|
MOST Bus
MOST (Media Oriented Systems Transport) is a high-speed multimedia network technology for the automotive industry. It can be used for applications inside or outside the car. The serial MOST bus uses a daisy-chain topology or ring topology and synchronous serial communication to transport audio, video, voice and data signals via plastic optical fiber (POF) (MOST25, MOST150) or electrical conductor (MOST50, MOST150) physical layers. MOST technology had been used in car brands worldwide, including BMW, and General Motors. MOST is a registered trademark of Standard Microsystems Corporation (SMSC), now owned by Microchip Technology. Principles of communication The MOST specification defines the physical and the data link layer as well as all seven layers of the OSI model for data communication. For the system developer, MOST is primarily a protocol definition. It provides the user with a standardized application programming interface (API) to access device functionality. The commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automotive Industry
The automotive industry comprises a wide range of company, companies and organizations involved in the design, Business development, development, manufacturing, marketing, selling, Maintenance, repairing, and Custom car, modification of motor vehicles. It is one of the world's largest industry (economics), industries by revenue (from 16% such as in France up to 40% in countries such as Slovakia). The word ''automotive'' comes from the Greek language, Greek ''autos'' (self), and Latin ''motivus'' (of motion), referring to any form of self-powered vehicle. This term, as proposed by Elmer Ambrose Sperry, Elmer Sperry (1860–1930), first came into use to describe automobiles in 1898. History The automotive industry began in the 1860s with hundreds of manufacturers pioneering the Brass Era car, horseless carriage. Early car manufacturing involved manual assembly by a human worker. The process evolved from engineers working on a stationary car to a conveyor belt system where the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uncompressed Audio
Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to digitally represent analog signals. It is the standard form of digital audio in computers, compact discs, digital telephony and other digital audio applications. In a PCM stream, the amplitude of the analog signal is sampled at uniform intervals, and each sample is quantized to the nearest value within a range of digital steps. Alec Reeves, Claude Shannon, Barney Oliver and John R. Pierce are credited with its invention. Linear pulse-code modulation (LPCM) is a specific type of PCM in which the quantization levels are linearly uniform. This is in contrast to PCM encodings in which quantization levels vary as a function of amplitude (as with the A-law algorithm or the μ-law algorithm). Though ''PCM'' is a more general term, it is often used to describe data encoded as LPCM. A PCM stream has two basic properties that determine the stream's fidelity to the original analog signal: the sampling rate, which is the number of times ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
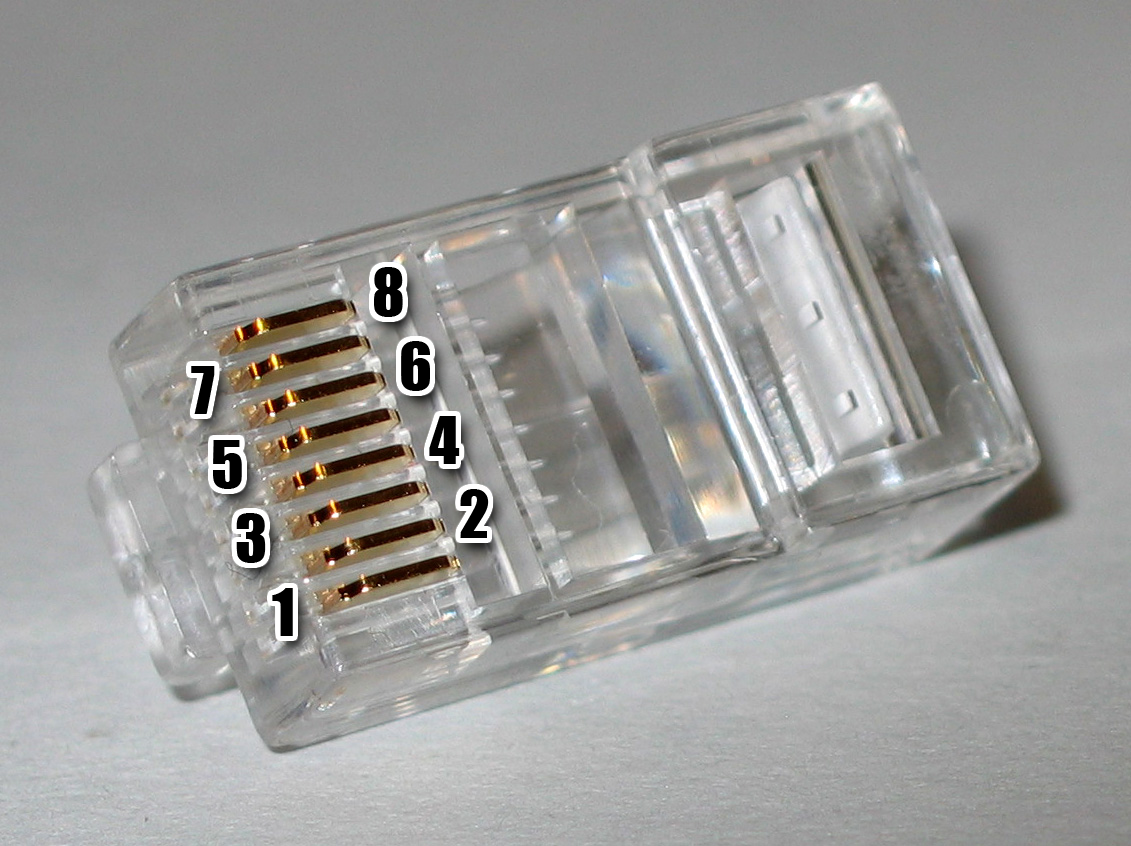
Ethernet Over Twisted Pair
Ethernet over twisted-pair technologies use twisted-pair cables for the physical layer of an Ethernet computer network. They are a subset of all Ethernet physical layers. Early Ethernet used various grades of coaxial cable, but in 1984, StarLAN showed the potential of simple unshielded twisted pair. This led to the development of 10BASE-T and its successors 100BASE-TX, 1000BASE-T, 10GBASE-T and 40GBASE-T, supporting speeds of 10 and 100 megabit per second, then 1, 10 and 40 gigabit per second respectively. Two new variants of 10 megabit per second Ethernet over a ''single'' twisted pair, known as 10BASE-T1S and 10BASE-T1L, were standardized in IEEE Std 802.3cg-2019. 10BASE-T1S has its origins in the automotive industry and may be useful in other short-distance applications where substantial electrical noise is present. 10BASE-T1L is a long-distance Ethernet, supporting connections up to 1 km in length. Both of these standards are finding applications implementi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines. The IEEE has a corporate office in New York City and an operations center in Piscataway, New Jersey. The IEEE was formed in 1963 as an amalgamation of the American Institute of Electrical Engineers and the Institute of Radio Engineers. History The IEEE traces its founding to 1884 and the American Institute of Electrical Engineers. In 1912, the rival Institute of Radio Engineers was formed. Although the AIEE was initially larger, the IRE attracted more students and was larger by the mid-1950s. The AIEE and IRE merged in 1963. The IEEE is headquartered in New York City, but most business is done at the IEEE Operations Center in Piscataway, New Jersey, opened in 1975. The Australian Section of the IEEE existed between 1972 and 1985, after which it s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BroadR-Reach
BroadR-Reach (later also known as ''OPEN Alliance BroadR-Reach'' or ''OABR'') technology is an Ethernet physical layer standard designed for automotive connectivity applications. BroadR-Reach allows multiple in-vehicle systems to simultaneously access information over unshielded single twisted pair cable. BroadR-Reach was invented and is promoted by Broadcom Corporation, now Broadcom Limited. Networks Using BroadR-Reach technology in automotive enables the migration from multiple closed applications to an open Ethernet-based network. This allows automotive manufacturers to incorporate multiple electronic systems and devices, such as advanced safety features (i.e. 360-degree surround view parking assistance, rear-view cameras and collision avoidance systems) and comfort and infotainment features. The automotive-qualified BroadR-Reach Ethernet physical layer standard can be combined with IEEE 802.3 compliant switch technology to deliver 100 Mbit/s over unshielded single twist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Informatik GmbH
{{Infobox company , name = Vector Informatik , logo = , type = GmbH , slogan = , foundation = April 1, 1988, location = Stuttgart, Germany, key_people = Managing directors * Dr. Thomas Beck * Dr. Matthias Traub , num_employees = 4000 (Vector Group worldwide, 2023), industry = Software, products = CANalyzer, CANoe, CANape, CANdelaStudio, PREEvision, revenue = 798,8 million EUR (2021)1.16 billion EUR (Vector Group worldwide, 2023), homepage vector.com Vector Informatik develops software tools and components for networking of electronic systems based on the serial bus systems CAN, LIN, FlexRay, MOST, Ethernet, AFDX, ARINC 429,Supported Bus Systems and Protocols on vector.com loaded April 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FPGA
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a type of configurable integrated circuit that can be repeatedly programmed after manufacturing. FPGAs are a subset of logic devices referred to as programmable logic devices (PLDs). They consist of an array of programmable logic device, programmable logic block, logic blocks with a connecting grid, that can be configured "in the field" to interconnect with other logic blocks to perform various digital functions. FPGAs are often used in limited (low) quantity production of custom-made products, and in research and development, where the higher cost of individual FPGAs is not as important, and where creating and manufacturing a custom circuit would not be feasible. Other applications for FPGAs include the telecommunications, automotive, aerospace, and industrial sectors, which benefit from their flexibility, high signal processing speed, and parallel processing abilities. A FPGA configuration is generally written using a hardware descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Devices
Analog Devices, Inc. (ADI), also known simply as Analog, is an American multinational corporation, multinational semiconductor company specializing in data conversion, signal processing, and power management technology, headquartered in Wilmington, Massachusetts. The company manufactures analog, Mixed-signal integrated circuit, mixed-signal and digital signal processing, digital signal processing (DSP) integrated circuits (ICs) used in electronic equipment. These technologies are used to convert, condition and process real-world phenomena, such as light, sound, temperature, motion, and pressure into electrical signals. Analog Devices has approximately 100,000 customers in the following industries: communications, computer, instrumentation, military/aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics applications.Bloomberg.ADI: Analog Devices Inc Summary" Retrieved January 30, 2011. History The company was founded by two MIT graduates, Ray Stata and Matthew Lorber in 1965. The same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Microsystems Corporation
Microchip Technology Incorporated is a publicly listed American semiconductor corporation that manufactures microcontroller, mixed-signal, analog, and Flash-IP integrated circuits. Its corporate headquarters is located in Chandler, Arizona. Its wafer fabs are located in Gresham, Oregon, and Colorado Springs, Colorado. The company's assembly/test facilities are in Chachoengsao, Thailand, and Calamba and Cabuyao, Philippines. Microchip Technology offers support and resources to educators, researchers and students in an effort to increase awareness and knowledge of embedded applications. History Origins Microchip Technology was founded in 1987 when General Instrument spun off its microelectronics division as a wholly owned subsidiary. The newly formed company was a supplier of programmable non-volatile memory, microcontrollers, digital signal processors, card chip on board, and consumer integrated circuits. An initial public offering (IPO) later in the year was cancel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carmaker
The automotive industry comprises a wide range of companies and organizations involved in the design, development, manufacturing, marketing, selling, repairing, and modification of motor vehicles. It is one of the world's largest industries by revenue (from 16% such as in France up to 40% in countries such as Slovakia). The word ''automotive'' comes from the Greek ''autos'' (self), and Latin ''motivus'' (of motion), referring to any form of self-powered vehicle. This term, as proposed by Elmer Sperry (1860–1930), first came into use to describe automobiles in 1898. History The automotive industry began in the 1860s with hundreds of manufacturers pioneering the horseless carriage. Early car manufacturing involved manual assembly by a human worker. The process evolved from engineers working on a stationary car to a conveyor belt system where the car passed through multiple stations of more specialized engineers. In the 1960s, robotic equipment was introduced, and most car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Light Emitting Diode
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy in the form of photons. The color of the light (corresponding to the energy of the photons) is determined by the energy required for electrons to cross the band gap of the semiconductor. White light is obtained by using multiple semiconductors or a layer of light-emitting phosphor on the semiconductor device. Appearing as practical electronic components in 1962, the earliest LEDs emitted low-intensity infrared (IR) light. Infrared LEDs are used in remote-control circuits, such as those used with a wide variety of consumer electronics. The first visible-light LEDs were of low intensity and limited to red. Early LEDs were often used as indicator lamps, replacing small incandescent bulbs, and in seven-segment displays. Later developments produced LEDs available in visible, ultraviolet (UV), an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isochronous Signal
In telecommunications, an isochronous signal is a signal in which the time interval separating any two significant instants is equal to the unit interval or a multiple of the unit interval. Variations in the time intervals are constrained within specified limits. "Isochronous" is a characteristic of one signal, while " synchronous" indicates a relationship between two or more signals. See also * Synchronization in telecommunications * Synchronous network * Mesochronous network * Plesiochronous system * Asynchronous system The primary focus of this article is asynchronous control in digital electronic systems. In a synchronous system, operations ( instructions, calculations, logic, etc.) are coordinated by one, or more, centralized clock signals. An asynchro ... References Telecommunications engineering Synchronization {{Telecomm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |