|
List Of Environmental Issues
This is an alphabetical list of environmental issues, harmful aspects of human activity on the biophysical environment. They are loosely divided into causes, effects and mitigation, noting that effects are interconnected and can cause new effects. Issues * Greenhouse gas emissions — Coal-fired power station • Carbon dioxide • Methane • Fluorinated gases * Human population — Biocapacity • climate change • Carrying capacity • Exploitation • Industrialisation • I = PAT • Land degradation • Land reclamation • Optimum population • Overshoot (population) • Population density • Population density • Population dynamics • Population growth • Projections of population growth • Total fertility rate • Urbanization • Waste • Water conflict • Water scarcity • Overdrafting * Hydrology — Environmental impacts of reservoirs • Tile drainage • Hydrology (agriculture) • Flooding • Landslide * Intensive farming — Agricultural subsidy • B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Issues
Environmental issues are effects of human activity on the biophysical environment, most often of which are harmful effects that cause environmental degradation. Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment on the individual, organizational or governmental levels, for the benefit of both the environment and humans. Environmentalism is a social and environmental movement that addresses environmental issues through advocacy, legislation education, and activism. Environment destruction caused by humans is a global, ongoing problem. Water pollution also cause problems to marine life. Most scholars think that the project peak global world population of between 9-10 billion people, could live sustainably within the earth's ecosystems if human society worked to live sustainably within planetary boundaries. The bulk of environmental impacts are caused by the most wealthy populations in the globe consuming too much industrial goods. The UN Environmental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Density
Population density (in agriculture: standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopulation Density Geography.about.com. March 2, 2011. Retrieved on December 10, 2011. In simple terms, population density refers to the number of people living in an area per square kilometre, or other unit of land area. Biological population densities Population density is population divided by total land area, sometimes including seas and oceans, as appropriate. Low densities may cause an extinction vortex and further reduce fertility. This is called the Allee effect after the scientist who identified it. Examples of the causes of reduced fertility in low population densities are * Increased problems with locating sexual mates * Increased inbreeding Human densities Population density is the number of people per unit of area, usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrology (agriculture)
Agricultural hydrology is the study of water balance components intervening in farm water, agricultural water management, especially in irrigation and drainage. Water balance components The water balance components can be grouped into components corresponding to zones in a vertical cross-section in the soil forming reservoirs with inflow, outflow and storage of water: # the surface reservoir (''S'') # the root zone or unsaturated (vadose zone) (''R'') with mainly vertical flows # the aquifer (''Q'') with mainly horizontal flows # a transition zone (''T'') in which vertical and horizontal flows are converted The general water balance reads: * inflow = outflow + change of storage and it is applicable to each of the reservoirs or a combination thereof. In the following balances it is assumed that the water table is inside the transition zone. Surface water balance The incoming water balance components into the surface reservoir (''S'') are: #Rai – Vertically incoming water to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tile Drainage
Tile drainage is a form of agricultural drainage system that removes excess sub-surface water from fields to allow sufficient air space within the soil, proper cultivation, and access by heavy machinery to tend and harvest crops. While surface water can be drained by pumping, open ditches, or both, tile drainage is often the most effective means of draining subsurface water. The phrase "tile drainage" derives from its original composition from ceramic tiles of fired clay, which were similar to terracotta pipes yet not always shaped as pipes. In the 19th century a "C" shaped channel tile commonly was placed like an arch atop a flat tile, denominated the "mug" and "sole", respectively. Today, tile drainage is any variation of this original system that functions in the same mode. Commonly HDPE and PVC tubing denominated "tile line" is used, although precast concrete and ceramic tiles are still used. Typical pathways for agricultural drainage and the occasionally used pathways for tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Impacts Of Reservoirs
The environmental impact of reservoirs comes under ever-increasing scrutiny as the global demand for water and energy increases and the number and size of reservoirs increases. Dams and reservoirs can be used to supply drinking water, generate hydroelectric power, increase the water supply for irrigation, provide recreational opportunities, and flood control. In 1960 the construction of Llyn Celyn and the flooding of Capel Celyn provoked political uproar which continues to this day. More recently, the construction of Three Gorges Dam and other similar projects throughout Asia, Africa and Latin America have generated considerable environmental and political debate. Currently, 48 percent of rivers and their hydro-ecological systems are affected by reservoirs and dams. Upstream impacts Fragmentation of river ecosystems A dam acts as a barrier between the upstream and downstream movement of migratory river animals, such as salmon and trout. Some communities have also begun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is called a hydrologist. Hydrologists are scientists studying earth or environmental science, civil or environmental engineering, and physical geography. Using various analytical methods and scientific techniques, they collect and analyze data to help solve water related problems such as environmental preservation, natural disasters, and water management. Hydrology subdivides into surface water hydrology, groundwater hydrology (hydrogeology), and marine hydrology. Domains of hydrology include hydrometeorology, surface hydrology, hydrogeology, drainage-basin management, and water quality, where water plays the central role. Oceanography and meteorology are not included because water is only one of many important aspects within those fields. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overdrafting
Overdrafting is the process of extracting groundwater beyond the equilibrium yield of an aquifer. Groundwater is one of the largest sources of fresh water and is found underground. Groundwater depletion is comparable to a bank account in which more money is withdrawn than deposited. The primary cause of groundwater depletion is the excessive pumping of groundwater up from underground aquifers. There are two sets of yields: safe yield and sustainable yield. Safe yield is the amount of groundwater that can be withdrawn over a period of time without exceeding the long-term recharge rate or affecting the aquifer integrity. Sustainable yield is the amount of water extraction that can be sustained indefinitely without negative hydrological impacts, taking into account both recharge rate and surface water impacts. There are two types of aquifers: confined and unconfined. In confined aquifers, there is an overbearing layer called aquitard, which contains impermeable materials through wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
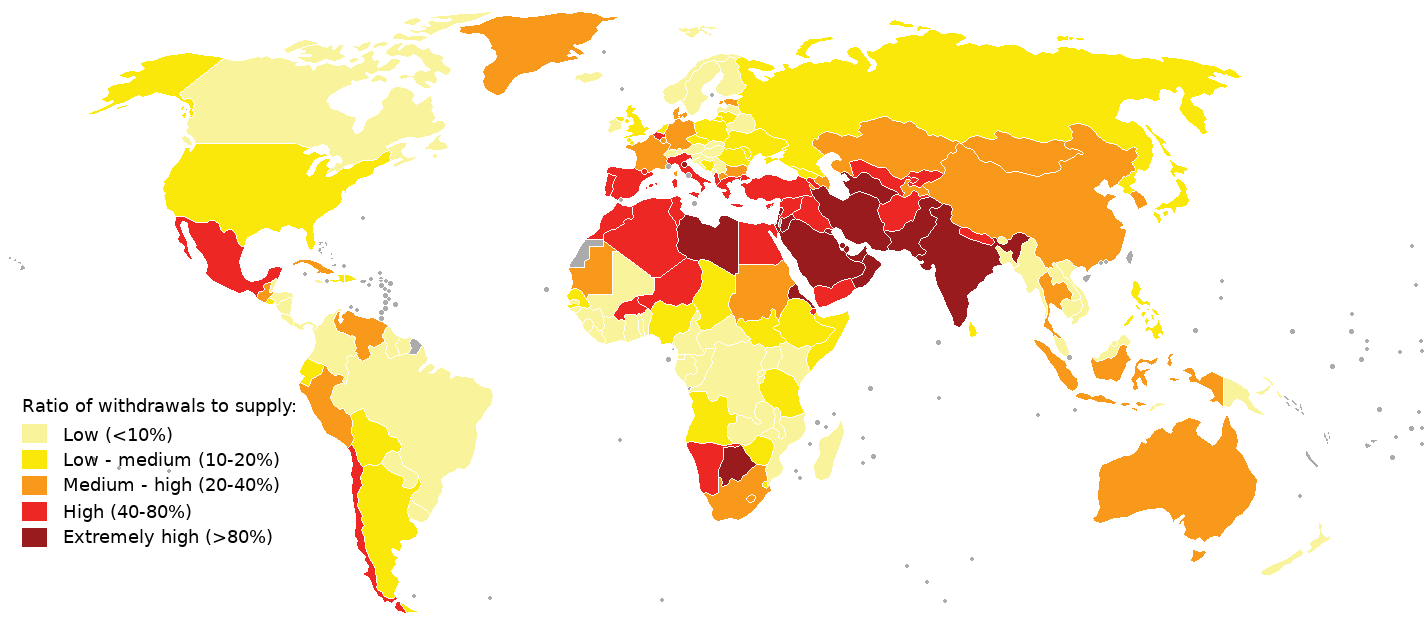
Water Scarcity
Water scarcity (closely related to water stress or water crisis) is the lack of fresh water Water resources, resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity: physical or economic water scarcity. Physical water scarcity is where there is not enough water to meet all demands, including that needed for ecosystems to function effectively. Desert climate, Arid areas for example Central and West Asia, and North Africa often suffer from physical water scarcity. On the other hand, economic water scarcity is caused by a lack of investment in infrastructure or technology to draw water from rivers, aquifers, or other water sources, or insufficient human capacity to satisfy the demand for water. Much of Sub-Saharan Africa has economic water scarcity. The essence of global water scarcity is the geographic and temporal mismatch between fresh water demand and availability. At the global level and on an annual basis, enough freshwater is available to meet such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
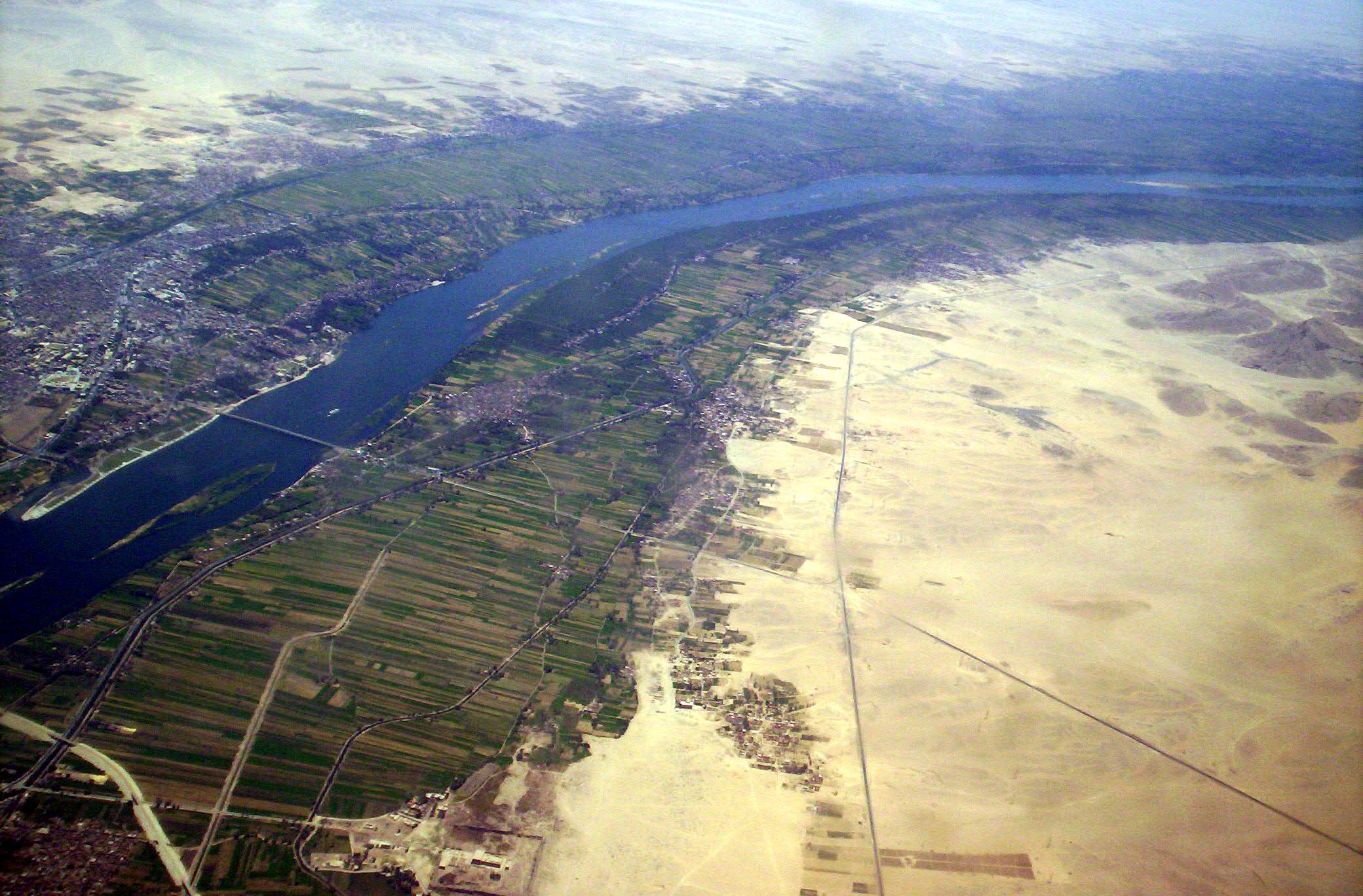
Water Conflict
Water conflict is a term describing a conflict between countries, states, or groups over water the rights to access water resources. The United Nations recognizes that water disputes result from opposing interests of water users, public or private. A wide range of water conflicts appear throughout history, though rarely are traditional wars waged over water alone. Instead, water has historically been a source of tension and a factor in conflicts that start for other reasons. Water conflicts arise for several reasons, including territorial disputes, a fight for resources, and strategic advantage. Water conflicts can occur on the intrastate and interstate levels. Interstate conflicts occur between two or more neighboring countries that share a transboundary water source, such as a river, sea, or groundwater basin. For example, the Middle East has only 1% of the world's freshwater shared among 5% of the world's population. Intrastate conflicts take place between two or more parties i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waste
Waste (or wastes) are unwanted or unusable materials. Waste is any substance discarded after primary use, or is worthless, defective and of no use. A by-product, by contrast is a joint product of relatively minor economic value. A waste product may become a by-product, joint product or resource through an invention that raises a waste product's value above zero. Examples include municipal solid waste (household trash/refuse), hazardous waste, wastewater (such as sewage, which contains bodily wastes ( feces and urine) and surface runoff), radioactive waste, and others. Definitions What constitutes waste depends on the eye of the beholder; one person's waste can be a resource for another person. Though waste is a physical object, its generation is a physical and psychological process. The definitions used by various agencies are as below. United Nations Environment Program According to the Basel Convention on the Control of Transboundary Movements of Hazardous Wastes a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly the process by which towns and cities are formed and become larger as more people begin living and working in central areas. Although the two concepts are sometimes used interchangeably, urbanization should be distinguished from urban growth. Urbanization refers to the ''proportion'' of the total national population living in areas classified as urban, whereas urban growth strictly refers to the ''absolute'' number of people living in those areas. It is predicted that by 2050 about 64% of the developing world and 86% of the developed world will be urbanized. That is equivalent to approximately 3 billion urbanites by 2050, much of which will occur in Africa and Asia. Notably, the United Nations has also recently projected that nearly all gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Total Fertility Rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if: # she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime # she were to live from birth until the end of her reproductive life. It is obtained by summing the single-year age-specific rates at a given time. As of 2021, the total fertility rate varied from 0.81 in South Korea to 6.91 in Niger. Fertility tends to be correlated with the level of economic development. Historically, developed countries usually have a significantly lower fertility rate, generally correlated with greater wealth, education, urbanization, and other factors. Conversely, in undeveloped countries, fertility rates tend to be higher. Families desire children for their labor and as caregivers for their parents in old age. Fertility rates are also higher due to the lack of access to contraceptives, stricter adherence to traditional relig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |