|
Maryland General Assembly
The Maryland General Assembly is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Maryland that convenes within the State House in Annapolis. It is a bicameral body: the upper chamber, the Maryland Senate, has 47 representatives, and the lower chamber, the Maryland House of Delegates, has 141 representatives. Members of both houses serve four-year terms. Each house elects its own officers, judges the qualifications and election of its own members, establishes rules for the conduct of its business, and may punish or expel its own members. The General Assembly convenes its legislative session for 90 days each year to act on more than 2,300 bills including the state's annual budget, which it must pass before adjourning ''sine die''. The General Assembly's 446th session convened on January 10, 2024. History The forerunner of the Maryland General Assembly was the colonial institution, an Assembly of Free Marylanders (and also Council of Maryland). Maryland's foundational charter cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maryland Senate
The Maryland Senate, sometimes referred to as the Maryland State Senate, is the upper house of the General Assembly, the state legislature of the U.S. state of Maryland. Composed of 47 senators elected from an equal number of constituent single-member districts, the Senate is responsible, along with the Maryland House of Delegates, for passage of laws in Maryland, and for confirming executive appointments made by the Governor of Maryland. It evolved from the upper house of the colonial assembly created in 1650 when Maryland was a proprietary colony controlled by Cecilius Calvert. It consisted of the Governor and members of the Governor's appointed council. With slight variation, the body to meet in that form until 1776, when Maryland, now a state independent of British rule, passed a new constitution that created an electoral college to appoint members of the Senate. This electoral college was abolished in 1838 and members began to be directly elected from each county and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
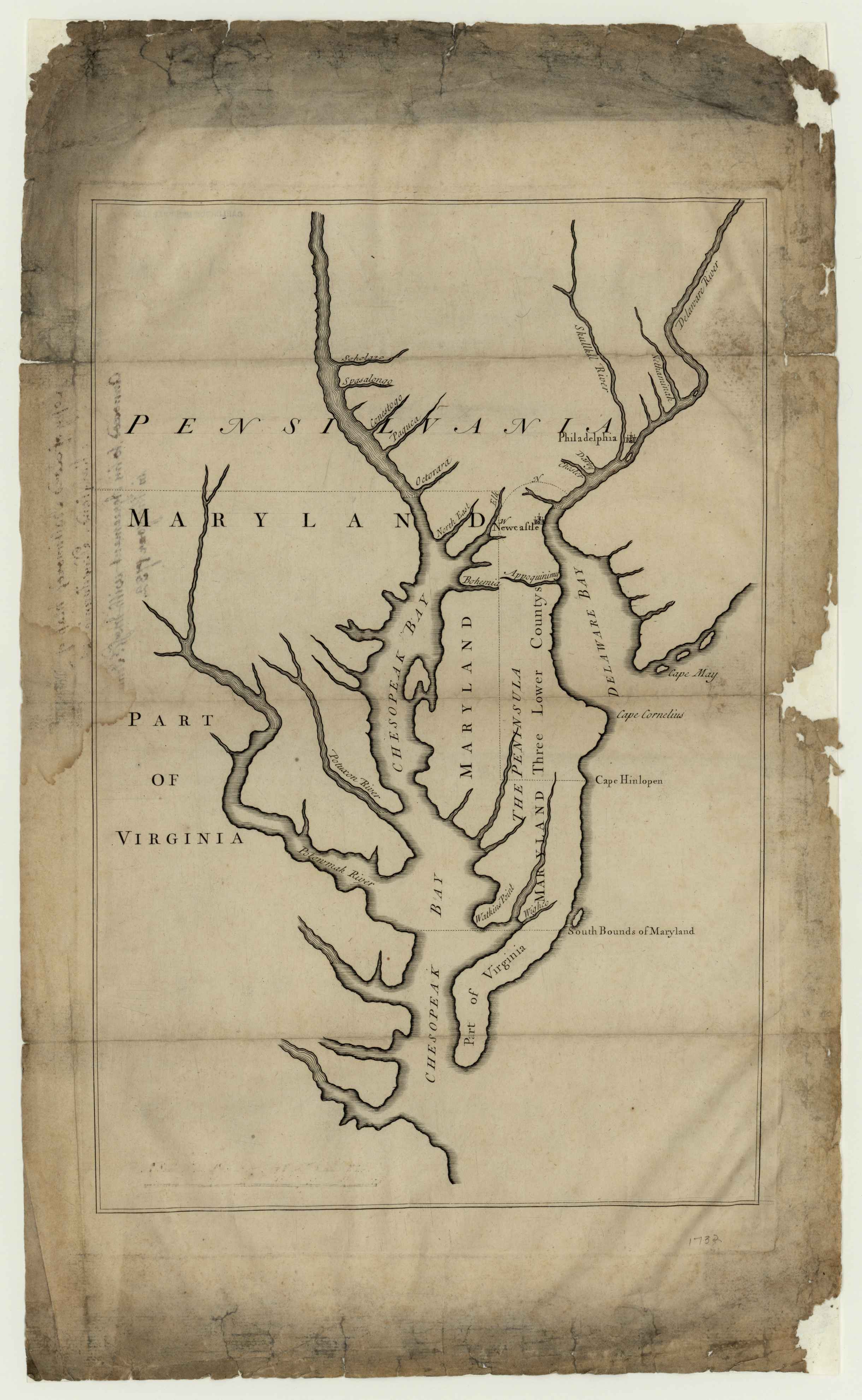
Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east, as well as with the Atlantic Ocean to its east, and the national capital and federal district of Washington, D.C. to the southwest. With a total area of , Maryland is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, ninth-smallest state by land area, and its population of 6,177,224 ranks it the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 18th-most populous state and the List of states and territories of the United States by population density, fifth-most densely populated. Maryland's capital city is Annapolis, Maryland, Annapolis, and the state's most populous city is Baltimore. Maryland's coastline was first explored by Europeans in the 16th century. Prior to that, it was inhabited by several Native Americans in the United States ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of America, Confederacy ("the South"), which was formed in 1861 by U.S. state, states that had Secession in the United States, seceded from the Union. The Origins of the American Civil War, central conflict leading to war was a dispute over whether Slavery in the United States, slavery should be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prohibited from doing so, which many believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War, Decades of controversy over slavery came to a head when Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion, won the 1860 presidential election. Seven Southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COVID-19 Pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic (also known as the coronavirus pandemic and COVID pandemic), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), began with an disease outbreak, outbreak of COVID-19 in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. Soon after, it spread to other areas of Asia, and COVID-19 pandemic by country and territory, then worldwide in early 2020. The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the outbreak a public health emergency of international concern (PHEIC) on 30 January 2020, and assessed the outbreak as having become a pandemic on 11 March. COVID-19 symptoms range from asymptomatic to deadly, but most commonly include fever, sore throat, nocturnal cough, and fatigue. Transmission of COVID-19, Transmission of the virus is often airborne transmission, through airborne particles. Mutations have variants of SARS-CoV-2, produced many strains (variants) with varying degrees of infectivity and virulence. COVID-19 vaccines were developed rapidly and deplo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reynolds V
Reynolds may refer to: Places Australia * Hundred of Reynolds, a cadastral unit in South Australia * Hundred of Reynolds (Northern Territory), a cadastral unit in the Northern Territory of Australia United States * Reynolds, Mendocino County, California, a former settlement * Reynolds, Georgia, a town in Taylor County * Reynolds, Illinois, a village in Mercer and Rock Island counties * Reynolds, Indiana, a town in White County * Reynolds, Dallas County, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Reynolds, Reynolds County, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Reynolds, Nebraska, a village in Jefferson County * Reynolds, North Dakota, a city * Reynolds Township, Lee County, Illinois, a town * Reynolds Township, Michigan, a civil township of Montcalm County * Reynolds Township, Minnesota, a town in Todd County * Reynolds County, Missouri, a county in southeast Missouri Outer space * Reynolds (crater), impact crater on Mars Business * Reynolds Brothers, a New Jersey clot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore
Baltimore is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland. With a population of 585,708 at the 2020 census and estimated at 568,271 in 2024, it is the 30th-most populous U.S. city. The Baltimore metropolitan area is the 20th-largest metropolitan area in the country at 2.84 million residents. The city is also part of the Washington–Baltimore combined statistical area, which had a population of 9.97 million in 2020. Baltimore was designated as an independent city by the Constitution of Maryland in 1851. Though not located under the jurisdiction of any county in the state, it forms part of the central Maryland region together with the surrounding county that shares its name. The land that is present-day Baltimore was used as hunting ground by Paleo-Indians. In the early 1600s, the Susquehannock began to hunt there. People from the Province of Maryland established the Port of Baltimore in 1706 to support the tobacco trade with Europe and established the Town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American Revolutionary War, which was launched on April 19, 1775, in the Battles of Lexington and Concord. Leaders of the American Revolution were Founding Fathers of the United States, colonial separatist leaders who, as British subjects, initially Olive Branch Petition, sought incremental levels of autonomy but came to embrace the cause of full independence and the necessity of prevailing in the Revolutionary War to obtain it. The Second Continental Congress, which represented the colonies and convened in present-day Independence Hall in Philadelphia, formed the Continental Army and appointed George Washington as its commander-in-chief in June 1775, and unanimously adopted the United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Commons Of England
The House of Commons of England was the lower house of the Parliament of England (which Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542, incorporated Wales) from its development in the 14th century to the union of England and Scotland in 1707, when it was replaced by the House of Commons of Great Britain after the 1707 Act of Union was passed in both the English and Scottish parliaments at the time. In 1801, with the union of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Ireland, Ireland, that house was in turn replaced by the House of Commons of the United Kingdom. Origins The Parliament of England developed from the Magnum Concilium that advised the English monarch in medieval times. This royal council, meeting for short periods, included ecclesiastics, noblemen, and representatives of the county, counties (known as "knights of the shire"). The chief duty of the council was to approve taxes proposed by the Crown. In many cases, however, the council demanded the redress of the peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Lord
A count palatine (Latin ''comes palatinus''), also count of the palace or palsgrave (from German ''Pfalzgraf''), was originally an official attached to a royal or imperial palace or household and later a nobleman of a rank above that of an ordinary count. The title originated in the Late Roman Empire. In the Middle Ages especially and into modern times, it is associated with the Holy Roman Empire,"palatine, adj.1 and n.1". OED Online. June 2019. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/136245?redirectedFrom=count+palatine& (accessed July 31, 2019). especially Electoral Palatinate. The office, jurisdiction or territory of a count palatine was a county palatine or palatinate. In England the forms earl palatine and palatine earldom are rare alternative terms. Importance of a count palatine in medieval Europe ''Comes palatinus'' This Latin title is the original, but is also pre-feudal: it originated as Roman ''comes'', which was a non-hereditary court title of hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjournment Sine Die
Adjournment ''sine die'' (from Latin 'without a date') is the conclusion of a meeting by a deliberative assembly, such as a legislature or organizational board, without setting a date to reconvene. The assembly can reconvene, either in its present form or a reconstituted form, if preexisting laws and rules provide for this. Otherwise the adjournment effectively dissolves the assembly. A court may also adjourn a matter ''sine die'', which means that the matter is stayed until further notice. In a ''sine die'' adjournment of this type, the hearing stands open indefinitely, and could theoretically be resumed if the situation changed. For example, a case may be adjourned ''sine die'' if there is no possibility of proceeding in the foreseeable future, such as when the defendant is in prison and cannot participate in legal proceedings. United States usage The Congress of the United States customarily adjourns a session ''sine die'' on the morning of January 3, immediately before th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower House
A lower house is the lower chamber of a bicameral legislature, where the other chamber is the upper house. Although styled as "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide, the lower house has come to wield more power or otherwise exert significant political influence. Common attributes In comparison with the upper house, lower houses frequently display certain characteristics (though they vary by jurisdiction). Powers In a parliamentary system, the lower house: * In the modern era, has much more power, usually due to restrictions on the upper house. ** Exceptions to this are Australia, Italy, and Romania, where the upper and lower houses have similar power. * Is able to override the upper house in some ways. * Can vote a motion of no confidence against the government, as well as vote for or against any proposed candidate for head of government at the beginning of the parliamentary term. In a presidential system, the lower house: * Generally has less power th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper House
An upper house is one of two Legislative chamber, chambers of a bicameralism, bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the lower house. The house formally designated as the upper house is usually smaller and often has more restricted power than the lower house. A legislature composed of only one house (and which therefore has neither an upper house nor a lower house) is described as unicameralism, unicameral. History While the Roman Senate, senate of the ancient roman kingdom 755 BC was the first assembly of aristocrats counseling the king, the first upper house of a bicameral legislature was the medieval House of Lords consisting of the archbishops, bishops, abbots and nobility, which emerged during the reign of King Edward III around 1341 when the Parliament clearly separated into two distinct Debating chamber, chambers, the House of Commons of England, House of Commons, consisting of the shire and borough representatives, and the House of Lords. 1808 Spain adopted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |