|
Magic In The Greco-Roman World
Magic in the Greco-Roman world – that is, ancient Greece, ancient Rome, and the other cultures with which they interacted, especially ancient Egypt – comprises supernatural practices undertaken by individuals, often privately, that were not under the oversight of official priesthoods attached to the various state, community, and household cults and temples as a matter of public religion. Private magic was practiced throughout Greek and Roman cultures as well as among Jews and early Christians of the Roman Empire. Primary sources for the study of Greco-Roman magic include the Greek Magical Papyri, curse tablets, amulets, and literary texts such as Ovid's ''Fasti'' and Pliny the Elder's ''Natural History''. Terminology Pervasive throughout the Eastern Mediterranean and Western Asia until late antiquity and beyond, ''mágos'', "Magian" or "magician", was influenced by (and eventually displaced) Greek '' goēs'' (γόης), the older word for a practitioner of mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Wall Painting - Hermaphrodite With Satyr And Maenad - Pompeii (IX 1 22) - Napoli MAN 27875
A wall is a structure and a surface that defines an area; carries a load; provides security, shelter, or soundproofing; or serves a decorative purpose. There are various types of walls, including border barriers between countries, brick walls, defensive walls in fortifications, and retaining walls that hold back dirt, stone, water, or noise. Walls can also be found in buildings, where they support roofs, floors, and ceilings, enclose spaces, and provide shelter and security. The construction of walls can be categorized into framed walls and mass-walls. Framed walls transfer the load to the foundation through posts, columns, or studs and typically consist of structural elements, insulation, and finish elements. Mass-walls are made of solid materials such as masonry, concrete, adobe, or rammed earth. Walls may also house utilities like electrical wiring or plumbing and must conform to local building and fire codes. Walls have historically served defensive purposes, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
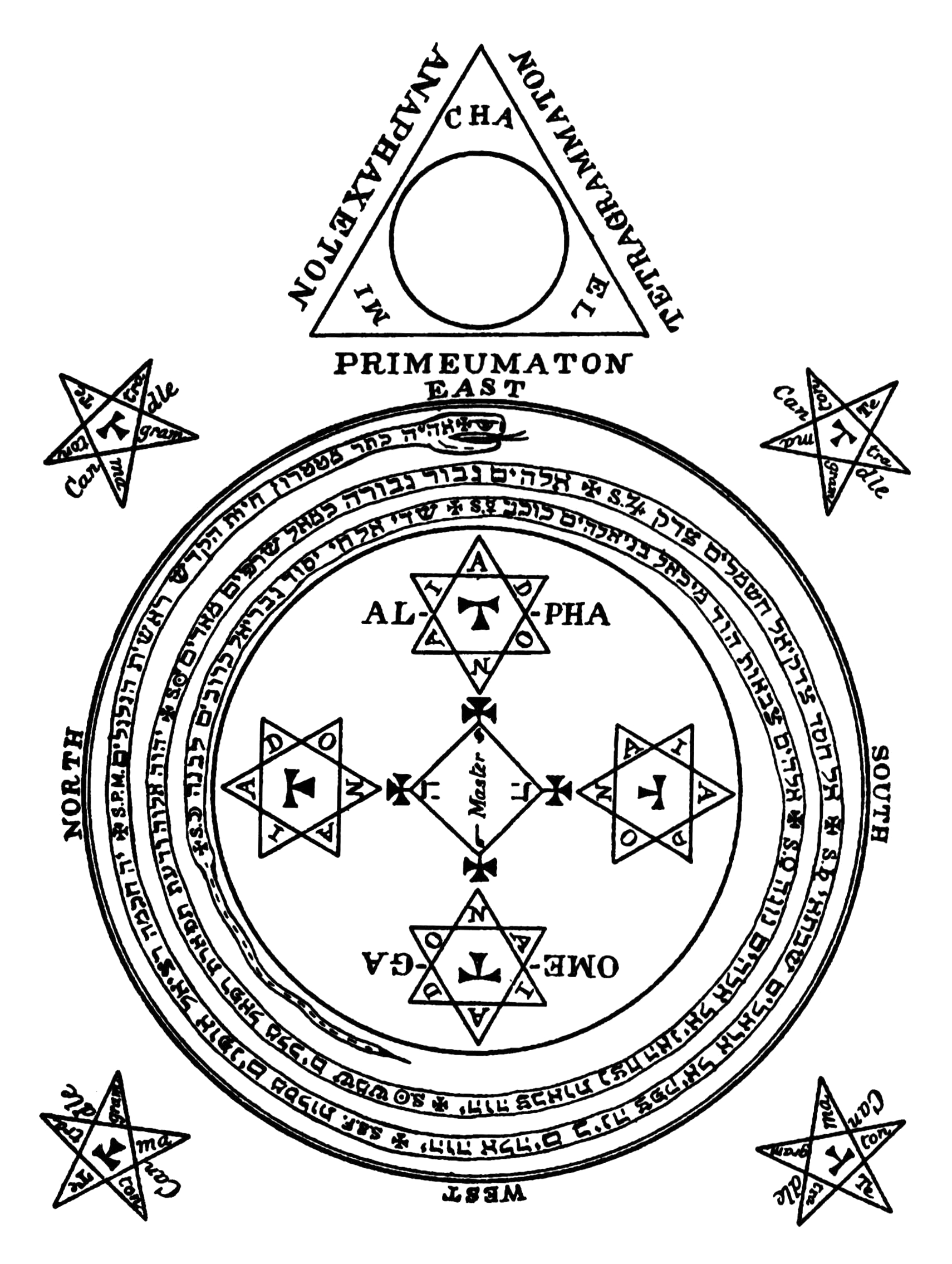
Goetia
(, ) is a type of European sorcery, often referred to as witchcraft, that has been transmitted through grimoires—books containing instructions for performing magical practices. The term "goetia" finds its origins in the Greek word "goes", which originally denoted diviners, magicians, healers, and seers. Initially, it held a connotation of low magic, implying fraudulent or deceptive ''mageia'' as opposed to theurgy, which was regarded as divine magic. Grimoires, also known as "books of spells" or "spellbooks", serve as instructional manuals for various magical endeavors. They cover crafting magical objects, casting spells, performing divination, and summoning supernatural entities, such as angels, spirits, deities, and demons. Although the term "grimoire" originates from Europe, similar magical texts have been found in diverse cultures across the world. The history of grimoires can be traced back to ancient Mesopotamia, where magical incantations were inscribed on c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Suetonius
Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus (), commonly referred to as Suetonius ( ; – after AD 122), was a Roman historian who wrote during the early Imperial era of the Roman Empire. His most important surviving work is ''De vita Caesarum'', commonly known in English as '' The Twelve Caesars'', a set of biographies of 12 successive Roman rulers from Julius Caesar to Domitian. Other works by Suetonius concerned the daily life of Rome, politics, oratory, and the lives of famous writers, including poets, historians, and grammarians. A few of these books have partially survived, but many have been lost. Life Gaius Suetonius Tranquillus was probably born about AD 69, a date deduced from his remarks describing himself as a "young man" 20 years after Nero's death. His place of birth is disputed, but most scholars place it in Hippo Regius, a small north African town in Numidia, in modern-day Algeria. It is certain that Suetonius came from a family of moderate social position, that his fat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ephesus
Ephesus (; ; ; may ultimately derive from ) was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek city on the coast of Ionia, in present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built in the 10th century BC on the site of Apasa, the former Arzawan capital, by Attica, Attic and Ionians, Ionian Greek colonists. During the Classical Greece, Classical Greek era, it was one of twelve cities that were members of the Ionian League. The city came under the control of the Roman Republic in 129 BC. The city was famous in its day for the nearby Temple of Artemis (completed around 550 BC), which has been designated one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Its many monumental buildings included the Library of Celsus and a theatre capable of holding 24,000 spectators. Ephesus was a recipient city of one of the Pauline epistles and one of the seven churches of Asia addressed in the Book of Revelation. The Gospel of John may have been written there,Stephen L Harris, Harris, Stephen L., ''Under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hans Dieter Betz
Hans Dieter Betz (born May 21, 1931) is an American scholar of the New Testament and Early Christianity at the University of Chicago. He has made influential contributions to research on Paul's Letter to the Galatians, the Sermon on the Mount and the Greco-Roman context of Early Christianity. Biography Hans Dieter Betz was born and raised in Germany.Betz, Hans Dieter. ''The Sermon on the Mount. A Commentary''. Minneapolis: Fortress Press, 1995. He received his theological education at Bethel and Mainz in Germany, and at Cambridge in England. Having studied with Herbert Braun, he graduated as Doctor of Theology and "Habilitation" at Mainz (1957, 1966); Dr. h.c. Erlangen. His list of scholarly publications includes New Testament literature, esp. on Paul's letters, as well as on Hellenistic history of religions, writing in English and German. He served also as editor of the lexica "Religion in Geschichte und Gegenwart" (4th ed. 1998-2005) and "Religion Past and Present" (2007-2014) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Eros (mythology)
Eros (, ; ) is the Greek god of love and sexual intercourse, sex. The Romans referred to him as Cupid or Amor. In the earliest account, he is a Greek primordial deities, primordial god, while in later accounts he is the child of Aphrodite. He is usually presented as a handsome young man, though in some appearances he is a juvenile boy full of mischief, ever in the company of his mother. In both cases, he is winged and carries his signature bow and arrows, which he uses to make both mortals and immortal gods fall in love, often under the guidance of Aphrodite. His role in myths is mostly complementary, and he often appears in the presence of Aphrodite and the other love gods and often acts as a catalyst for people to fall in love, but has little unique mythology of his own; the most major exception being the myth of Cupid and Psyche, Eros and Psyche, the story of how he met and fell in love with his wife. Eros and Cupid, are also known, in art tradition, as a Putto (pl. Putti). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Symposium
In Ancient Greece, the symposium (, ''sympósion'', from συμπίνειν, ''sympínein'', 'to drink together') was the part of a banquet that took place after the meal, when drinking for pleasure was accompanied by music, dancing, recitals, or conversation.Peter Garnsey, ''Food and Society in Classical Antiquity'' (Cambridge University Press, 1999), p. 13online Sara Elise Phang, ''Roman Military Service: Ideologies of Discipline in the Late Republic and Early Principate'' (Cambridge University Press, 2008), pp. 263–264. Literary works that describe or take place at a symposium include two Socratic dialogues, Plato's '' Symposium'' and Xenophon's '' Symposium'', as well as a number of Greek poems, such as the elegies of Theognis of Megara. Symposia are depicted in Greek and Etruscan art that shows similar scenes. In modern usage, it has come to mean an academic conference or meeting, such as a scientific conference. The Latin equivalent of a Greek symposium in Roman s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Plato
Plato ( ; Greek language, Greek: , ; born BC, died 348/347 BC) was an ancient Greek philosopher of the Classical Greece, Classical period who is considered a foundational thinker in Western philosophy and an innovator of the written dialogue and dialectic forms. He influenced all the major areas of theoretical philosophy and practical philosophy, and was the founder of the Platonic Academy, a philosophical school in History of Athens, Athens where Plato taught the doctrines that would later become known as Platonism. Plato's most famous contribution is the theory of forms, theory of forms (or ideas), which aims to solve what is now known as the problem of universals. He was influenced by the pre-Socratic thinkers Pythagoras, Heraclitus, and Parmenides, although much of what is known about them is derived from Plato himself. Along with his teacher Socrates, and his student Aristotle, Plato is a central figure in the history of Western philosophy. Plato's complete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Family Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which speak of Timon in particular in the most affectionate terms. Studies and life Plutarch studied mathematics and philosophy in Athens under Ammonius of Athens, Ammonius from AD 66 to 67. He attended th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; ; 355/354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian. At the age of 30, he was elected as one of the leaders of the retreating Ancient Greek mercenaries, Greek mercenaries, the Ten Thousand, who had been part of Cyrus the Younger's attempt to seize control of the Achaemenid Empire. As the military historian Theodore Ayrault Dodge wrote, "the centuries since have devised nothing to surpass the genius of this warrior". For at least two millennia, it has been debated whether or not Xenophon was first and foremost a general, historian, or philosopher. For the majority of time in the past two millennia, Xenophon was recognized as a philosopher. Quintilian in Institutio Oratoria, ''The Orator's Education'' discusses the most prominent historians, orators and philosophers as examples of eloquence and recognizes Xenophon's historical work, but ultimately places Xenophon next to Plato as a philosopher. Today, Xenophon is recognized as one of the gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histories'', a detailed account of the Greco-Persian Wars, among other subjects such as the rise of the Achaemenid dynasty of Cyrus. He has been described as " The Father of History", a title conferred on him by the ancient Roman orator Cicero, and the " Father of Lies" by others. The ''Histories'' primarily cover the lives of prominent kings and famous battles such as Marathon, Thermopylae, Artemisium, Salamis, Plataea, and Mycale. His work deviates from the main topics to provide a cultural, ethnographical, geographical, and historiographical background that forms an essential part of the narrative and provides readers with a wellspring of additional information. Herodotus was criticized in his times for his inclusion of "legends an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Astrology
Astrology is a range of Divination, divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that propose that information about human affairs and terrestrial events may be discerned by studying the apparent positions of Celestial objects in astrology, celestial objects. Different cultures have employed forms of astrology since at least the 2nd millennium BCE, these practices having originated in Calendrical calculation, calendrical systems used to predict seasonal shifts and to interpret celestial cycles as signs of divine communications. Most, if not all, cultures have attached importance to what they observed in the sky, and some—such as the Hindu astrology, Hindus, Chinese astrology, Chinese, and the Maya civilization, Maya—developed elaborate systems for predicting terrestrial events from celestial observations. Western astrology, one of the oldest astrological systems still in use, can trace its roots to 19th–17th century BCE Mesopotamia, fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |