|
Manifest Typing
In computer science, manifest typing is explicit identification by the software programmer of the ''type'' of each variable being declared. For example: if variable ''X'' is going to store integers then its ''type'' must be declared as integer. The term "manifest typing" is often used with the term latent typing to describe the difference between the static, compile-time type membership of the object and its run-time type identity. In contrast, some programming languages use ''implicit typing'' (a.k.a. type inference) where the type is deduced from context at compile-time or allow for dynamic typing in which the variable is just declared and may be assigned a value of any type at runtime. It's important to know the difference between manifest/implicit typing and static/dynamic typing. The first one describes how the variables (and it's types) are defined, while the second describes whether the language checks the types at compile or execution time. Examples Consider the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Programmer
A programmer, computer programmer or coder is an author of computer source code someone with skill in computer programming. The professional titles ''software developer'' and ''software engineer'' are used for jobs that require a programmer. Identification Sometimes a programmer or job position is identified by the language used or target platform. For example, assembly programmer, web developer. Job title The job titles that include programming tasks have differing connotations across the computer industry and to different individuals. The following are notable descriptions. A ''software developer'' primarily implements software based on specifications and fixes bugs. Other duties may include reviewing code changes and testing. To achieve the required skills for the job, they might obtain a computer science or associate degree, attend a programming boot camp or be self-taught. A ''software engineer'' usually is responsible for the same tasks as a dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Typing
In computer programming, latent typing refers to a type system where types are associated with values In ethics and social sciences, value denotes the degree of importance of some thing or action, with the aim of determining which actions are best to do or what way is best to live ( normative ethics), or to describe the significance of different a ... and not variables. An example latently typed language is Scheme. This typically requires run-time type checking and so is commonly used synonymously with dynamic typing. See also * Duck typing References Data types Type systems {{compu-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Static Variable
In computer programming, a static variable is a variable that has been allocated "statically", meaning that its lifetime (or "extent") is the entire run of the program. This is in contrast to shorter-lived automatic variables, whose storage is stack allocated and deallocated on the call stack; and in contrast to dynamically allocated objects, whose storage is allocated and deallocated in heap memory. Variable lifetime is contrasted with scope (where a variable can be used): "global" and "local" refer to scope, not lifetime, but scope often implies lifetime. In many languages, global variables are always static, but in some languages they are dynamic, while local variables are generally automatic, but may be static. In general, is the allocation of memory at compile time, before the associated program is executed, unlike dynamic memory allocation or automatic memory allocation where memory is allocated as required at run time. History Static variables date at least ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compile Time
In computer science, compile time (or compile-time) describes the time window during which a language's statements are converted into binary instructions for the processor to execute. The term is used as an adjective to describe concepts related to the context of program compilation, as opposed to concepts related to the context of program execution ( run time). For example, ''compile-time requirements'' are programming language requirements that must be met by source code before compilation and ''compile-time properties'' are properties of the program that can be reasoned about during compilation. The actual length of time it takes to compile a program is usually referred to as ''compilation time''. Overview Most compilers have at least the following compiler phases (which therefore occur at compile-time): syntax analysis, semantic analysis, and code generation. During optimization phases, constant expressions in the source code can also be evaluated at compile-time usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
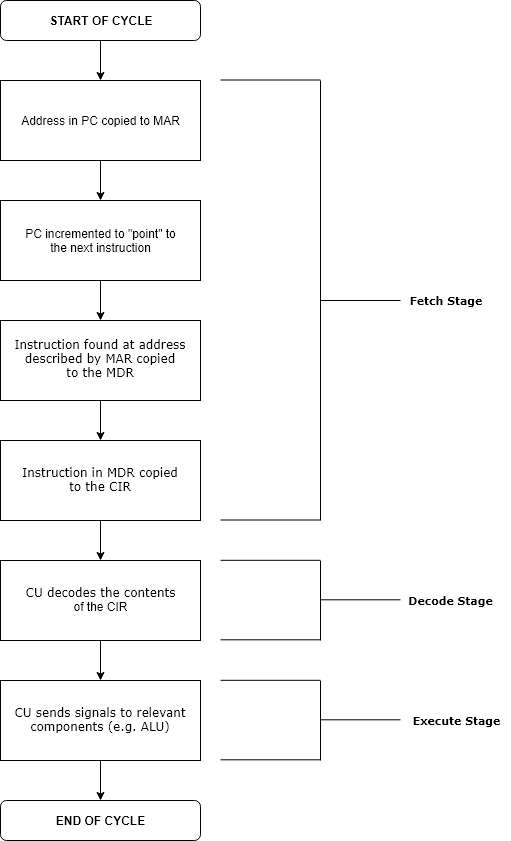
Run Time (program Lifecycle Phase)
Execution in computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine interprets and acts on the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a particular action which must be carried out, in order for a specific problem to be solved. Execution involves repeatedly following a " fetch–decode–execute" cycle for each instruction done by the control unit. As the executing machine follows the instructions, specific effects are produced in accordance with the semantics of those instructions. Programs for a computer may be executed in a batch process without human interaction or a user may type commands in an interactive session of an interpreter. In this case, the "commands" are simply program instructions, whose execution is chained together. The term run is used almost synonymously. A related meaning of both "to run" and "to execute" refers to the specific action of a user starting (or ''launching'' o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type Inference
Type inference, sometimes called type reconstruction, refers to the automatic detection of the type of an expression in a formal language. These include programming languages and mathematical type systems, but also natural languages in some branches of computer science and linguistics. Nontechnical explanation In a typed language, a term's type determines the ways it can and cannot be used in that language. For example, consider the English language and terms that could fill in the blank in the phrase "sing _." The term "a song" is of singable type, so it could be placed in the blank to form a meaningful phrase: "sing a song." On the other hand, the term "a friend" does not have the singable type, so "sing a friend" is nonsense. At best it might be metaphor; bending type rules is a feature of poetic language. A term's type can also affect the interpretation of operations involving that term. For instance, "a song" is of composable type, so we interpret it as the thing created ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type System
In computer programming, a type system is a logical system comprising a set of rules that assigns a property called a ''type'' (for example, integer, floating point, string) to every '' term'' (a word, phrase, or other set of symbols). Usually the terms are various language constructs of a computer program, such as variables, expressions, functions, or modules. A type system dictates the operations that can be performed on a term. For variables, the type system determines the allowed values of that term. Type systems formalize and enforce the otherwise implicit categories the programmer uses for algebraic data types, data structures, or other data types, such as "string", "array of float", "function returning boolean". Type systems are often specified as part of programming languages and built into interpreters and compilers, although the type system of a language can be extended by optional tools that perform added checks using the language's original type synta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced'' '' – like the letter c'') is a general-purpose programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted Central processing unit, CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems code (especially in Kernel (operating system), kernels), device drivers, and protocol stacks, but its use in application software has been decreasing. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the most widely used programming langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C23 (C Standard Revision)
C23, formally ISO/IEC 9899:2024, is the current open standard for the C programming language, which supersedes C17 (standard ISO/IEC 9899:2018). It was started in 2016 informally as C2x, and was published on October 31, 2024. The freely available draft most similar to the one published is document N3220 (see Available texts, below). The first WG14 meeting for the C2x draft was held in October 2019, virtual remote meetings were held in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic, then various teleconference meetings continued to occur through 2024. In C23, the value of __STDC_VERSION__ changes from 201710L to 202311L. The common names "C17" and "C23" reflect these values, which are frozen prior to final adoption, rather than the years in the ISO standards identifiers (9899:2018 and 9899:2024). Features Changes integrated into the latest working draft of C23 are listed below. Standard Library New functions * Add memset_explicit() function in to erase sensitive data, where memory stor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard ML
Standard ML (SML) is a General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, High-level programming language, high-level, Modular programming, modular, Functional programming, functional programming language with compile-time type checking and type inference. It is popular for writing compilers, for programming language research, and for developing automated theorem proving, theorem provers. Standard ML is a modern dialect of ML (programming language), ML, the language used in the Logic for Computable Functions (LCF) theorem-proving project. It is distinctive among widely used languages in that it has a formal specification, given as typing rules and operational semantics in ''The Definition of Standard ML''. Language Standard ML is a functional programming language with some impure features. Programs written in Standard ML consist of Expression (computer science), expressions in contrast to statements or commands, although some expressions of type Unit type, unit are only eva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |