|
Mad1
Mad1 is a non-essential protein which in yeast has a function in the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC). This checkpoint monitors chromosome attachment to spindle microtubules and prevents cells from starting anaphase until the spindle is built up. The name Mad refers to the observation that mutant cells are mitotic arrest deficient (MAD) during microtubule depolymerization. Mad1 recruits the anaphase inhibitor Mad2 to unattached kinetochores and is essential for Mad2-Cdc20 complex formation ''in vivo'' but not ''in vitro''. ''In vivo'', Mad1 acts as a competitive inhibitor of the Mad2-Cdc20 complex. Mad1 is phosphorylated by Mps1 which then leads together with other activities to the formation of the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC). Thereby it inhibits the activity of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C). Homologues of Mad1 are conserved in eukaryotes from yeast to mammals. Introduction In the early 90s, yeast genes were identified which mutations resulted in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetochores
A kinetochore (, ) is a flared oblique-shaped protein structure associated with duplicated chromatids in eukaryotic cells where the spindle fibers, which can be thought of as the ropes pulling chromosomes apart, attach during cell division to pull sister chromatids apart. The kinetochore assembles on the centromere and links the chromosome to microtubule polymers from the mitotic spindle during mitosis and meiosis. The term kinetochore was first used in a footnote in a 1934 Cytology book by Lester W. Sharp and commonly accepted in 1936. Sharp's footnote reads: "The convenient term ''kinetochore'' (= movement place) has been suggested to the author by J. A. Moore", likely referring to John Alexander Moore who had joined Columbia University as a freshman in 1932. Monocentric organisms, including vertebrates, fungi, and most plants, have a single centromeric region on each chromosome which assembles a single, localized kinetochore. Holocentric organisms, such as nematodes and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spindle Assembly Checkpoint
The spindle checkpoint, also known as the metaphase-to-anaphase transition, the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC), the metaphase checkpoint, or the mitotic checkpoint, is a cell cycle checkpoint during metaphase of mitosis or meiosis that prevents the separation of the duplicated chromosomes (Mitosis#Anaphase, anaphase) until each chromosome is properly attached to the Spindle apparatus, spindle. To achieve proper segregation, the two kinetochores on the sister chromatids must be attached to opposite spindle poles (bipolar orientation). Only this pattern of attachment will ensure that each daughter cell (biology), cell receives one copy of the chromosome. The defining biochemical feature of this checkpoint is the stimulation of the anaphase-promoting complex by mitosis, M-phase Cyclin-dependent kinase complex, cyclin-CDK complexes, which in turn causes the proteolysis, proteolytic destruction of cyclins and proteins that hold the sister chromatids together. Overview and importan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BUB1
Mitotic checkpoint serine/threonine-protein kinase BUB1 also known as BUB1 (budding uninhibited by benzimidazoles 1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''BUB1'' gene. Bub1 is a serine/threonine protein kinase first identified in genetic screens of ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae (baker's yeast)''. The protein is bound to kinetochores and plays a key role in the establishment of the spindle checkpoint, mitotic spindle checkpoint and chromosome congression. The mitotic checkpoint kinase is evolutionarily conserved in organisms as diverse as ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' and humans. Loss-of-function mutations or absence of Bub1 has been reported to result in aneuploidy, chromosomal instability (chromosome instability syndrome, CIN) and premature senescence. Structure Bub1p comprises a conserved N-terminus, N-terminal region, a central non-conserved region and a C-terminus, C-terminal serine/threonine kinase domain. The N-terminal region mediates binding of Hs-BUB1 to the mit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cdc20
The cell division cycle protein 20 homolog is an essential regulator of cell division that is encoded by the ''CDC20'' gene in humans. To the best of current knowledge its most important function is to activate the anaphase promoting complex (APC/C), a large 11-13 subunit complex that initiates chromatid separation and entrance into anaphase. The APC/CCdc20 protein complex has two main downstream targets. Firstly, it targets securin for destruction, enabling the eventual destruction of cohesin and thus sister chromatid separation. It also targets S and M-phase (S/M) cyclins for destruction, which inactivates S/M cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) and allows the cell to exit from mitosis. A closely related protein, Cdc20homologue-1 (Cdh1) plays a complementary role in the cell cycle. CDC20 appears to act as a regulatory protein interacting with many other proteins at multiple points in the cell cycle. It is required for two microtubule-dependent processes: nuclear movement prior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
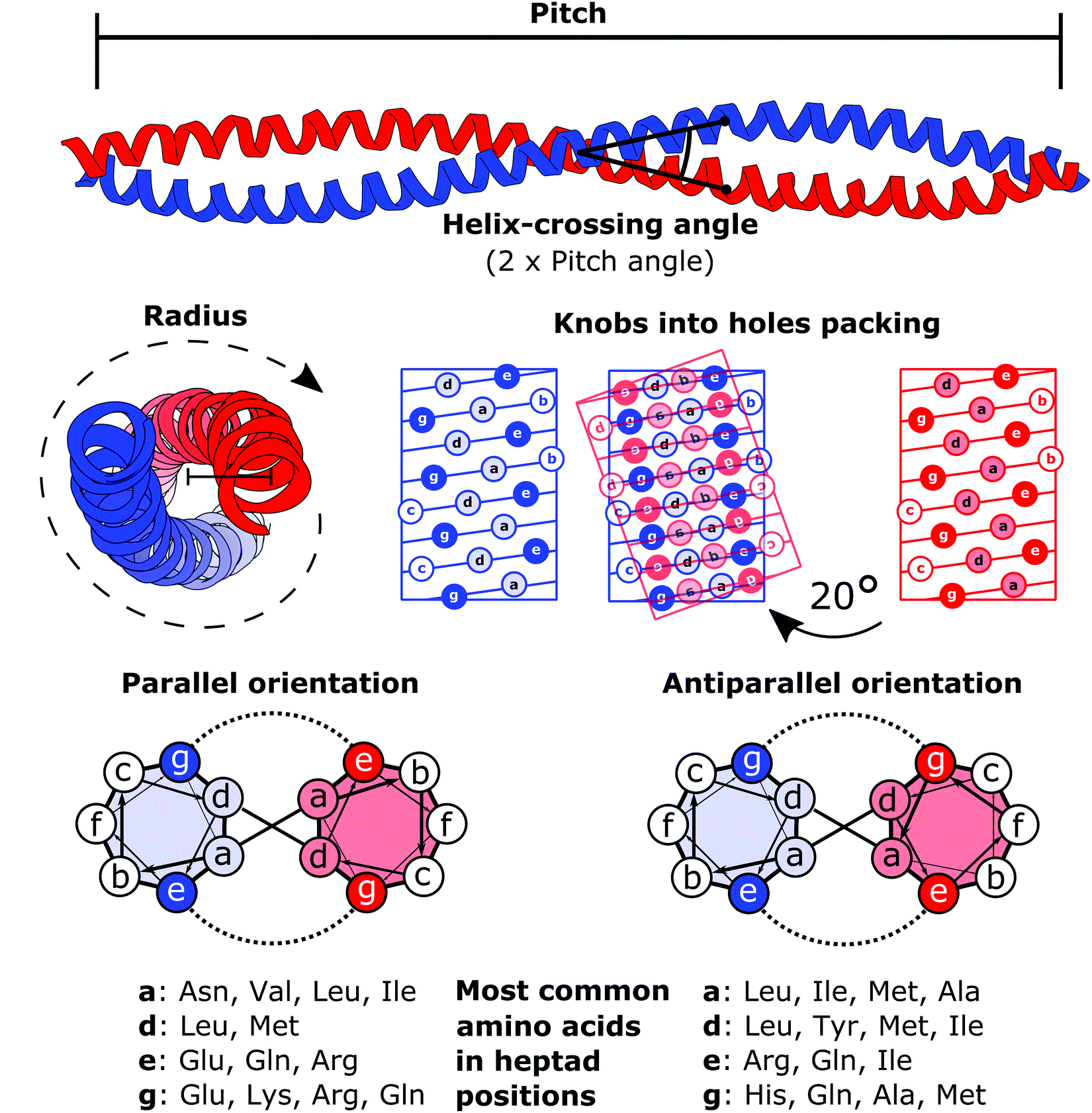
Coiled-coil
A coiled coil is a structural motif in proteins in which two to seven alpha-helices are coiled together like the strands of a rope. ( Dimers and trimers are the most common types.) They have been found in roughly 5-10% of proteins and have a variety of functions. They are one of the most widespread motifs found in protein-protein interactions. To aid protein study, several tools have been developed to predict coiled-coils in protein structures. Many coiled coil-type proteins are involved in important biological functions, such as the regulation of gene expression — e.g., transcription factors. Notable examples are the oncoproteins c-Fos and c-Jun, as well as the muscle protein tropomyosin. Discovery The possibility of coiled coils for α-keratin was initially somewhat controversial. Linus Pauling and Francis Crick independently came to the conclusion that this was possible at about the same time. In the summer of 1952, Pauling visited the laboratory in England where Cric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimer Mad1 Mad2
Dimer may refer to: * Dimer (chemistry), a chemical structure formed from two similar sub-units ** Protein dimer, a protein quaternary structure ** d-dimer ** TH-dimer * Dimer model, an item in statistical mechanics, based on ''domino tiling'' * Julius Dimer (1871–1945), German chess master See also * Dimery (botany), having two parts in a distinct whorl of a plant structure * Di (other), a prefix * Dymer (other) * -mer, a suffix * Oligomer In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relativ ... * Peierls transition, sometimes called dimerization {{Disambiguation, surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperphosphorylation
Protein phosphorylation is a reversible post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein, causing it to become activated, deactivated, or otherwise modifying its function. Approximately 13,000 human proteins have sites that are phosphorylated. The reverse reaction of phosphorylation is called dephosphorylation, and is catalyzed by protein phosphatases. Protein kinases and phosphatases work independently and in a balance to regulate the function of proteins. The amino acids most commonly phosphorylated are serine, threonine, tyrosine, and histidine. These phosphorylations play important and well-characterized roles in signaling pathways and metabolism. However, other amino acids can also be phosphorylated post-translationally, including arginine, lysine, aspartic acid, glutamic acid and cysteine, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell (biology), cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These events include the growth of the cell, duplication of its DNA (DNA replication) and some of its organelles, and subsequently the partitioning of its cytoplasm, chromosomes and other components into two daughter cells in a process called cell division. In eukaryotic cells (having a cell nucleus) including animal, plant, fungal, and protist cells, the cell cycle is divided into two main stages: interphase, and the M phase that includes mitosis and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, and replicates its DNA and some of its organelles. During the M phase, the replicated Chromosome, chromosomes, organelles, and cytoplasm separate into two new daughter cells. To ensure the proper replication of cellular components and division, there are control mechanisms kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorylation
In biochemistry, phosphorylation is described as the "transfer of a phosphate group" from a donor to an acceptor. A common phosphorylating agent (phosphate donor) is ATP and a common family of acceptor are alcohols: : This equation can be written in several ways that are nearly equivalent that describe the behaviors of various protonated states of ATP, ADP, and the phosphorylated product. As is clear from the equation, a phosphate group per se is not transferred, but a phosphoryl group (PO3-). Phosphoryl is an electrophile. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology. Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Protein phosphorylation often activates (or deactivates) many enzymes. During respiration Phosphorylation is essential to the processes of both anaerobic and aerobic respiration, which involve the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the "high-energy" exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |