacecraft, which consists of a reusable space capsule and an expendable trunk module, has two variants: the 4-person Crew Dragon and Cargo Dragon, a replacement for the Dragon 1 cargo capsule. The spacecraft launches atop a Falcon 9 Block 5 rocket, and the capsule returns to Earth through splashdown. Crew Dragon's primary role is to transport crews to and from the ISS under NASA's Commercial Crew Program, a task handled by the Space Shuttle until it was retired in 2011. It will be joined by Boeing's Starliner in this role when NASA certifies it. Crew Dragon is also used for commercial flights to ISS and other destinations and is expected to be used to transport people to and from Axiom Space's planned space station. Cargo Dragon brings cargo to the ISS ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragon 1
SpaceX Dragon 1 is a class of fourteen partially reusable cargo spacecraft developed by SpaceX, an American private space transportation company. The spacecraft flew 23 missions between 2010 and 2020. Dragon was launched into orbit by the company's Falcon 9 launch vehicle to resupply the International Space Station (ISS). It was succeeded by the SpaceX Dragon 2, Dragon 2 spacecraft which has both crewed and cargo versions. During its maiden flight in December 2010, Dragon became the first commercially built and operated spacecraft to be recovered successfully from orbit. On 25 May 2012, Dragon COTS Demo Flight 2, became the first commercial spacecraft to successfully Space rendezvous, rendezvous with and attach to the ISS. SpaceX contracted to deliver cargo to the ISS under NASA's Commercial Resupply Services program, and Dragon began regular cargo flights in October 2012. With the Dragon spacecraft and the Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus (spacecraft), Cygnus, NASA sought to in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |