|
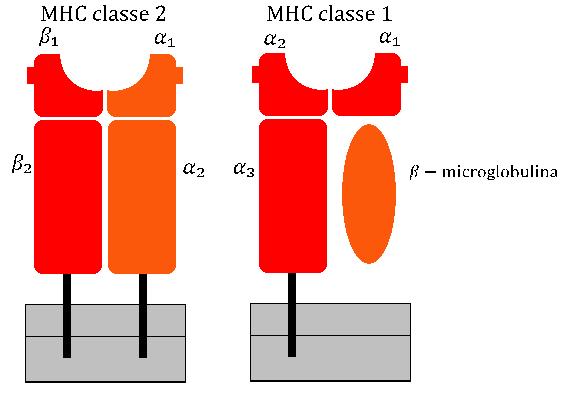
MHC Class II
MHC Class II molecules are a class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules normally found only on professional antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, macrophages, some endothelial cells, thymic epithelial cells, and B cells. These cells are important in initiating immune responses. Antigens presented by MHC class II molecules are exogenous, originating from extracellular proteins rather than cytosolic and endogenous sources like those presented by MHC class I. The loading of a MHC class II molecule occurs by phagocytosis. Extracellular proteins are endocytosed into a phagosome, which subsequently fuses with a lysosome to create a phagolysosome. Within the phagolysosome, lysosomal enzymes degrade the proteins into peptide fragments. These fragments are then loaded into the peptide-binding groove of the MHC class II molecule. Once loaded, the MHC class II-peptide complexes are transported to the plasma membrane via vesicular transport, where they prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Histocompatibility Complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large Locus (genetics), locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for Cell (biology), cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. Its name comes from its discovery during the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules, which is to bind an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bring the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T cell, T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own pheno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vesicular Transport
A vesicular transport protein, or vesicular transporter, is a membrane protein that regulates or facilitates the movement of specific molecules across a vesicle's membrane. As a result, vesicular transporters govern the concentration of molecules within a vesicle. Types Examples include: * Archain * ARFs * Clathrin * Caveolin * Dynamin and related proteins, such as the EHD protein family * Rab proteins * SNAREs * Vesicular transport adaptor proteins e.g. Sorting nexins * Synaptotagmin * TRAPP complex * Synaptophysin * Auxilin Pathways There are multiple pathways, each using its own coat and GTPase. * COP 1 (Cytosolic coat protein complex ) : retrograde transport; Golgi ----> Endoplasmic reticulum * COP 2 (Cytosolic coat protein complex ) : anterograde transport; RER -----> cis-Golgi * Clathrin : trans-Golgi ----> Lysosomes, Plasma membrane ----> Endosomes (receptor-mediated endocytosis) See also * Membrane transport protein A membrane transport protein is a membrane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monocytes
Monocytes are a type of leukocyte or white blood cell. They are the largest type of leukocyte in blood and can differentiate into macrophages and monocyte-derived dendritic cells. As a part of the vertebrate innate immune system monocytes also influence adaptive immune responses and exert tissue repair functions. There are at least three subclasses of monocytes in human blood based on their phenotypic receptors. Structure Monocytes are amoeboid in appearance, and have nongranulated cytoplasm. Thus they are classified as agranulocytes, although they might occasionally display some azurophil granules and/or vacuoles. With a diameter of 15–22 μm, monocytes are the largest cell type in peripheral blood. Monocytes are mononuclear cells and the ellipsoidal nucleus is often lobulated/indented, causing a bean-shaped or kidney-shaped appearance. Monocytes compose 2% to 10% of all leukocytes in the human body. Development Monocytes are produced by the bone marrow from precur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CIITA
CIITA is a human gene which encodes a protein called the class II, major histocompatibility complex, transactivator. Mutations in this gene are responsible for the bare lymphocyte syndrome in which the immune system is severely compromised and cannot effectively fight infection. Chromosomal rearrangement of CIITA is involved in the pathogenesis of Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal B cell lymphoma. Function CIITA mRNA can only be detected in human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system class II-positive cell lines and tissues. This highly restricted tissue distribution suggests that expression of HLA class II genes is to a large extent under the control of CIITA. However, CIITA does not appear to directly bind to DNA. Instead CIITA functions through activation of the transcription factor RFX5. Hence CIITA is classified as a transcriptional coactivator. The CIITA protein contains an acidic transcriptional activation domain, 4 LRRs ( leucine-rich repeats) and a GTP binding d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon γ
Interferon gamma (IFNG or IFN-γ) is a dimerized soluble cytokine that is the only member of the type II class of interferons. The existence of this interferon, which early in its history was known as immune interferon, was described by E. F. Wheelock as a product of human leukocytes stimulated with phytohemagglutinin, and by others as a product of antigen-stimulated lymphocytes. It was also shown to be produced in human lymphocytes. or tuberculin-sensitized mouse peritoneal lymphocytes challenged with Mantoux test (PPD); the resulting supernatants were shown to inhibit growth of vesicular stomatitis virus. Those reports also contained the basic observation underlying the now widely employed interferon gamma release assay used to test for tuberculosis. In humans, the IFNG protein is encoded by the ''IFNG'' gene. Through cell signaling, interferon gamma plays a role in regulating the immune response of its target cell. A key signaling pathway that is activated by type II ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 appear in the genetic code of life. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups ( alpha- , beta- , gamma- amino acids, etc.); other categories relate to polarity, ionization, and side-chain group type ( aliphatic, acyclic, aromatic, polar, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino-acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life on Earth and its emergence. Amino acids are formally named by the IUPAC- IUBMB Joint Commi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterodimer
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex or multimer formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' has roots meaning "two parts", '' di-'' + '' -mer''. A protein dimer is a type of protein quaternary structure. A protein homodimer is formed by two identical proteins while a protein heterodimer is formed by two different proteins. Most protein dimers in biochemistry are not connected by covalent bonds. An example of a non-covalent heterodimer is the enzyme reverse transcriptase, which is composed of two different amino acid chains. An exception is dimers that are linked by disulfide bridges such as the homodimeric protein NEMO. Some proteins contain specialized domains to ensure dimerization (dimerization domains) and specificity. The G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptors have the ability to form both homo- and hetero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bare Lymphocyte Syndrome
Bare lymphocyte syndrome is a condition caused by mutations in certain genes of the major histocompatibility complex or involved with the processing and presentation of MHC molecules. It is a form of severe combined immunodeficiency. Presentation Bare lymphocyte syndrome, type II (BLS II) is a rare recessive genetic condition in which a group of genes called the major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC class II) are not expressed. In BLS II the immune system is severely compromised and cannot effectively fight infection due to an inability for antigen presenting cells to activate CD4⁺ t-cells as no TCR recognition of MHC II/peptide complexes can occur. Clinically, this is similar to severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID), in which lymphocyte precursor cells are improperly formed. Absolute T-cell count is also reduced, due to impaired development with the absence of MHC II. BLS I is characterised by a lack of MHC I molecules. Symptoms can include recurrent bacterial infect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HLA-DO
Human leukocyte histocompatibility complex DO (HLA-DO) is an intracellular, Protein dimer, dimeric non-classical Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) MHC class II, class II protein composed of HLA-DOA, α- and HLA-DOB, β-subunits which interact with HLA-DM in order to fine tune Immunodominance, immunodominant epitope selection. As a non-classical MHC class II molecule, HLA-DO is a non-polymorphic accessory protein that aids in antigenic peptide Chaperone (protein), chaperoning and loading, as opposed to its classical counterparts, which are Polymorphism (biology), polymorphic and involved in antigen presentation. Though more remains to be elucidated about the function of HLA-DO, its unique distribution in the mammalian body—namely, the exclusive expression of HLA-DO in B cells, Thymus, thymic medullary epithelial cells, and dendritic cells—indicate that it may be of physiological importance and has inspired further research. Although HLA-DM can be found without HLA-DO, HLA-D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HLA-DM
HLA-DM (human leukocyte antigen DM) is an intracellular protein involved in the mechanism of antigen presentation on Antigen-presenting cell, antigen presenting cells (APCs) of the immune system. It does this by assisting in peptide loading of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II membrane-bound proteins. HLA-DM is encoded by the genes HLA-DMA and HLA-DMB. HLA-DM is a molecular chaperone that works in lysosomes and endosomes in cells of the immune system. It works in APCs like macrophages, dendritic cells, and B cells by interacting with MHC class II molecules. HLA-DM protects the MHC class II molecules from breaking down, and regulates which proteins or peptides bind to them as well. This regulates how and when a peptide acts as an antigen initiating an immune response. Thus, HLA-DM is necessary for the immune system to respond effectively to a foreign invader. Impairment in HLA-DM function can result in immunodeficiency and autoimmune diseases. Genetics The genes fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HLA-DR
HLA-DR is an MHC class II cell surface receptor encoded by the human leukocyte antigen complex on chromosome 6 region 6p21.31. The complex of HLA-DR (Human Leukocyte Antigen – DR isotype) and peptide, generally between 9 and 30 amino acids in length, constitutes a ligand for the T-cell receptor (TCR). HLA (human leukocyte antigens) were originally defined as cell surface antigens that mediate graft-versus-host disease. Identification of these antigens has led to greater success and longevity in organ transplant. Antigens most responsible for graft loss are HLA-DR (first six months), HLA-B (first two years), and HLA-A (long-term survival). Good matching of these antigens between host and donor is most critical for achieving graft survival. HLA-DR is also involved in several autoimmune conditions, disease susceptibility and disease resistance. It is also closely linked to HLA-DQ and this linkage often makes it difficult to resolve the more causative factor in disease. HLA-DR mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HLA-DQ
HLA-DQ (DQ) is a cell surface receptor protein found on antigen-presenting cells. It is an αβ heterodimer of type MHC class II. The α and β chains are encoded by two loci, HLA-DQA1 and HLA-DQB1, that are adjacent to each other on chromosome band 6p21.3. Both α-chain and β-chain vary greatly. A person often produces two α-chain and two β-chain variants and thus 4 isoforms of DQ. The DQ loci are in close genetic linkage to HLA-DR, and less closely linked to HLA-DP, HLA-A, HLA-B and HLA-C. Different isoforms of DQ can bind to and present different antigens to T-cells. In this process T-cells are stimulated to grow and can signal B-cells to produce antibodies. DQ functions in recognizing and presenting foreign antigens (proteins derived from potential pathogens). But DQ is also involved in recognizing common self-antigens and presenting those antigens to the immune system in order to develop tolerance from a very young age. When tolerance to self protein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |