|
Mamfe Languages
The Mamfe or Nyang languages are three languages that form a branch of Southern Bantoid languages spoken in southwest Cameroon Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R .... They are: : Denya, Kendem and Kenyang (Nyang). They are clearly related to each other, though they are not close. References Southern Bantoid languages {{mamfe-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Its coastline lies on the Bight of Biafra, part of the Gulf of Guinea, and the Atlantic Ocean. Due to its strategic position at the crossroads between West Africa and Central Africa, it has been categorized as being in both camps. Cameroon's population of nearly 31 million people speak 250 native languages, in addition to the national tongues of English and French, or both. Early inhabitants of the territory included the Sao civilisation around Lake Chad and the Baka people (Cameroon and Gabon), Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest. Portuguese discoveries, Portuguese explorers reached the coast in the 15th century and named the area ''Rio dos Camarões'' (''Shrimp River''), which became ''C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic–Congo Languages
The Atlantic–Congo languages make up the largest demonstrated family of languages in Africa. They have characteristic noun class systems and form the core of the Niger–Congo family hypothesis. They comprise all of Niger–Congo apart from Mande, Dogon, Ijoid, Siamou, Kru, the Katla and Rashad languages (previously classified as Kordofanian), and perhaps some or all of the Ubangian languages. Hans Gunther Mukanovsky's "Western Nigritic" corresponded roughly to modern Atlantic–Congo. In the infobox, the languages which appear to be the most divergent are placed at the top. The Atlantic branch is defined in the narrow sense (as Senegambian), while the former Atlantic branches Mel and the isolates Sua, Gola and Limba are split out as primary branches; they are mentioned next to each other because there is no published evidence to move them; Volta–Congo is intact apart from Senufo and Kru. ''Glottolog'', based primarily on Güldemann (2018), has a more limi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
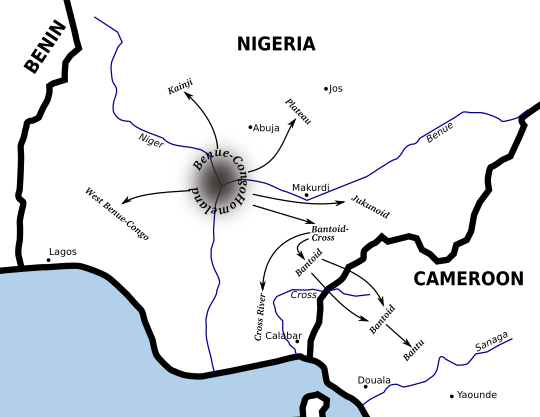
Benue–Congo Languages
Benue–Congo (sometimes called East Benue–Congo) is a major branch of the Volta-Congo languages which covers most of Sub-Saharan Africa. Subdivisions Central Nigerian (or Platoid) contains the Plateau languages, Plateau, Jukunoid languages, Jukunoid and Kainji languages, Kainji families, and Bantoid–Cross combines the Bantoid languages, Bantoid and Cross River languages, Cross River groups. Bantoid is only a collective term for every subfamily of Bantoid–Cross except Cross River, and this is no longer seen as forming a valid branch, however one of the subfamilies, Southern Bantoid, is still considered valid. It is Southern Bantoid which contains the Bantu languages, which are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa. This makes Benue–Congo one of the largest subdivisions of the Niger–Congo language family, both in number of languages, of which ''Ethnologue'' counts 976 (2017), and in speakers, numbering perhaps 350 million. Benue–Congo also includes a few minor Languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantoid
Bantoid is a major branch of the Benue–Congo language family. It consists of the Northern Bantoid languages and the Southern Bantoid languages, a division which also includes the Bantu languages that constitute the overwhelming majority and after which Bantoid is named. History The term "Bantoid" was first used by Krause in 1895 for languages that showed resemblances in vocabulary to Bantu. Joseph Greenberg, in his 1963 ''The Languages of Africa'', defined Bantoid as the group to which Bantu belongs together with its closest relatives; this is the sense in which the term is still used today. However, according to Roger Blench, the Bantoid languages probably do not actually form a coherent group. Internal classification A proposal that divided Bantoid into North Bantoid and South Bantoid was introduced by Williamson. In this proposal, the Mambiloid and Dakoid languages (and later Tikar) are grouped together as North Bantoid, while everything else Bantoid is subsumed under So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Bantoid Languages
Southern Bantoid (or South Bantoid) is a branch of the Bantoid language family. It consists of the Bantu languages along with several small branches and isolates of eastern Nigeria and west-central Cameroon (though the affiliation of some branches is uncertain). Since the Bantu languages are spoken across most of Sub-Saharan Africa, Southern Bantoid comprises 643 languages as counted by ''Ethnologue'', though many of these are mutually intelligible. History Southern Bantoid was first introduced by Williamson in a proposal that divided Bantoid into North and South branches. The unity of the North Bantoid group was subsequently called into question, and Bantoid itself may be polyphyletic A polyphyletic group is an assemblage that includes organisms with mixed evolutionary origin but does not include their most recent common ancestor. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as Homoplasy, homoplasies ..., but the work did establish Southern Banto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denya Language
Denyang is a Southern Bantoid language of Cameroon Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ... Manyu languages ( of the Anyang tribe). It is spoken by five main clans: Ayang, Baku, Betieku, Bantah, Awanchi, they are divergent enough to perhaps be considered separate languages. References Languages of Cameroon Mamfe languages {{mamfe-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kendem Language
Kendem, or Bokwa-Kendem, is a minor Southern Bantoid language of the Mamfe family. It is spoken in three villages in Cameroon Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ..., Kendem, Kekpoti and Bokwa. References Mamfe languages Languages of Cameroon {{mamfe-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenyang Language
Kenyang (Nyang, Banyang, Manyang) is the most spoken language of the Mamfe language group. It is spoken in the Manyu and Meme departments of the Southwest Region of Cameroon. Kenyang speakers in Cameroon are known as Bayangi (Bayangui) people and are called Bayangi (Bayangui). There are three main dialects of Kenyang: Lower Kenyang, spoken in Eyumojock and Mamfe Central subdivisions, Upper Kenyang, spoken in Upper Bayang subdivision and Kitwii, spoken in Meme department. The Upper Kenyang and Lower Kenyang dialects are more closely related to each other than to Kitwii. Variant names of Kitwii include, Kicwe, Twii, Bakoni, Northern Balong, Upper Balong and Manyeman. Phonology and orthography The phonemes of Kenyang are listed in the tables below, with their orthographic representation written in angled brackets: Consonants The voiceless stops /p t k/ are realized as unreleased word-finally: ə̀p̚('to descend'), ə̀t̚('to wipe') and ɔ̀k̚('to grind'). Before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mamfe Languages
The Mamfe or Nyang languages are three languages that form a branch of Southern Bantoid languages spoken in southwest Cameroon Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R .... They are: : Denya, Kendem and Kenyang (Nyang). They are clearly related to each other, though they are not close. References Southern Bantoid languages {{mamfe-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |