|
Megafauna
In zoology, megafauna (from Ancient Greek, Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and Neo-Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") are large animals. The precise definition of the term varies widely, though a common threshold is approximately , this lower end being centered on humans, with other thresholds being more relative to the sizes of animals in an ecosystem, the spectrum of lower-end thresholds ranging from to . Large body size is generally associated with other traits, such as having a slow rate of reproduction and, in large herbivores, reduced or negligible adult mortality from being killed by predators. Megafauna species have considerable effects on their local environment, including the suppression of the growth of woody vegetation and a consequent reduction in wildfire frequency. Megafauna also play a role in regulating and stabilizing the abundance of smaller animals. During the Pleistocene, megafauna were diverse across the globe, with most continental ecosystems exhibiting s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Pleistocene Extinctions
The Late Pleistocene to the beginning of the Holocene saw the extinction of the majority of the world's megafauna, typically defined as animal species having body masses over , which resulted in a collapse in faunal density and diversity across the globe. The extinctions during the Late Pleistocene are differentiated from previous extinctions by their extreme size bias towards large animals (with small animals being largely unaffected), and widespread absence of ecological succession to replace these extinct megafaunal species, and the regime shift of previously established faunal relationships and habitats as a consequence. The timing and severity of the extinctions varied by region and are generally thought to have been driven by humans, climatic change, or a combination of both. Human impact on megafauna populations is thought to have been driven by hunting ("overkill"), as well as possibly environmental alteration. The relative importance of human vs climatic factors in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Schultz Martin
Paul Schultz Martin (born in Allentown, Pennsylvania in 1928, died in Tucson, Arizona September 13, 2010)Mari N. Jensen. '. University of Arizona. Retrieved 2010-09-17. was an American geoscientist at the University of Arizona who developed the theory that the Pleistocene extinction of large mammals worldwide was caused by overhunting by humans. Martin's work bridged the fields of ecology, anthropology, geosciences, and paleontology. In 1953, Martin received his bachelor's degree in zoology from Cornell University. In 1953 and 1956 he completed his master's and doctorate programs at the University of Michigan and then proceeded with postdoctoral research at Yale University and the University of Montreal. Martin's early interest embraced ornithology and herpetology and he conducted extensive fieldwork from 1948 to 1953 in Tamaulipas, Mexico. He published biogeographies on the birds of the Sierra de Tamaulipas and the herpetofauna of the Gómez Farias (= El Cielo) region of T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
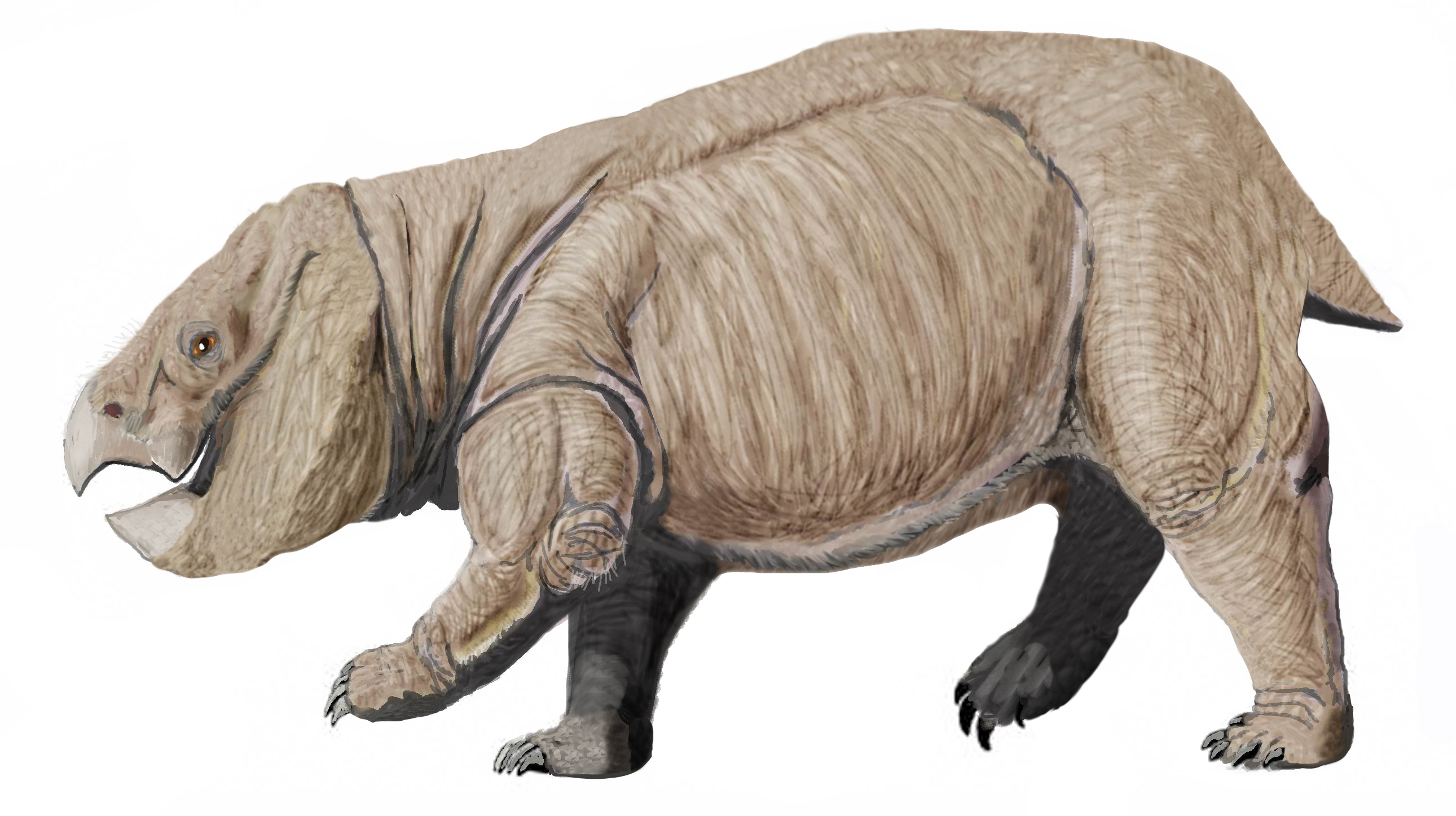
Megaherbivore
Megaherbivores (Greek :wiktionary:μέγας, μέγας megas "large" and Latin ''herbivora'' "herbivore") are large herbivores that can exceed in weight. The earliest herbivores to reach such sizes like the Pareiasauria, pareiasaurs appeared in the Permian period. During most of the Mesozoic, the megaherbivore niche was largely dominated by Dinosaur, dinosaurs up until their extinction during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. After this period, small mammalian species evolved into large herbivores in the Paleogene. As part of the Late Pleistocene megafauna extinctions, 80% of megaherbivore species became extinct, with megaherbivores becoming entirely extinct in Europe, Australia and the Americas. Recent megaherbivores include elephants, Rhinoceros, rhinos, Hippopotamus, hippos, and giraffes. There are nine extant species of terrestrial megaherbivores living in Africa and Asia. The African bush elephant is the largest extant species. Extant megaherbivores are keyst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoologists and paleontologists use ''fauna'' to refer to a typical collection of animals found in a specific time or place, e.g. the " Sonoran Desert fauna" or the " Burgess Shale fauna". Paleontologists sometimes refer to a sequence of faunal stages, which is a series of rocks all containing similar fossils. The study of animals of a particular region is called faunistics. Etymology ''Fauna'' comes from the name Fauna, a Roman goddess of earth and fertility, the Roman god Faunus, and the related forest spirits called Fauns. All three words are cognates of the name of the Greek god Pan, and ''panis'' is the Modern Greek equivalent of fauna (πανίς or rather πανίδα). ''Fauna'' is also the word fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as the Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently defined as the time between 129,000 and c. 11,700 years ago. The late Pleistocene equates to the proposed Tarantian Age of the geologic time scale, preceded by the officially ratified Chibanian (commonly known as the Middle Pleistocene). The beginning of the Late Pleistocene is the transition between the end of the Penultimate Glacial Period and the beginning of the Last Interglacial around 130,000 years ago (corresponding with the beginning of Marine Isotope Stage 5). The Late Pleistocene ends with the termination of the Younger Dryas, some 10th millennium BC, 11,700 years ago when the Holocene Epoch began. The term Upper Pleistocene is currently in use as a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippopotamus
The hippopotamus (''Hippopotamus amphibius;'' ; : hippopotamuses), often shortened to hippo (: hippos), further qualified as the common hippopotamus, Nile hippopotamus and river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extant species in the family Hippopotamidae, the other being the pygmy hippopotamus (''Choeropsis liberiensis'' or ''Hexaprotodon liberiensis''). Its name comes from the ancient Greek for "river horse" (). After elephants and rhinoceroses, the hippopotamus is the next largest land mammal. It is also the largest extant land artiodactyl. Despite their physical resemblance to pigs and other terrestrial even-toed ungulates, the closest living relatives of the hippopotamids are cetaceans (whales, dolphins, porpoises, etc.), from which they diverged about 55 million years ago. Hippos are recognisable for their barrel-shaped torsos, wide-opening mouths with large canine tusks, nearly hairless bodies, pillar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnivores
An omnivore () is an animal that regularly consumes significant quantities of both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutrients and energy of the sources absorbed. Often, they have the ability to incorporate food sources such as algae, fungi, and bacteria into their diet. Omnivores come from diverse backgrounds that often independently evolved sophisticated consumption capabilities. For instance, dogs evolved from primarily carnivorous organisms (Carnivora) while pigs evolved from primarily herbivorous organisms (Artiodactyla). Despite this, physical characteristics such as tooth morphology may be reliable indicators of diet in mammals, with such morphological adaptation having been observed in bears. The variety of different animals that are classified as omnivores can be placed into further sub-categories depending on their feeding behaviors. Frug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'', native to Sub-Saharan Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body (biology), body; a short, rounded head; round ears; and a dark, hairy tuft at the tip of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adult male lions are larger than females and have a prominent mane. It is a social species, forming groups called prides. A lion's pride consists of a few adult males, related females, and cubs. Groups of female lions usually hunt together, preying mostly on medium-sized and large ungulates. The lion is an apex predator, apex and keystone predator. The lion inhabits grasslands, savannahs, and shrublands. It is usually more diurnality, diurnal than other wild cats, but when persecuted, it adapts to being active nocturnality, at night and crepuscular, at twilight. During the Neolithic period, the lion ranged throughout Africa and Eurasia, from Southeast Europe to India, but it has been reduced to fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bear
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family (biology), family Ursidae (). They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats throughout most of the Northern Hemisphere and partially in the Southern Hemisphere. Bears are found on the continents of North America, South America, and Eurasia. Common characteristics of modern bears include large bodies with stocky legs, long snouts, small rounded ears, shaggy hair, plantigrade paws with five nonretractile claws, and short tails. While the polar bear is mostly carnivorous, and the giant panda is mostly herbivorous, the remaining six species are omnivorous with varying diets. With the exception of courtship display, courting individuals and mothers with their young, bears are typically solitary animals. They may be diurnality, diurnal or nocturnal and have an excellent sense of smell. Despite their heavy build and awk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area.Sayre, April Pulley (1999), ''Africa'', Twenty-First Century Books. . With nearly billion people as of , it accounts for about of the world's human population. Demographics of Africa, Africa's population is the youngest among all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Based on 2024 projections, Africa's population will exceed 3.8 billion people by 2100. Africa is the least wealthy inhabited continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including Geography of Africa, geography, Climate of Africa, climate, corruption, Scramble for Africa, colonialism, the Cold War, and neocolonialism. Despite this lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnivores
A carnivore , or meat-eater (Latin, ''caro'', genitive ''carnis'', meaning meat or "flesh" and ''vorare'' meaning "to devour"), is an animal or plant whose nutrition and energy requirements are met by consumption of animal tissues (mainly muscle, fat and other soft tissues) as food, whether through predation or scavenging. Nomenclature Mammal order The technical term for mammals in the order Carnivora is ''carnivoran'', and they are so-named because most member species in the group have a carnivorous diet, but the similarity of the name of the order and the name of the diet causes confusion. Many but not all carnivorans are meat eaters; a few, such as the large and small cats (Felidae) are ''obligate'' carnivores (see below). Other classes of carnivore are highly variable. The ursids (bears), for example: while the Arctic polar bear eats meat almost exclusively (more than 90% of its diet is meat), almost all other bear species are omnivorous, and one species, the giant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
K-strategists
In ecology, selection theory relates to the selection of combinations of traits in an organism that trade off between quantity and quality of offspring. The focus on either an increased quantity of offspring at the expense of reduced individual parental investment of -strategists, or on a reduced quantity of offspring with a corresponding increased parental investment of -strategists, varies widely, seemingly to promote success in particular environments. The concepts of quantity or quality offspring are sometimes referred to as "cheap" or "expensive", a comment on the expendable nature of the offspring and parental commitment made. The stability of the environment can predict if many expendable offspring are made or if fewer offspring of higher quality would lead to higher reproductive success. An unstable environment would encourage the parent to make many offspring, because the likelihood of all (or the majority) of them surviving to adulthood is slim. In contrast, more stable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |