|
Máel Ruba
Máel Ruba ( 642–722) is an Irish saint of the Celtic Church who was active in the Christianisation of the Picts and Gaels of Scotland. Originally a monk from Bangor Abbey, County Down, Gaelic Ireland, he founded the monastic community of Applecross ( , 'The Sanctuary') in Wester Ross, one of the best attested early Christian monasteries in what is now Scotland. Forms of his name include Máelrubai (Old Irish spelling), Maol Rubha (MoRubha/MaRuibhe) (Scottish Gaelic spelling), or Malruibhe, and it is sometimes latinised as Rufus, Life Máel Ruba was descended from Niall, King of Ireland, via his father Elganach. His mother, Subtan, was a niece of Saint Comgall (d. 597 or 602) of Bangor. Máel Ruba was born in the area of Derry and was educated at Bangor. In 671, when he was thirty, he sailed from Ireland to Scotland with a group of monks. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ainmean-Àite Na H-Alba
Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba (; "Gaelic Place-Names of Scotland") is the national advisory partnership for Gaelic place names in Scotland. Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba are based at Sabhal Mòr Ostaig on Skye. History Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba began as the Gaelic Names Liaison Committee, established in 2000 by the Ordnance Survey to improve consistency in Gaelic names on their mapping products. The committee expanded to become the Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba partnership in 2006. Functions Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba research and agree on place names, using local knowledge, historical sources and the principles of the Gaelic Orthographic Conventions. These names are used by local councils, roads authorities and the Ordnance Survey for signs and maps. AÀA are also producing a National Place-Names Database. This database was launched in August 2010, and contains over 3000 entries. Partnerships The partners are Argyll and Bute Council, Bòrd na Gàidhlig, Comhairle nan Eilean Siar, Highlands and I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Forres
Forres (; ) is a town and former royal burgh in the north of Scotland on the County of Moray, Moray coast, approximately northeast of Inverness and west of Elgin, Moray, Elgin. Forres has been a winner of the Scotland in Bloom award on several occasions. There are many geographical and historical attractions nearby such as the River Findhorn, and there are also classical, historical artifacts and monuments within the town itself, such as Forres Tolbooth and Nelson's Tower. Brodie Castle, the home of the Brodie Clan, lies to the west of the town, close to the A96. Pre-history and archaeology Between 2002 and 2013 some 70 hectares of land was investigated by archaeologists in advance of a proposed residential development on the southern fringes of the town. They found an extensive Iron Age settlement and evidence that people lived in the area from the Neolithic British Isles, Neolithic (Radiocarbon dating, radiocarbon dates from the 4th to the mid-3rd millennium BC were found) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isle Of Lewis
The Isle of Lewis () or simply Lewis () is the northern part of Lewis and Harris, the largest island of the Western Isles or Outer Hebrides archipelago in Scotland. The two parts are frequently referred to as if they were separate islands. The total area of Lewis is . Lewis is, in general, the lower-lying part of the island: the other part, Harris, Outer Hebrides, Harris, is more mountainous. Due to its larger area and flatter, more fertile land, Lewis contains three-quarters of the population of the Western Isles, and the largest settlement, Stornoway. The island's diverse habitats are home to an assortment of flora and fauna, such as the golden eagle, red deer and Pinniped, seal, and are recognised in a number of Conservation area (United Kingdom), conservation areas. Lewis has a Presbyterian tradition and a rich history. It was once part of the Norsemen, Norse Kingdom of the Isles. Today, life is very different from elsewhere in Scotland, with Sabbath in Christianity, Sabbath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Raasay
Raasay (; ), sometimes the Isle of Raasay, is an island between the Isle of Skye and the mainland of Scotland. It is separated from Skye by the Sound of Raasay and from Applecross by the Inner Sound, Scotland, Inner Sound. It is famous for being the birthplace of Scottish Gaelic literature, Gaelic poet Sorley MacLean, an important figure in the Scottish Renaissance. Traditionally the home of Clan Sweeney, Clan MacSween, the island was ruled by the Clan MacLeod, MacLeods from the 15th to the 19th century. Subsequently, a series of private landlords held title to the island, which is now largely in public ownership. Raasay House, which was visited by James Boswell and Samuel Johnson in 1773, is now a hotel, restaurant, bar and outdoor activity centre. Raasay means "Isle of the Roe Deer" and the island is home to an endemism, endemic subspecies of bank vole. Geology and geography About north to south and east to west (at its widest), Raasay's terrain is varied. The high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
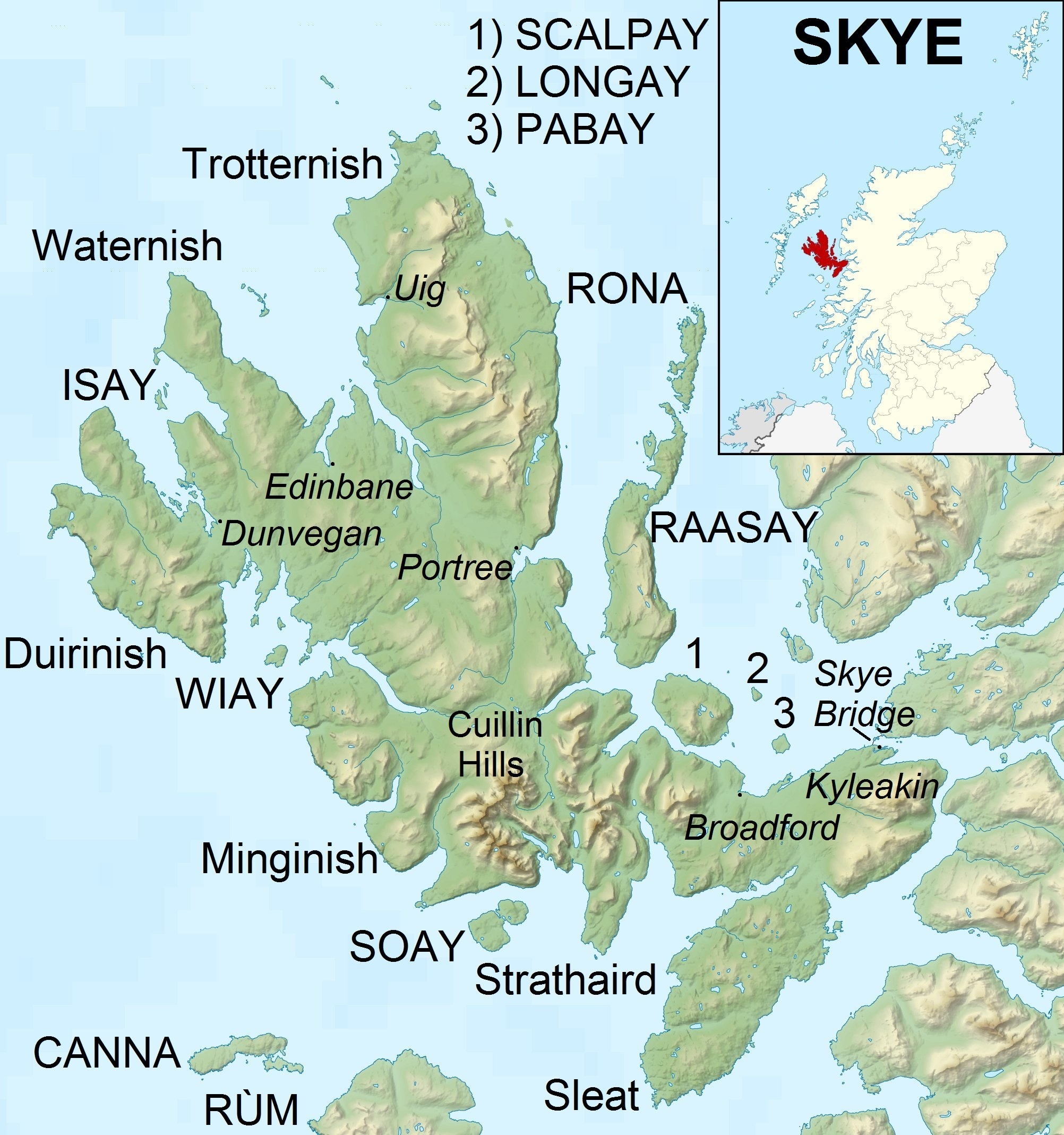
Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye, is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origin."Gaelic Culture" . VisitScotland. Retrieved 5 January 2013. The island has been occupied since the period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Argyll
Argyll (; archaically Argyle; , ), sometimes called Argyllshire, is a Shires of Scotland, historic county and registration county of western Scotland. The county ceased to be used for local government purposes in 1975 and most of the area now forms part of the larger Argyll and Bute Council areas of Scotland, council area. Argyll is of ancient origin, and broadly corresponds to the ancient kingdom of less the parts which were in Ireland. Argyll was also a diocese of Argyll, medieval bishopric with its cathedral at Lismore, Scotland, Lismore. In medieval times the area was divided into a number of provincial lordships. One of these, covering only the central part of the later county, was called Argyll. It was initially an earldom, elevated to become a dukedom in 1701 with the creation of the Duke of Argyll. Other lordships in the area included Cowal, Kintyre, Knapdale, and Lorne, Scotland, Lorn. From at least the 14th century there was a Sheriff of Argyll, whose jurisdictio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Derry
Derry, officially Londonderry, is the second-largest City status in the United Kingdom, city in Northern Ireland, and the fifth-largest on the island of Ireland. Located in County Londonderry, the city now covers both banks of the River Foyle. Cityside and the old walled city being on the west bank and Waterside, Derry, Waterside on the east, with two road bridges and one footbridge crossing the river in-between. The population of the city was 85,279 in the 2021 census, while the Derry Urban Area had a population of 105,066 in 2011. The district administered by Derry City and Strabane District Council contains both Londonderry Port and City of Derry Airport. Derry is close to the Irish border, border with County Donegal, with which it has had a close link for many centuries. The person traditionally seen as the founder of the original Derry is Saint , a holy man from , the old name for almost all of modern County Donegal, of which the west bank of the Foyle was a part befor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Saint Comgall
Saint Comgall (c. 510–520 – 597/602), an early Irish saint, was the founder and abbot of the great Irish monastery at Bangor in Ireland. MacCaffrey,James (1908). " St. Comgall". In ''Catholic Encyclopedia''. 4. New York: Robert Appleton Company. Life Comgall was born sometime between 510 and 520 in Dál nAraidi, Ulster according to the Irish annals near the place now known as Magheramorne in present-day County Antrim. Comgall's father was Setna, a Pictish warrior; his mother's name was Briga. After serving as a soldier in his early life, he was educated under Fintan of Clonenagh and also studied under Finnian of Movilla, Mobhí Clárainech at Glasnevin, and Ciarán of Clonmacnoise."History of Bangor Abbey", Parish of Bangor Abbey He was ordained deacon and priest by Bishop Lugidius, either at [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
King Of Ireland
Monarchical systems of government have existed in Ireland from ancient times. This continued in all of Ireland until 1949, when the Republic of Ireland Act removed most of Ireland's residual ties to the British monarch. Northern Ireland, as part of the United Kingdom, remains under a monarchical system of government. The office of High King of Ireland effectively ended with the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland (1169–1171) in which the island was declared a fief of the Holy See under the Lordship of the King of England. In practice, conquered territory was divided amongst various Anglo-Norman noble families who assumed title over both the land and the people with the prior Irish inhabitants being either displaced or subjugated under the previously alien system of serfdom. Though the revolutionary change in the status quo was undeniable, the Anglo-Norman invaders would fail to conquer many of the Gaelic kingdoms of Ireland, which continued to exist, often expanding for centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Niall Of The Nine Hostages
Niall Noígíallach (; Old Irish "having nine hostages"), or Niall of the Nine Hostages, was a legendary, semi-historical Irish king who was the ancestor of the Uí Néill dynasties that dominated Ireland from the 6th to the 10th centuries. Historical Irish annalistic and chronicle sources place his reign in the late 4th and early 5th centuries, but modern scholars date him about half a century later. Historicity and dates Niall is presumed, based on the importance of his sons and grandsons, to have been a historical person,Francis J. Byrne, ''Irish Kings and High-Kings'', Second Edition, Dublin: Four Courts Press, 2001, but the early Irish annals say little about him. The '' Annals of Inisfallen'' date his death before 382, and the '' Chronicon Scotorum'' to 411.Kathleen Hughes, "The church in Irish society, 400–800, in Dáibhí Ó Cróinín (ed.), ''A New History of Ireland Vol I: Prehistoric and Early Ireland'', Oxford University Press, 2005, pp. 306–308 The later '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Latinisation Of Names
Latinisation (or Latinization) of names, also known as onomastic Latinisation (or onomastic Latinization), is the practice of rendering a ''non''-Latin name in a Neo-Latin, modern Latin style. It is commonly found with historical proper names, including personal names and toponyms, and in the standard binomial nomenclature of the life sciences. It goes further than romanisation, which is the transliteration of a word to the Latin alphabet from another script (e.g. Cyrillic). For authors writing in Latin, this change allows the name to function grammatically in a sentence through declension. In a scientific context, the main purpose of Latinisation may be to produce a name which is internationally consistent. Latinisation may be carried out by: * transforming the name into Latin sounds (e.g. for ), or * adding Latinate suffixes to the end of a name (e.g. for ''Heinrich Meibom (doctor), Meibom),'' or * translating a name with a specific meaning into Latin (e.g. for Italian ; b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |