|
Martinho De Ataíde, 2nd Count Of Atouguia
Dom Martinho de Ataíde (c. 1415 – 1499), 2nd Count of Atouguia, was a 15th-century Portuguese nobleman and diplomat. In 1455, he was granted the lordship of the Canary Islands, by donation from King Henry IV of Castile, Henry IV of Castile, which he later sold to the Duarte de Meneses, 3rd Count of Viana, Count of Viana. Biography He was the eldest son of Álvaro Gonçalves de Ataíde, 1st Count of Atouguia and Dona Guiomar de Castro, of the House of Cadaval. He succeeded in the title, shortly after his father's death, by a royal decree from Afonso V of Portugal, Afonso V of Portugal, dated 14 February 1452. He thus became the 2nd Count of Atouguia da Baleia, Atouguia, his title being later confirmed by royal letters of 1482 and 1487. Missions in Ceuta and Castile He was with his father at the Battle of Alfarrobeira, on the side of King Afonso V of Portugal, Afonso V. The sovereign, soon after making him Count, sent him on a mission to the Portuguese fortress of Ceuta, ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ataíde Family
Ataíde is the name of a noble family from the Kingdom of Portugal, many of whose members played important roles in the course of the Portuguese maritime exploration, Portuguese overseas exploration and expansion and in the internal and foreign policies of Portugal and its empire. History Origin The origin of the Ataíde family can be documented since the 12th century, its progenitor being Don (honorific), D. Egas Duer (c. 1140 – c. 1180), a fidalgo of the County of Portugal (and likely a member of the Early Middle Ages, early medieval :pt:Casa de Riba Douro, House of Riba Douro), who was the 1st Lord of the Honra of :pt:Ataíde, Ataíde («''propter honorem Domne Egee Duer''»), located in what was then the county of Santa Cruz de Riba Tâmega (near present-day Amarante, Portugal, Amarante), in the northern Portuguese region of Entre Douro e Minho. Egas Duer's son, Martim Viegas, was the first to use the surname Ataíde, derived from the name of the ''Honra'' of which he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand, Duke Of Viseu
Infante Ferdinand, Duke of Viseu and Beja (or ''Fernando,'' , 17 November 1433 – 18 September 1470) was the third son of Edward, King of Portugal and his wife Eleanor of Aragon. Biography Ferdinand was born in Almeirim on 17 November 1433, and died in Setúbal on 18 September 1470. He was twice sworn Prince of Portugal (title granted to the presumptive heir to the throne): first between 1438 and 1451, once his older brother became king Afonso V of Portugal and had no children; and for the second time, in 1451, when Prince João was born, but died months later. When Afonso V's first daughter, Princess Joan, was born (1452), Infante Ferdinand finally lost this title. In 1452, Ferdinand fled the country looking for adventure. Some say he wanted to go to the north African cities controlled by the Portuguese; others say that he wanted to join his uncle, the King Alfonso I of Naples, in his campaigns in southern Italy. It seems Ferdinand had the hope to inherit his uncle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Count Of Marialva
The Count of Marialva () was a Portuguese title of nobility created by a royal decree, issued in 1440, by King Afonso V of Portugal, and granted to Vasco Fernandes Coutinho, 1st Count of Marialva, Vasco Fernandes Coutinho (from a family descendency dating to the old Portuguese nobility), the third Marshal of Portugal. List of counts # Vasco Fernandes Coutinho, 1st Count of Marialva, Vasco Fernandes Coutinho (1385); # Gonçalo Coutinho, 2nd Count of Marialva (1415); # João Coutinho, 3rd Count of Marialva (1450); # Francisco Coutinho, 4th Count of Marialva (1480), married to Beatriz de Meneses, 2nd Countess of Loulé; # Guiomar Coutinho, 5th Countess of Marialva (1510), 3rd Count of Loulé, Countess of Loulé, who married Fernando, Duke of Guarda. References * {{citation , title=Nobreza de Portugal e Brasil , volume=III , publisher=Direcção de Afonso Eduardo Martins Zuquete/Editorial Enciclopédia , edition=II , location=Lisbon, Portugal , year=1989 , language=Portuguese , pag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Real
The ''real'' (, meaning "royal", plural: ''réis'' or rchaic''reais'') was the unit of currency of Portugal and the Portuguese Empire from around 1430 until 1911. It replaced the '' dinheiro'' at the rate of 1 real = libras = 70 soldos = 840 dinheiros and was itself replaced by the '' escudo'' (as a result of the Republican revolution of 1910) at a rate of 1 escudo = 1000 réis. The ''escudo'' was further replaced by the euro at a rate of 1 euro = 200.482 ''escudos'' in 2002. History The first ''real'' was introduced by King Fernando I around 1380.Numária nacional Tesouros Numismáticos Portugueses It was a silver coin and had a value of 120 '' dinheiros'' (10 ''soldos'' or ''libra''). In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infante Fernando, Duke Of Viseu
Infante Ferdinand, Duke of Viseu and Beja (or ''Fernando,'' , 17 November 1433 – 18 September 1470) was the third son of Edward, King of Portugal and his wife Eleanor of Aragon. Biography Ferdinand was born in Almeirim on 17 November 1433, and died in Setúbal on 18 September 1470. He was twice sworn Prince of Portugal (title granted to the presumptive heir to the throne): first between 1438 and 1451, once his older brother became king Afonso V of Portugal and had no children; and for the second time, in 1451, when Prince João was born, but died months later. When Afonso V's first daughter, Princess Joan, was born (1452), Infante Ferdinand finally lost this title. In 1452, Ferdinand fled the country looking for adventure. Some say he wanted to go to the north African cities controlled by the Portuguese; others say that he wanted to join his uncle, the King Alfonso I of Naples, in his campaigns in southern Italy. It seems Ferdinand had the hope to inherit his uncle's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Palma
La Palma (, ), also known as ''La isla bonita'' () and historically San Miguel de La Palma, is the most northwesterly island of the Canary Islands, a Spanish autonomous community and archipelago in Macaronesia in the North Atlantic Ocean. La Palma has an area of making it the fifth largest of the eight main Canary Islands. The total population at the start of 2023 was 84,338, of whom 15,522 lived in the capital, Santa Cruz de La Palma and 20,375 in Los Llanos de Aridane. Its highest mountain is the Roque de los Muchachos, at , being second among the peaks of the Canaries after the Teide massif on Tenerife. In 1815, the German geologist Leopold von Buch visited the Canary Islands. It was as a result of his visit to Tenerife, where he visited the Las Cañadas caldera, and then later to La Palma, where he visited the Taburiente caldera, that the Spanish word for cauldron or large cooking pot – "caldera" – was introduced into the geological vocabulary. In the center of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
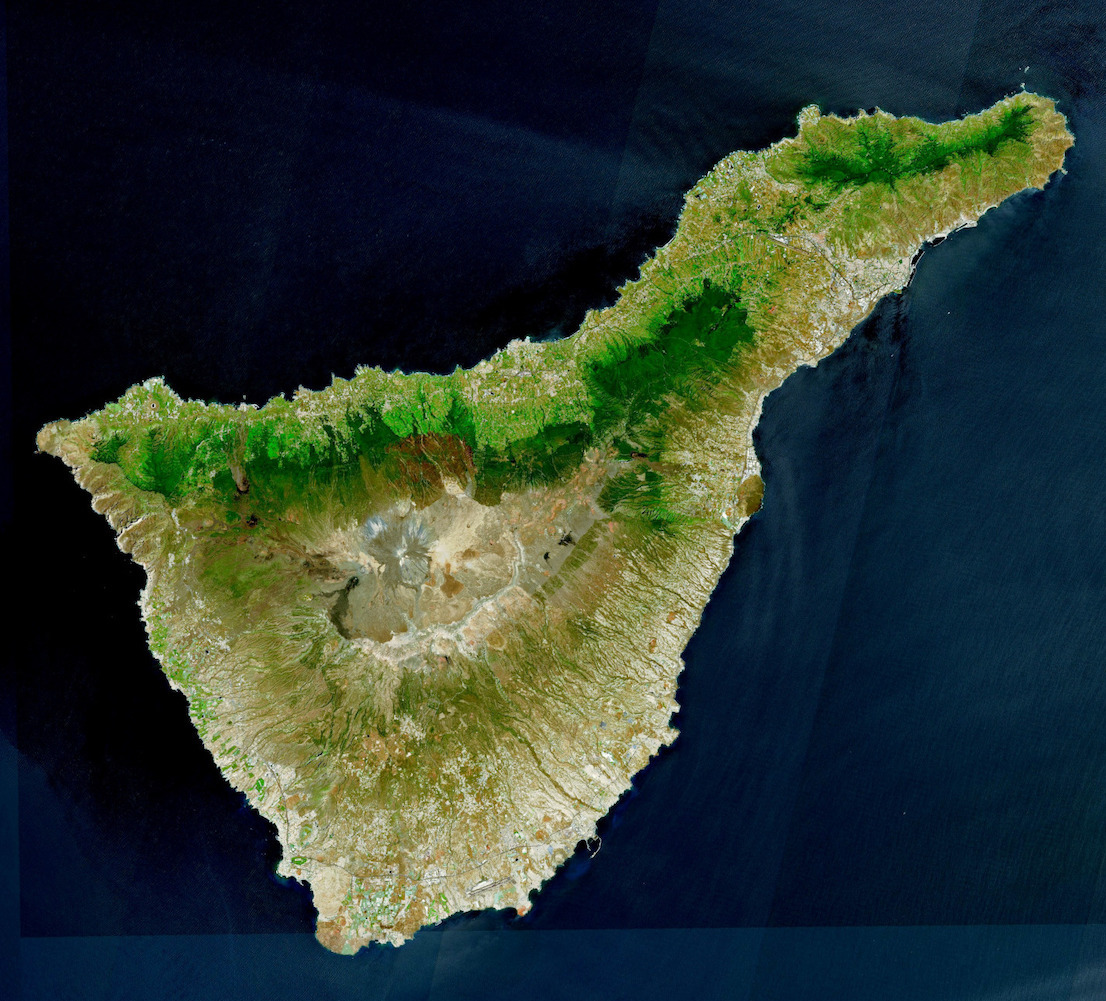
Tenerife
Tenerife ( ; ; formerly spelled ''Teneriffe'') is the largest and most populous island of the Canary Islands, an Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain. With a land area of and a population of 965,575 inhabitants as of April 2025, it is the most populous island in Spain and the entire Macaronesia region. Tenerife is also home to 42.7% of the total population of the archipelago. More than seven million tourists (7,384,707 in 2024) visit Tenerife each year, making it by far the most visited island in the archipelago. It is one of the most important tourist destinations in Spain and the world, hosting one of the world's largest carnivals, the Carnival of Santa Cruz de Tenerife. The capital of the island, , is also the seat of the island council (). That city and are the co-capitals of the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of the Canary Islands. The two cities are both home to governmental institutions, such as the offices of the preside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gran Canaria
Gran Canaria (, ; ), also Grand Canary Island, is the third-largest and second-most-populous island of the Canary Islands, a Spain, Spanish archipelago off the Atlantic coast of Northwest Africa. the island had a population of that constitutes approximately 40% of the population of the archipelago. Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, the capital of the island, is the largest city of the Canary Islands and the ninth-largest of Spain. Gran Canaria is located in the Atlantic Ocean in a region known as Macaronesia about off the northwestern coast of Africa and about from Europe. With an area of and an altitude of at Morro de la Agujereada, Gran Canaria is the third largest island of the archipelago in both area and altitude. Gran Canaria is also the third most populated island in Spain. History In Classical antiquity, antiquity, Gran Canaria was populated by the North African Guanches, Canarii, who may have arrived as early as 500 BC. In the Middle Ages, medieval period, after ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Henry The Navigator
Princy Henry of Portugal, Duke of Viseu (Portuguese language, Portuguese: ''Infante Dom (title), Dom Henrique''; 4 March 1394 – 13 November 1460), better known as Prince Henry the Navigator (), was a Infante of Portugal, Portuguese prince and a central figure in the early days of the Portuguese Empire and in the 15th-century European maritime exploration. Through his administrative direction, he is regarded as the main initiator of what would be known as the Age of Discovery. Henry was the fourth child of King John I of Portugal, who founded the House of Aviz. After procuring the new caravel ship, Henry was responsible for the early development of Portuguese exploration and maritime trade with other continents through the systematic exploration of Western Africa, the islands of the Atlantic Ocean, and the search for new routes. He encouraged his father to conquer Ceuta (1415), the Muslim port on the North African coast across the Straits of Gibraltar from the Iberian Peninsula. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joan Of Portugal
Joan of Portugal ( �uˈɐnɐ 31 March 1439 – June 13, 1475) was the Queen of Castile as the second wife of King Henry IV of Castile. The posthumous daughter of King Edward of Portugal and Eleanor of Aragon, she was born in the Quinta do Monte Olivete Villa, Almada. Early life Joan was born as one of nine children of King Edward of Portugal and his wife Eleanor of Aragon. Joan was born on the 31th of March, 1439 at Quinta do Monte Olivete (modern day Almeda), after her father's death. In 1440, Eleanor was politically outmaneuvered from the regency of Joan's brother Afonso and was forced into exile in Castile together with the infant Joan. In Castile, Joan and her mother lived at the monastery of Santa María de Medina del Campo, dependent on charity. Joan's mother was deeply unhappy as she longed for the children she had to leave behind in Portugal. In 1444 Eleanor applied for them to return to Portugal, but she died in February 1445 at Toledo. There were rumor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castile (historical Region)
Castile or Castille (; ) is a territory of imprecise limits located in Spain. The use of the concept of Castile relies on the assimilation (via a metonymy) of a 19th-century determinism, determinist geographical notion, that of Castile as Spain's ("tableland core", connected to the Meseta Central) with a long-gone historical entity of diachronically variable territorial extension (the Kingdom of Castile). The proposals advocating for a particular semantic codification/closure of the concept (a ''dialogical'' construct) are connected to Essentialism#In historiography, essentialist arguments relying on the Reification (fallacy), reification of something that does not exist beyond the social action of those Social constructivism, building Castile not only by Castilian nationalism, identifying with it as a homeland of any kind, but also Alterity, ''in opposition'' to it. A hot topic concerning the concept of Castile is its relation with Spain, insofar intellectuals, politicians, writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knights Hospitaller
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem, commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), is a Catholic military order. It was founded in the crusader Kingdom of Jerusalem in the 12th century and had headquarters there until 1291, thereafter being based in Kolossi Castle in Cyprus (1302–1310), the island of Rhodes (1310–1522), Malta (1530–1798), and Saint Petersburg (1799–1801). The Hospitallers arose in the early 12th century at the height of the Cluniac movement, a reformist movement within the Benedictine monastic order that sought to strengthen religious devotion and charity for the poor. Earlier in the 11th century, merchants from Amalfi founded a hospital in Jerusalem dedicated to John the Baptist where Benedictine monks cared for sick, poor, or injured Christian pilgrims to the Holy Land. Blessed Gerard, a lay brother of the Benedictine order, became its head when it was established. After the Christian conquest of Jerusalem in 1099 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |