|
Market Impact
In financial markets, market impact is the effect that a market participant has when it buys or sells an asset. It is the extent to which the buying or selling moves the price against the buyer or seller, i.e., upward when buying and downward when selling. It is closely related to market liquidity; in many cases "liquidity" and "market impact" are synonymous. Especially for large investors, e.g., financial institutions, market impact is a key consideration before any decision to move money within or between financial markets. If the amount of money being moved is large (relative to the turnover of the asset(s) in question), then the market impact can be several percentage points and needs to be assessed alongside other transaction costs (costs of buying and selling). Market impact can arise because the price needs to move to tempt other investors to buy or sell assets (as counterparties), but also because professional investors may position themselves to profit from knowledge th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Financial Markets
A financial market is a market in which people trade financial securities and derivatives at low transaction costs. Some of the securities include stocks and bonds, raw materials and precious metals, which are known in the financial markets as commodities. The term "market" is sometimes used for what are more strictly ''exchanges'', that is, organizations that facilitate the trade in financial securities, e.g., a stock exchange or commodity exchange. This may be a physical location (such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), London Stock Exchange (LSE), Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) or Johannesburg Stock Exchange (JSE Limited)) or an electronic system such as NASDAQ. Much trading of stocks takes place on an exchange; still, corporate actions (mergers, spinoffs) are outside an exchange, while any two companies or people, for whatever reason, may agree to sell the stock from the one to the other without using an exchange. Trading of currencies and bonds is largely on a bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Square Root
In mathematics, a square root of a number is a number such that y^2 = x; in other words, a number whose ''square'' (the result of multiplying the number by itself, or y \cdot y) is . For example, 4 and −4 are square roots of 16 because 4^2 = (-4)^2 = 16. Every nonnegative real number has a unique nonnegative square root, called the ''principal square root'' or simply ''the square root'' (with a definite article, see below), which is denoted by \sqrt, where the symbol "\sqrt" is called the '' radical sign'' or ''radix''. For example, to express the fact that the principal square root of 9 is 3, we write \sqrt = 3. The term (or number) whose square root is being considered is known as the ''radicand''. The radicand is the number or expression underneath the radical sign, in this case, 9. For non-negative , the principal square root can also be written in exponent notation, as x^. Every positive number has two square roots: \sqrt (which is positive) and -\sqrt (which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slippage (finance)
With regard to futures contracts as well as other financial instruments, slippage is the difference between where the computer signaled the entry and exit for a trade and where actual clients, with actual money, entered and exited the market using the computer's signals. Market impact, liquidity, and frictional costs may also contribute. Algorithmic trading is often used to reduce slippage, and algorithms can be backtested on past data to see the effects of slippage, but it is impossible to eliminate. Measurement Using initial mid price Nassim Nicholas Taleb (1997) defines slippage as the difference between the average execution price and the initial midpoint of the bid and the offer for a given quantity to be executed. Using initial execution price Knight and Satchell mention a flow trader needs to consider the effect of executing a large order on the market and to adjust the bid-ask spread accordingly. They calculate the liquidity cost as the difference between the execution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
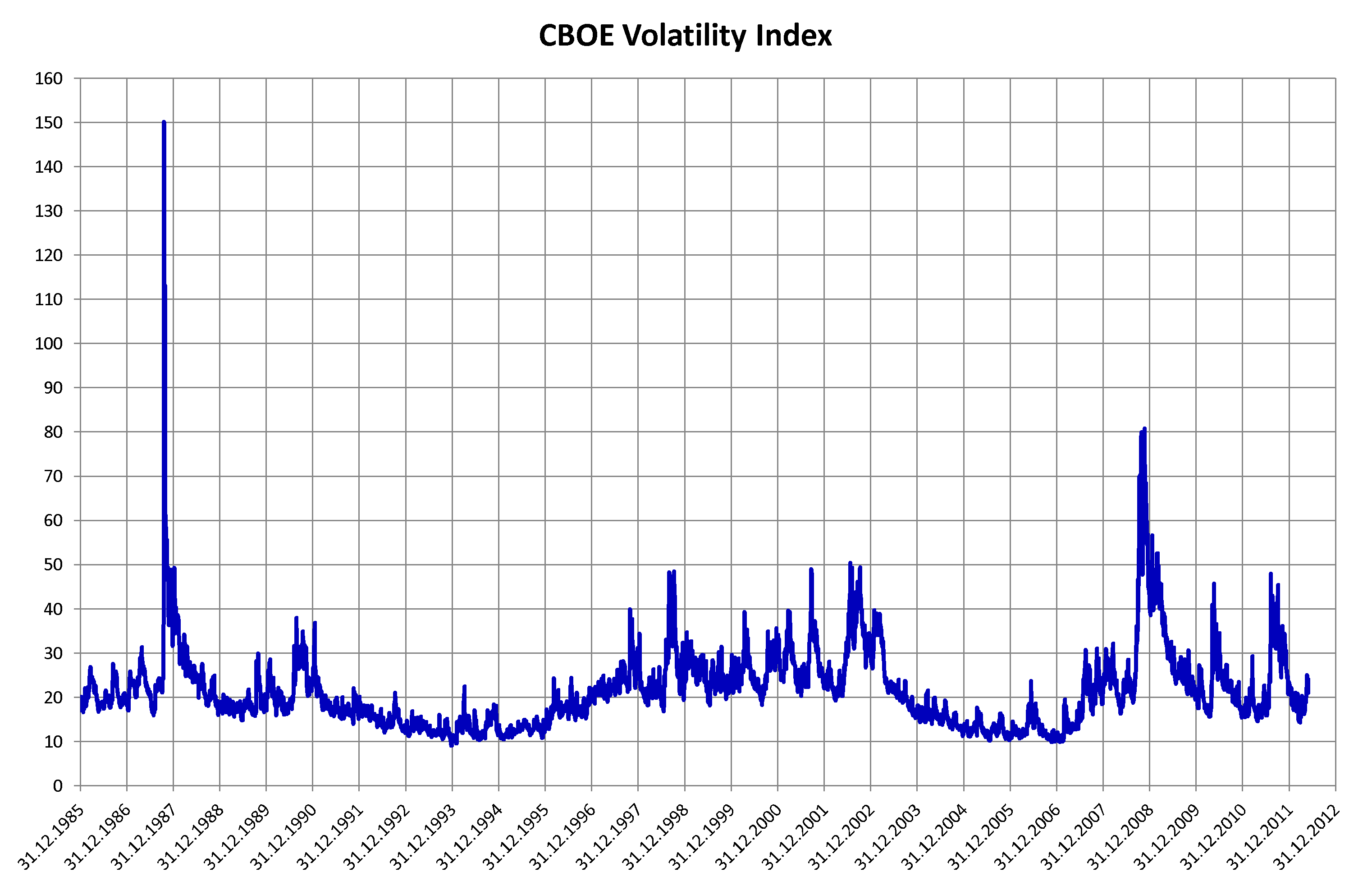
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility (usually denoted by "sigma, σ") is the Variability (statistics), degree of variation of a trading price series over time, usually measured by the standard deviation of logarithmic returns. Historic volatility measures a time series of past market prices. Implied volatility looks forward in time, being derived from the market price of a market-traded derivative (in particular, an option). Volatility terminology Volatility as described here refers to the actual volatility, more specifically: * actual current volatility of a financial instrument for a specified period (for example 30 days or 90 days), based on historical prices over the specified period with the last observation the most recent price. * actual historical volatility which refers to the volatility of a financial instrument over a specified period but with the last observation on a date in the past **near synonymous is realized volatility, the square root of the realized variance, in turn c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Float
In the context of stock markets, the public float or free float represents the portion of shares of a corporation that are in the hands of public investors as opposed to locked-in shares held by promoters, company officers, controlling-interest investors, or governments. This number is sometimes seen as a better way of calculating market capitalization, because it provides a more accurate reflection (than entire market capitalization) of what public investors consider the company to be worth. In this context, the ''float'' may refer to all the shares outstanding that can be publicly traded. Calculating public float The float is calculated by subtracting the locked-in shares from outstanding shares. For example, a company may have 10 million outstanding shares, with 3 million of them in a locked-in position; this company's float would be 7 million (multiplied by the share price). Stocks with smaller floats tend to be more volatile than those with larger floats. In general, the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microcap Stock
In business and investing, term microcap stock (also micro-cap) refers to the stock of Public company, public companies in the United States which have a market capitalization of roughly $50 million to $250 million. The shares of companies with a market capitalization of less than $50 million are typically referred to as nano-cap stocks. Many micro-cap and nano-cap stocks are traded Over-the-counter (finance), over-the-counter with their prices quoted on the OTCBB, OTC Link LLC, or the Pink Sheets LLC, Pink Sheets. The larger, more established micro-caps are listed on the NASDAQ#Market tiers, NASDAQ Capital Market or American Stock Exchange (AMEX). This is true in the US, but by contrast—in Australia, for example—nano-cap companies are commonly listed on the Australian Securities Exchange (ASX). Microcap stocks are in many ways different from other stocks since they are from companies with a small market capitalization and are usually traded on stock exchanges that do not requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logarithm
In mathematics, the logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, must be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of to base is , because is to the rd power: . More generally, if , then is the logarithm of to base , written , so . As a single-variable function, the logarithm to base is the inverse of exponentiation with base . The logarithm base is called the ''decimal'' or ''common'' logarithm and is commonly used in science and engineering. The ''natural'' logarithm has the number as its base; its use is widespread in mathematics and physics because of its very simple derivative. The ''binary'' logarithm uses base and is widely used in computer science, information theory, music theory, and photography. When the base is unambiguous from the context or irrelevant it is often omitted, and the logarithm is written . Logarithms were introduced by John Napier in 1614 as a means of simplifying calculation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Microstructure
Market microstructure is a branch of finance concerned with the details of how exchange occurs in markets. While the theory of market microstructure applies to the exchange of real or financial assets, more evidence is available on the microstructure in the financial field due to the availability of transactions data from them. The major thrust of market microstructure research examines the ways in which the working processes of a market affect determinants of transaction costs, prices, quotes, volume, and trading behavior. In the twenty-first century, innovations have allowed an expansion into the study of the impact of market microstructure on the incidence of market abuse, such as insider trading, market manipulation and broker-client conflict. Definition Maureen O'Hara defines market microstructure as "the study of the process and outcomes of exchanging assets under explicit trading rules. While much of economics abstracts from the mechanics of trading, microstructure liter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Liquidity
In business, economics or investment, market liquidity is a market's feature whereby an individual or firm can quickly purchase or sell an asset without causing a drastic change in the asset's price. Liquidity involves the trade-off between the price at which an asset can be sold, and how quickly it can be sold. In a liquid market, the trade-off is mild: one can sell quickly without having to accept a significantly lower price. In a relatively illiquid market, an asset must be discounted in order to sell quickly. A liquid asset is an asset which can be converted into cash within a relatively short period of time, or cash itself, which can be considered the most liquid asset because it can be exchanged for goods and services instantly at face value. Overview A liquid asset has some or all of the following features: it can be sold rapidly, with minimal loss of value, anytime within market hours. The essential characteristic of a liquid market is that there are always ready and wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transaction Cost
In economics, a transaction cost is a cost incurred when making an economic trade when participating in a market. The idea that transactions form the basis of economic thinking was introduced by the institutional economist John R. Commons in 1931. Oliver E. Williamson's ''Transaction Cost Economics'' article, published in 2008, popularized the concept of transaction costs. Douglass C. North argues that institutions, understood as the set of rules in a society, are key in the determination of transaction costs. In this sense, institutions that facilitate low transaction costs can boost economic growth.North, Douglass C. 1992. "Transaction costs, institutions, and economic performance", San Francisco, CA: ICS Press. Alongside production costs, transaction costs are one of the most significant factors in business operation and management. Definition Williamson defines transaction costs as a cost innate in running an economic system of companies, comprising the total costs of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |