|
Madagascar People's Armed Forces
The Madagascar Armed Forces (, ) is the national military of Madagascar. The IISS detailed the armed forces in 2012 as including an Army of 12,500+, a Navy of 500, and a 500-strong Air Force. The armed forces were involved in the 2009 Malagasy political crisis. During World War II, Malagasy troops fought in France, Morocco, and Syria. History The rise of centralized kingdoms among the Sakalava, Merina and other ethnic groups produced the island's first standing armies, first equipped with spears, but later with muskets, cannons and other firearms. King Ralambo (1575–1612) raised the first standing army in the highland Kingdom of Imerina with a handful of guns, although for at least two centuries the armies of the Sakalava were much larger and better equipped, possessing thousands of muskets obtained principally through trade with European partners. By the early 19th century, however, the army of the Kingdom of Imerina was able to bring much of the island under Merina cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
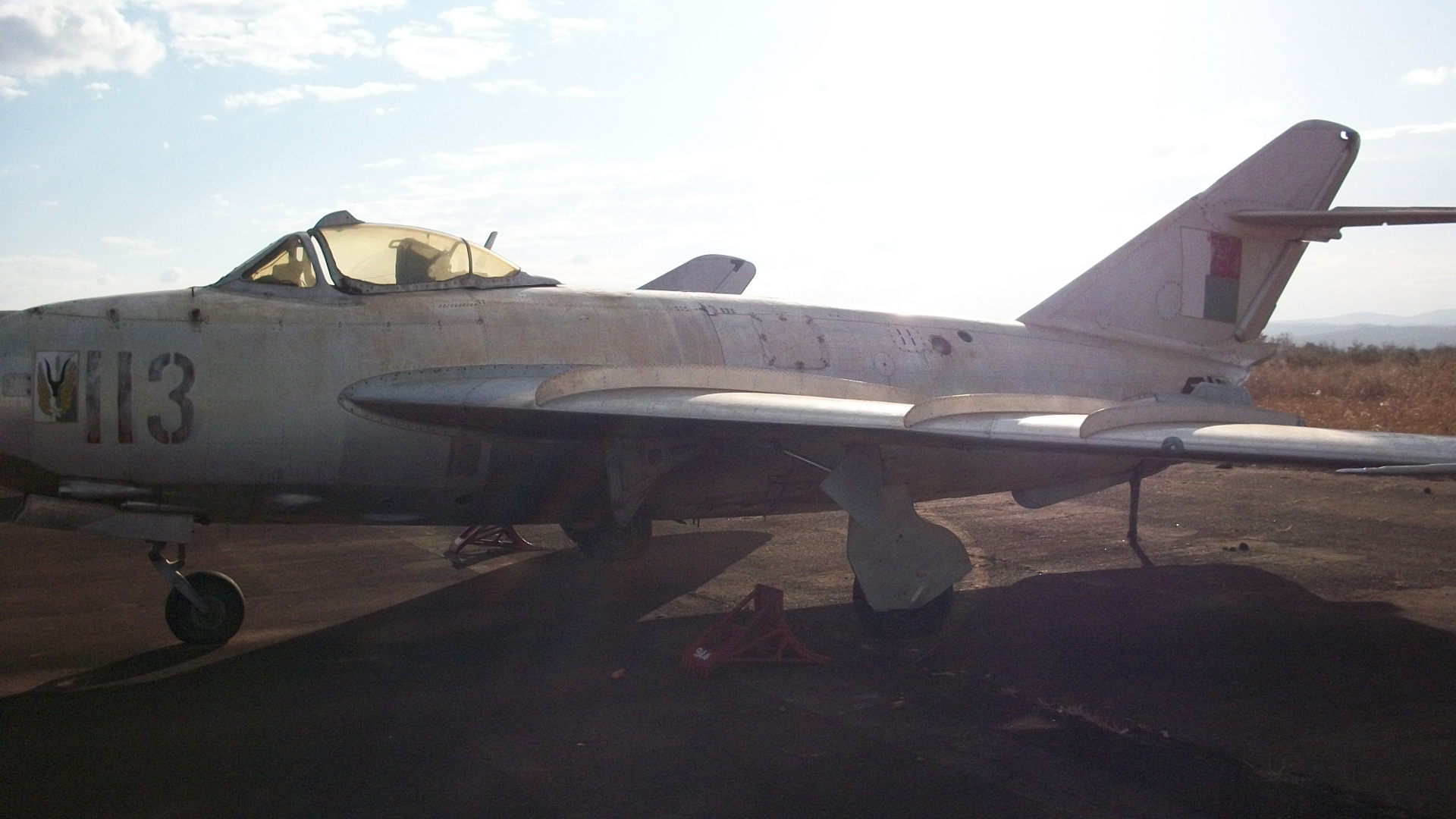
Malagasy Air Force
The Malagasy Air Force () is the aerial warfare branch of the Madagascar Armed Forces. History The Malagasy Air Force was founded in 1960 with mainly former French aircraft such as Douglas DC-3s, Max Holste MH.1521 Broussards and Dassault MD 312s. As of 1970, the air force had 400 personnel on strength, and operated 10 transport aircraft, 11 liaison aircraft, three trainer aircraft and 10 helicopters. The Malagasy Air Force received four MiG-17F fighters from North Korea in 1979. The first Mil Mi-8s were delivered in 1976, and two Antonov An-26s followed in 1980. Several Alouette IIIs were also received in the early 1980s. At an unknown time in the 1980s, the Malagasy Air Force received 10 MiG-21bis fighters and two MiG-21UM trainers. MiG-21s are confirmed to have been operational between 1990 and 2001. They flew little, and all of them were eventually put into storage. In 2009 the Malagasy Air Force acquired four ex-Belgian Alouette IIs. For over a decade the only aircraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakalava People
The Sakalava are an ethnic group of Madagascar. They are primarily found on the western edge of Madagascar from Toliara in the south to the Sambirano River in the north. The Sakalava constitute about 6.2 percent of the total population, or about 2,079,000 in 2018. Their name means "people of the long valleys." Ethnic identity The Sakalava are a number of smaller ethnic groups that once comprised an empire, rather than an ethnic group in its own right. The origin of the word ''Sakalava'' itself is still subject to controversy, as well as its actual meaning. The most common explanation is the modern Malagasy translation of Sakalava meaning long ravines, denoting the relatively flat nature of the land in western Madagascar. Another theory is that the word is possibly from the Arabic ''saqaliba'', which is in turn derived from Late Latin ''sclavus'', meaning slave. History Sakalavas are considered to be a mix of Austronesian and Bantu peoples. Austronesian peoples from various ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gendarmerie
A gendarmerie () is a paramilitary or military force with law enforcement duties among the civilian population. The term ''gendarme'' () is derived from the medieval French expression ', which translates to " men-at-arms" (). In France and some Francophone nations, the gendarmerie is a branch of the armed forces that is responsible for internal security in parts of the territory (primarily in rural areas and small towns in the case of France), with additional duties as military police for the armed forces. It was introduced to several other Western European countries during the Napoleonic conquests. In the mid-twentieth century, a number of former French mandates and colonial possessions (such as Lebanon, Syria, the Ivory Coast and the Republic of the Congo) adopted a gendarmerie after independence. Similar forces exist in most European countries. The European Gendarmerie Force is a structure, aligned with the European Union, that facilitates joint operations. A similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2001 Malagasy Presidential Election
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
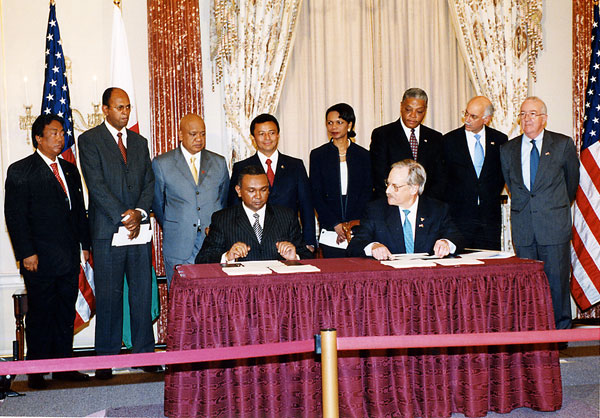
Marc Ravalomanana
Marc Ravalomanana (; born 12 December 1949) is a Malagasy politician who served as the sixth List of presidents of Madagascar, president of Madagascar from 2002 to 2009. Born into a farming Merina people, Merina family in Imerinkasinina, near the capital city of Antananarivo, Ravalomanana first rose to prominence as the founder and CEO of the vast dairy conglomerate TIKO, later launching successful wholesaler MAGRO and several additional companies. He entered politics upon founding the Tiako Iarivo political party in 1999 and successfully ran for the position of mayor of Antananarivo, holding the position from 1999 to 2001. As mayor he improved sanitary and security conditions in the city. In August 2001 he announced his candidacy as an independent candidate in the 2001 Malagasy presidential election, December 2001 presidential election. He then took office as president in 2002 amidst a dispute over election results in which he successfully pressed his claim to have won a majorit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Third Republic Of Madagascar
The Third Republic of Madagascar (officially called the Republic of Madagascar (, ) refers to the 18-year-long period in Malagasy history after the dissolution of the socialist regime in 1992. History A new draft constitution was approved by 75 percent of those voting in a national referendum on 19 August 1992. The first round of presidential elections followed on 25 November. Frontrunner Albert Zafy won 46 percent of the popular vote as the Forces Vives candidate, and Didier Ratsiraka, as leader of his own newly created progovernment front, the Militant Movement for Malagasy Socialism (Mouvement Militant pour le Socialisme Malgache – MMSM), won approximately 29 percent of the vote. The remaining votes were split among a variety of other candidates. Because neither candidate obtained a majority of the votes cast, a second round of elections between the two frontrunners was held on February 10, 1993. Zafy emerged victorious with nearly 67 percent of the popular vote. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Republic Of Madagascar
The Democratic Republic of Madagascar (, ) was a socialist state that existed on the island of Madagascar from 1975 to 1992. History Establishment (1975) Didier Ratsiraka was elected to a seven-year term as president in a national referendum on 21 December 1975, confirming the mandate for consensus and inaugurating Madagascar's Second Republic. The guiding principle of Ratsiraka's administration was the need for a socialist "revolution from above." Specifically, he sought to radically change Malagasy society in accordance with programs and principles incorporated into the Charter of the Malagasy Socialist Revolution, popularly referred to as the "Red Book" (). According to this document, the primary goal of the newly renamed Democratic Republic of Madagascar was to build a "new society" founded on socialist principles and guided by the actions of the "five pillars of the revolution": the Supreme Revolutionary Council (SRC), peasants and workers, young intellectuals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Didier Ratsiraka
Didier Ignace Ratsiraka (; 4 November 1936 – 28 March 2021) was a Malagasy politician and naval officer who was the third president of Madagascar from 1975 to 1993 and the fifth from 1997 to 2002. At the time of his death, he was the longest-serving president of Madagascar. He was first appointed president in 1975 by the military leadership, he was then reelected twice in 1982 and 1989. While he lost to Albert Zafy in 1992, Ratsiraka returned to office after winning the 1997 election. After the 2001 election, he and his opponent Marc Ravalomanana engaged in a lengthy standoff after the latter refused to participate in a runoff election; Ratsiraka eventually stepped down. Early life Didier Ratsiraka was born in Vatomandry, Atsinanana Region, French Madagascar, on 4 November 1936. His father, Albert Ratsiraka, was a member of the Parti des déshérités de Madagascar in the Moramanga District and a Malagasy official in the French colonial administration. Ratsiraka at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philibert Tsiranana
Philibert Tsiranana (18 October 1912 – 16 April 1978) was a Malagasy politician and leader who served as the seventh prime minister of Madagascar from 1958 to 1959, and then later the first president of Madagascar from 1959 to 1972. During the twelve years of his administration, the Republic of Madagascar experienced institutional stability that stood in contrast to the political turmoil many mainland African countries experienced in this period. This stability contributed to Tsiranana's popularity and his reputation as a remarkable statesman. Madagascar experienced moderate economic growth under his social democratic policies and came to be known as "the Happy Island." However, the electoral process was fraught with issues and his term ultimately terminated in a series of farmer and student protests that brought about the end of the First Republic and the establishment of the officially socialist Second Republic. The "benevolent schoolmaster" public image that Tsiranan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Madagascar
The Colony of Madagascar and Dependencies () was a French colony off the coast of Southeast Africa between 1897 and 1958 in what is now Madagascar. The colony was formerly a protectorate of France known as Malagasy Protectorate. The protectorate became a colony, following Queen Ranavalona III's exile to Réunion. In 1958, the colonial administration in Madagascar was abolished, and it became an autonomous territory of the French Community as the Malagasy Republic, which existed until 1975. History Background and French protectorate The United Kingdom had been an ally of Madagascar. In May 1862, John Russell, 1st Earl Russell, Britain's foreign secretary, instructed Connolly Pakenham that Radama II should keep the country away from foreign powers. In 1882, the French started to occupy much of Madagascar's northern and western territories. In 1883, the Franco-Hova Wars commenced between France and Merina Kingdom, but the outcome remained inconclusive. The British gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hierarchy Of Kingdom Of Merina Military
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an important concept in a wide variety of fields, such as architecture, philosophy, design, mathematics, computer science, organizational theory, systems theory, systematic biology, and the social sciences (especially political science). A hierarchy can link entities either directly or indirectly, and either vertically or diagonally. The only direct links in a hierarchy, insofar as they are hierarchical, are to one's immediate superior or to one of one's subordinates, although a system that is largely hierarchical can also incorporate alternative hierarchies. Hierarchical links can extend "vertically" upwards or downwards via multiple links in the same direction, following a path. All parts of the hierarchy that are not linked vertically to one anothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merina Kingdom
The Kingdom of Merina, also known as the Kingdom of Madagascar and officially the Kingdom of Imerina (; –1897), was a pre-colonial state off the coast of Southeast Africa that, by the 18th century, dominated most of what is now Madagascar. It spread outward from Imerina, the Central Highlands region primarily inhabited by the Merina ethnic group with a spiritual capital at Ambohimanga and a political capital west at Antananarivo, currently the seat of government for the modern state of Madagascar. The Merina kings and queens who ruled over greater Madagascar in the 19th century were the descendants of a long line of hereditary Merina royalty originating with Andriamanelo, who is traditionally credited with founding Imerina in 1540. In 1883, France invaded the Merina Kingdom to establish a protectorate. France invaded again in 1894 and conquered the kingdom, making it a French colony, in what became known as the Franco-Hova Wars. History Hova-Vazimba conflict Mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |